Treatment Options For Lymphangitis
Cuts and wounds are a common occurrence, and while these heal well in most cases, infections can occur. When an infection in the soft tissues spreads into the lymphatic system, this is known as lymphangitis, and common symptoms include swelling and pain in the lymph nodes. While the lymph glands located underneath the arm in the armpit is most likely to be affected, those in the elbow, beneath the jaw, and in the groin have been known to become swollen and infected in cases of lymphangitis. Left untreated, this infection of the lymphatic vessels can lead to sepsis, or blood poisoning. This rare but serious condition can lead to death in some cases. Prompt treatment can lead to a successful recovery.
Intravenous Antimicrobial Therapy
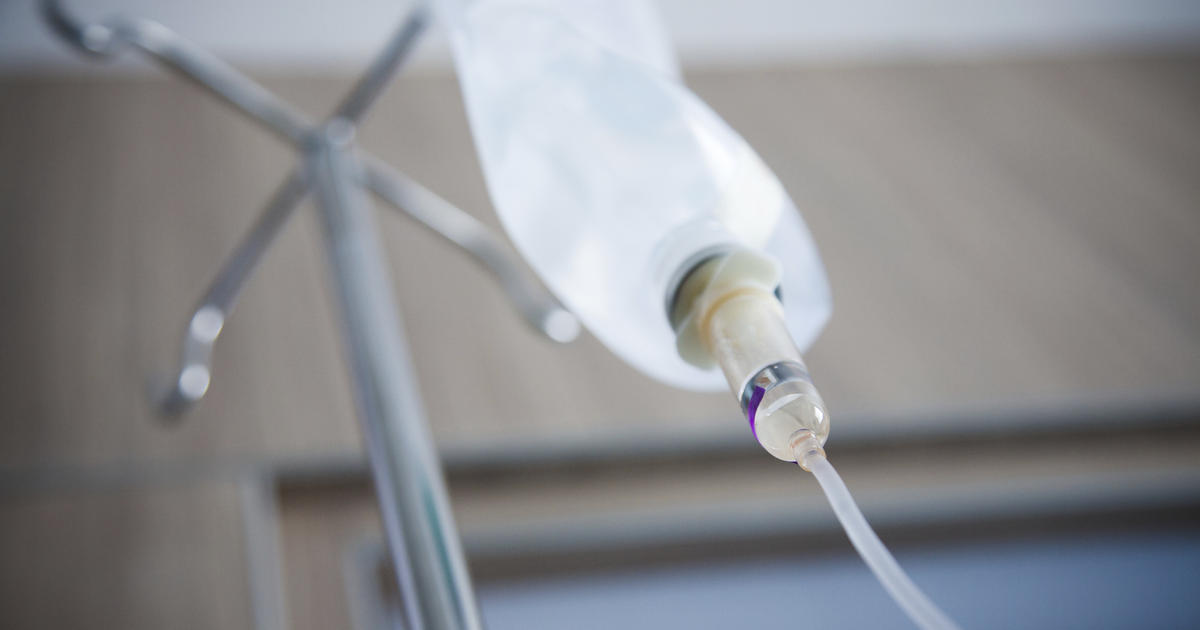
Antibiotics are typically necessary to clear up the infection in the soft tissues as well as any bacteria affecting the lymphatic system. Although oral antibiotics can be effective in some cases, once the infection has reached the lymph nodes, it can quickly spread into the bloodstream, leading to sepsis and possibly death. Oral antibiotics typically do not even begin to work in the body until twenty-four hours after the initial dose at the earliest. Because of the importance of timing, intravenous antimicrobial therapy can get the necessary medication working much quicker, with results being noticed in as little as a few hours. In most cases, the patient will be admitted to the hospital to continue intravenous antimicrobial therapy until the infection has cleared completely or enough to be handled with oral antibiotics at home.
Learn more about how to treat lymphangitis now.
Drain Abscesses With Surgery
If an abscess is determined to be the cause of lymphangitis, surgical drainage may be necessary. This is more likely if the abscess is large or if antibiotic treatment has not been successful. When a physician decides to drain abscesses with surgery, it is usually done as an outpatient procedure, though local or general anesthesia may be required. The surgeon will cut the skin over the abscess to allow the pus to be drained. A cotton swab may be used to clean out the wound and to ensure all of the infected material has been removed. An abscess is usually left open to heal, though a large one may be packed with a long ribbon of antiseptic dressing. This dressing will be changed until the wound has healed enough as determined by the surgeon.
Discover additional treatment options for lymphangitis now.
Surgical Removal Or Debridement
If a wound or skin infection is very severe, surgical removal or debridement might be deemed appropriate to allow the lymphatic system to heal. Debridement is a procedure in which infected, dead, or damaged tissue can be cut or scraped away to allow healthy tissue to grow in its place. When the offending tissue is removed, this decreases the chance for infection, preventing the possible spread of bacteria to the lymph nodes and potentially to the bloodstream. Removal of unhealthy tissue through debridement is also a way for the physician to obtain a sample for lab testing and allows for a cleaner edge for less scarring during the healing process.
Keep reading for more on how to treat lymphangitis now.
Apply A Hot Compress
Warm compresses can be beneficial in assisting with the treatment of lymphangitis. When patients apply a hot compress to the infections beneath the skin, it helps break up collections of bacteria and pus to allow for better healing. This can also reduce the associated pain and swelling. Placing a damp, warm compress on the swollen lymph nodes can have a similar effect. Additionally, this increases blood circulation to the area, allowing lymph fluids to move more freely, allowing collected fluids and infection to move out of the lymph glands to be removed from the body. Hot compresses can be used in connection with other treatment measures to help patients feel more comfortable while recovering.
Discover more ways to treat lymphangitis now.
Take Pain Medication As Directed
The pain associated with the inflammation of the lymph nodes can make it difficult to want to move around much, but movement is important to keep lymph fluid flowing to remove waste from the body. To keep your pain at bay, your physician may recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers to reduce pain and inflammation, or even acetaminophen for pain and fever. If pain is very severe, prescription medications may be recommended. There is a potential for side effects with many of the available pain relievers, so it is important to always take pain medication as directed to reduce the risk of complications.
