Warning Signs Of Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis occurs when the nerve roots or spinal cord become compressed. Most spinal stenosis patients experience it due to osteoarthritis. However, researchers say anyone over fifty years old is at risk of developing the condition. The diagnosis is based on the patient's medical history and symptoms. There are a wide variety of different symptoms, and the impact on different patients also varies. Some might experience only mild discomfort and pain. In contrast, others might have debilitating and chronic symptoms that inhibit day-to-day life.
Spinal stenosis treatment depends on where the condition is located as well as its severity. However, patients commonly require pain medication. They may also need tricyclic antidepressants or anti-seizure meds. Steroid injections, physical therapy, and even surgery for spinal stenosis are also used. A patient's spinal stenosis cure is a discussion they must have with their doctor.
Numbness And Tingling
Spinal stenosis occurs when the spaces in the spine narrow. This puts pressure on the nerves traveling throughout the spine, including the nerves within the spinal cord and the nerve roots of the peripheral nervous system. One of the most common symptoms is numbness and tingling. The condition most commonly develops in the neck and lower back. However, patients might experience numbness and tingling concentrated in other parts of the body as well. The tingling and numbness might become worse over time.
Some patients do not notice the symptoms initially, or they find them so mild they do not cause concern. However, doctors should evaluate any tingling and numbness, as it indicates a nervous system issue. When spinal stenosis involves narrowing in the neck, patients might experience numbness and tingling in a leg, foot, arm, or hand. When it occurs in the lower back, patients are less likely to experience hand numbness. However, they may still experience numbness in their leg or foot.
Issues With Balance And Walking
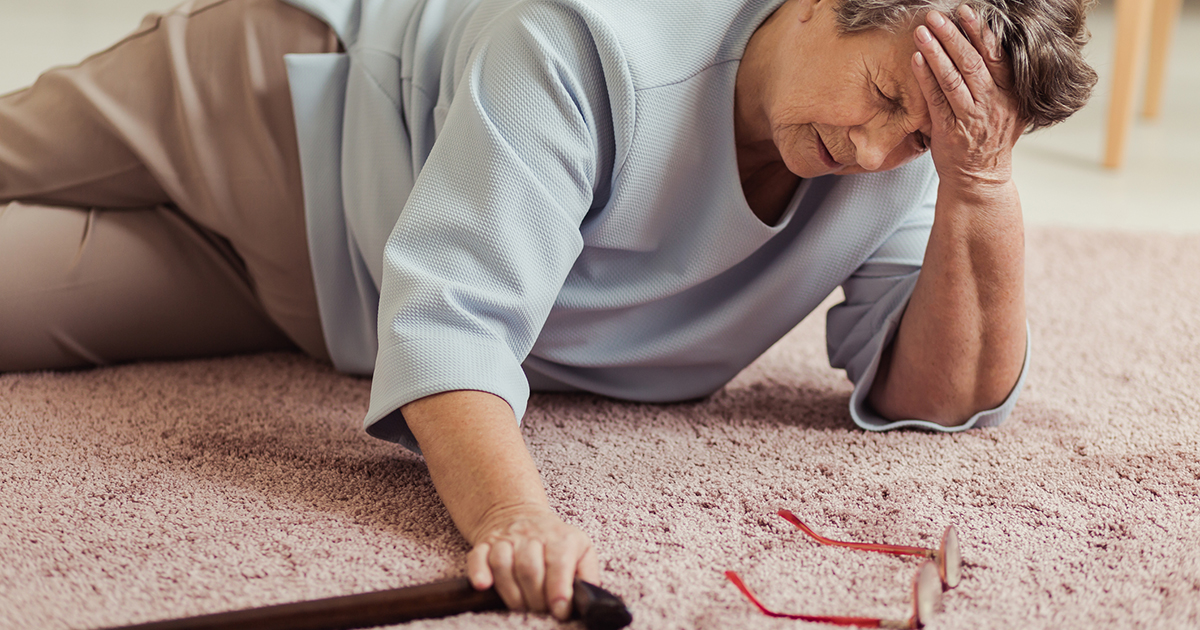

Gait abnormalities and issues with balance are most common when spinal stenosis occurs in the neck, otherwise known as cervical spinal stenosis. When the condition occurs in the lower back, patients might have some problems with balance. However, they tend to present differently. Lumbar spinal stenosis is more likely to cause one or both legs to become painful and cramp when individuals stand in one area for long periods or walk around.
Many patients report the pain eases partially or entirely when they sit down or bend forward, taking the pressure off their spine and legs. Some individuals might be able to walk short distances, but find they have problems with pain and balancing when they have to walk long distances. There might also be issues with walking if patients are dealing with numbness, as the loss of sensation can make it difficult to balance or interpret sensory information about the ground beneath them.
Pain In The Neck Or Back
Spinal stenosis can technically occur in any of the five main parts of the spine, though it is most common in the neck and lower back. Thus, one of the most common symptoms of spinal stenosis is neck or back pain. When patients have lumbar spinal stenosis, they might experience a burning pain that spreads from their lower back through their buttocks and down one or both legs. This is a condition known as sciatica, and it can be extremely debilitating.
Cervical spinal stenosis is one of the most common causes of neck pain in patients over fifty years old. As individuals get older, the spine is more likely to narrow due to aging and wear-and-tear. It is also possible to develop cervical stenosis after undergoing some trauma or impact to the neck. Sometimes the symptoms of stenosis and pain do not even occur until years after the trauma has healed. Neck pain caused by spinal stenosis is not always severe, but it does tend to be chronic or recurrent.
Urinary Incontinence

Urinary incontinence can occur with different kinds of spinal stenosis. However, it is a particularly common symptom of lumbar stenosis. The same is true of a loss of sexual ability or performance. When individuals have lumbar stenosis, there is no guarantee they will develop bladder or bowel dysfunction. However, some patients do experience this alongside the radiating pain from sciatica. Urinary incontinence varies widely from patient to patient. If the incontinence is mild enough, patients might not associate it with their back pain at all.
Mild urinary incontinence occurs when there is a lack of bladder control that leads to involuntary leaking. Moderate and severe urinary incontinence typically occurs when the loss of bladder control is serious enough to lead to accidents. Problems with urination have the potential to be embarrassing and affect an individual's day-to-day life. Patients might experience the sudden urge to urinate or need to urinate more times a day than they used to. They may also need to urinate so much that they cannot get to a toilet in time.
Weakness In The Body

Weakness in the body is one of the neurological effects that can occur due to spinal stenosis. The symptoms of this weakness are so varied and diffuse that it is difficult to pin down specific manifestations. If individuals experience sudden muscle weakness and numbness, it is essential to see a doctor to rule out neurological problems. Spinal stenosis leads to weakness because it compresses the nerves, which can lead to damage over time. The nerves are not able to transmit or receive signals as efficiently as they used to.
When spinal stenosis occurs in the neck, patients might experience weakness in their hands, arms, feet, or legs. When it occurs in the lower back, they're more likely to experience weakness in the lower extremities. Weakness in the foot can cause an individual's feet to 'slap' the ground when they walk. They might be more prone to falling or unbalancing as a result. Patients might also be unable to walk long distances or hold heavy objects.
