Signs Of An Immunodeficiency Disorder
An immunodeficiency disorder interferes with the body’s immune system and its ability to fight diseases. The immune system is comprised of white blood cells that kill pathogens and defend against viruses, bacteria, and parasitic worms. These cells contain macrophages, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils. Each cell attacks pathogens and engulfs them upon entering your body. They are formed in your spleen, tonsils, bone marrow, and lymph nodes.When you have an immunodeficiency disorder, your body’s natural defenses are lowered or absent and cannot stave off harmful organisms. You are more susceptible to acquiring fungal infections, lymphoma, and cancers. They can occur due to hormonal conditions, malnutrition, unsanitary, and the human immune deficiency virus. Symptoms may include frequent sinus infections, bronchitis, skin infections, ear infections, and meningitis.
Respiratory Infections
Your respiratory system allows you to inhale and exhale air. The air you breathe is a part of a necessary gas exchange for your lungs. During this process, your heart pumps oxygen into the internal organs and tissues in your body. Oxygen is turned into carbon dioxide and absorbed into your blood. The carbon dioxide is then carried back to the lungs through your red blood cells and removed when you exhale.
When you suffer from respiratory infections, this process does work and oxygen is not supplied to your organs. Pulmonary complications are one of the most common symptoms of an autoimmune disorder and cause chronic lung damage. There are common infections that are signs of an immunodeficiency disorder. They include bronchitis, which causes the lining of bronchial tubes to become inflamed; pneumonia, which inflames and builds up fluid in the air sacks of your lungs; and otitis media, an ear infection caused by bacteria or a virus that causes fluid in the ear and hearing loss.
Bacterial Infections

When you have a strong, healthy immune system, your body can fight off bacterial infections. But without a defense mechanism to protect you from illness, your body succumbs to infections quickly. Bacterial infections can occur on the inside and outside of your body and wreak havoc on your body. These contagions include Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and E. Coli.
Since your immune system is weak, you can easily contract some specific infections, which include strep throat, impetigo, and cellulitis. Strep throat is caused by Streptococcus and affects your throat. When you have this infection, your tonsils are swollen and sore. Impetigo is a skin infection resulting from bacteria. When infected, your skin becomes red, and pus-filled pimples appear. They break open and form a thick crust over them and can show up anywhere on your body. Cellulitis attacks the surface and underlying skin tissues. It is caused by Streptococcus and enters the body through a surgical cut, bruise, or wound. Those infected usually come down with a fever and chills. Their lymph glands become swollen, and a rash appears on the skin.
Fungal Infections
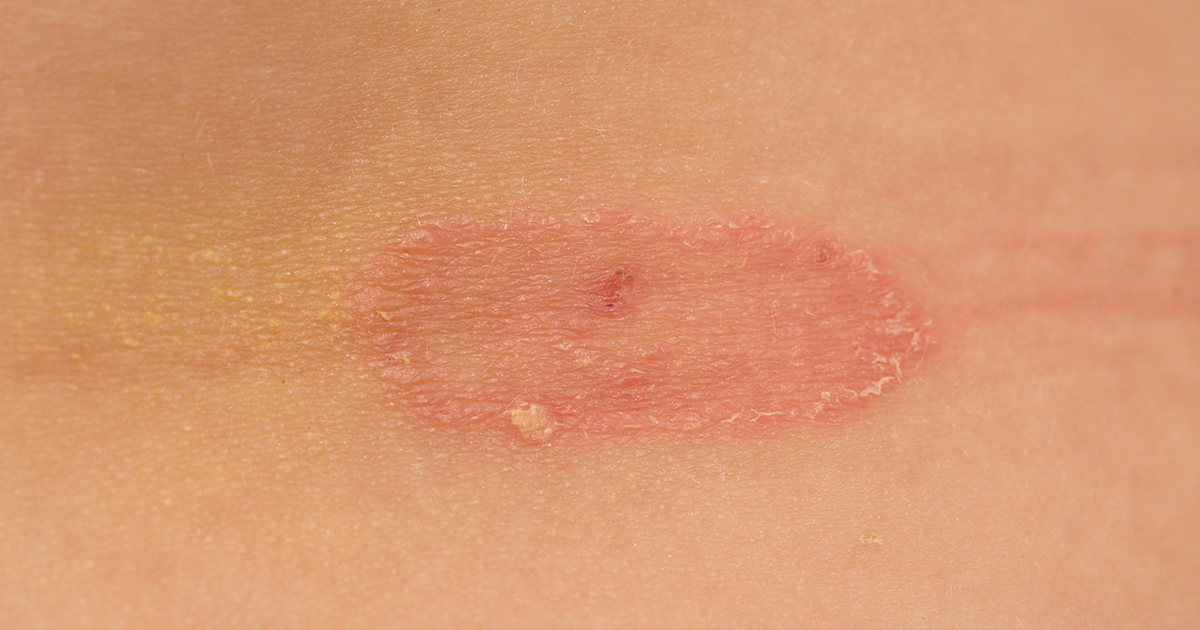
Fungal infections are caused by small living organisms called fungi, which include yeasts and molds. These organisms live in the human body naturally and remain under control. However, a compromised immune system cannot maintain the bodies flora or manage the growth of fungi, as they may become unmanageable and take over their host. This can lead to complications and serious health issues. Several types of infections that can signal an immunodeficiency disorder include yeast infections, ringworm, and aspergillosis. When you develop a yeast infection, this single-celled organism invades your body can infect any area on your body, including your skin, sexual organs, armpits, and toenails. It thrives in moist areas and produces a rash when present.
Ringworm is a contagious infection caused by tinea corporis a fungus that affects the skin. It forms a round, flat, and itchy rash. These sores can appear anywhere on the human body and spread through clothing, linens, and furniture. Aspergillosis is a mold that lives everywhere and does not affect people with healthy immune systems. It affects those who are not capable of fighting off disease and causes allergic reaction and lung infections.
Digestive Problems

If the immune system isn't strong enough to fight disease, the body becomes prone to developing digestive problems. The digestive system, as many know, is responsible for breaking down food into tiny particles the body can absorb. Proteins, fats, and carbohydrates are all necessary nutrients that keep you energized and promote cell repair. When someone is suffering from an immunodeficiency disorder, their digestive system is affected. They may deal with diarrhea or bacterial gastroenteritis.
Diarrhea causes loose, watery stools and pain in the abdomen. This can be a dangerous condition and lead to dehydration if not the symptoms are not addressed. Bacteria and viruses in contaminated food are usually the culprits of this painful stomach ache.
Bacterial gastroenteritis occurs when harmful bacteria enters your gut, causing inflammation in the stomach and intestine. The salmonella, shigella, and E. coli bacteria can make you ill when ingested. The symptoms of an infection include loss of appetite, vomiting, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea.
Delayed Growth And Development
A body without an immune system is unable to grow and sustain natural chemical and hormonal production, which causes issues with bones, weight, height, and blood circulation. When the body is under constant attack by bacteria, fungi, and viruses, a child’s development can be interrupted and delayed. Some of the delayed growth and development problems attributed to immunodeficiency disorders include dysarthria, hearing loss, autism spectrum disorders, vision problems, issues with motor skills, and dwarfism.
Dysarthria affects the muscles used for speech and causes slurred and slowed speech. Hearing loss results from the infections from bacteria that make ears fill up with fluid and interfere with hearing. Autism spectrum disorders are incurable conditions that inhibit a child’s ability to communicate and interact with others effectively.
In terms of vision problems, children can develop cataracts, poor vision, and retinopathy. With motor skills, children may have an inability to crawl or walk and use hands to grip toys and food utensils. Finally, dwarfism is a bone disorder linked to hormonal instability. Since children do not receive adequate nutrition, their skeletal system does not grow properly.
