10 Silent Signs Your Gut Microbiome Is Out Of Balance
The gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem of trillions of microorganisms residing in our digestive tract. These include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microscopic entities that play a crucial role in our overall health. Often dubbed as our "second brain," the gut microbiome influences not only digestion but also immune function, mental health, and even weight management. An imbalance in this delicate system, known as dysbiosis, can manifest in various subtle ways, impacting our well-being. By understanding the intricate relationship between our gut and overall health, we can take proactive steps to restore balance and enhance our quality of life.
1. The Role of Diet in Gut Health

Diet is a fundamental component of gut health, influencing the composition and function of the microbiome. A diet rich in fiber, diverse plant foods, and fermented products supports a balanced microbiome, fostering beneficial bacteria growth. Conversely, diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can lead to dysbiosis. Research shows that dietary changes can rapidly alter the gut microbiota, underscoring the importance of mindful eating. Understanding the connection between diet and gut health empowers individuals to make informed choices, promoting a thriving microbiome. Incorporating prebiotics and probiotics into your diet can further enhance gut health, supporting a diverse and resilient microbiome.
2. Recognizing Digestive Disturbances
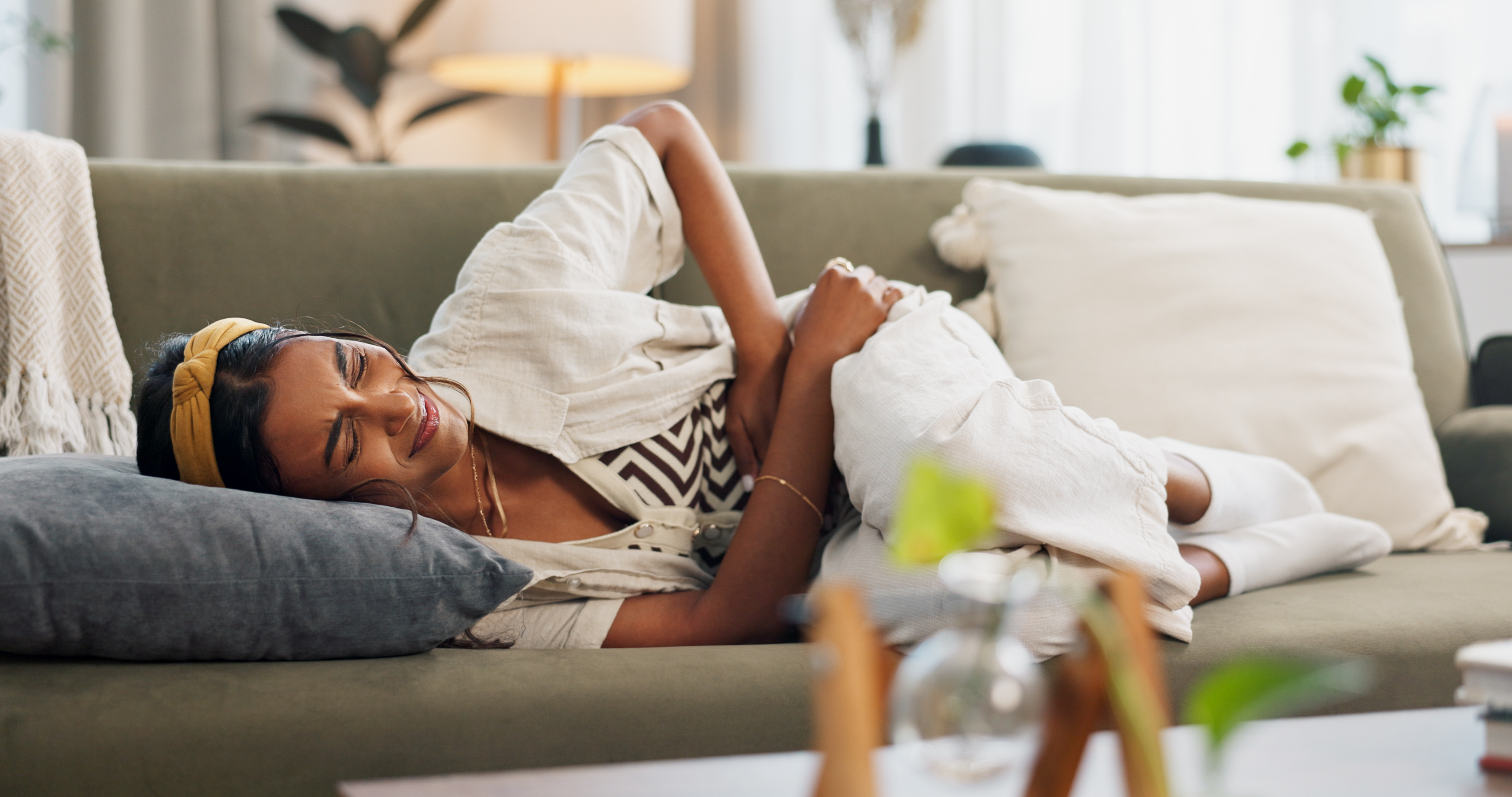

Digestive disturbances are often the first noticeable signs of gut microbiome imbalance. Symptoms such as bloating, gas, constipation, and diarrhea can indicate dysbiosis. These disruptions occur when harmful bacteria outnumber beneficial microbes, leading to impaired digestion and nutrient absorption. Chronic digestive issues may also exacerbate inflammation, contributing to a cycle of discomfort and imbalance. By recognizing these symptoms early, individuals can take steps to address the underlying causes and restore gut health. Simple dietary adjustments, stress management, and hydration can significantly improve digestive function, promoting a balanced microbiome.
3. The Gut-Brain Connection

The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system linking the central nervous system with the enteric nervous system in the gut. This connection plays a pivotal role in mood regulation, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can disrupt this communication, potentially leading to issues such as anxiety, depression, and brain fog. Studies suggest that gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, influencing mental health. By nurturing a healthy microbiome, individuals can support their mental well-being, fostering resilience against stress and promoting a positive outlook on life.
4. Immune System Implications

The gut microbiome is integral to immune system function, with approximately 70% of the immune system residing in the gut. A balanced microbiome helps regulate immune responses, protecting against pathogens and reducing inflammation. Dysbiosis, however, can compromise immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and autoimmune conditions. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for overall immune health. Strategies such as consuming a varied diet, reducing stress, and avoiding unnecessary antibiotics can support a robust immune system, enhancing the body's ability to defend against illness.
5. Skin Health and the Microbiome

The skin is a reflection of internal health, and the gut microbiome plays a significant role in skin condition. An imbalanced microbiome can contribute to skin issues such as acne, eczema, and psoriasis. This occurs through systemic inflammation and the gut-skin axis, where gut health directly influences skin health. By addressing gut dysbiosis, individuals can improve skin clarity and texture, reducing inflammation and promoting a radiant complexion. Incorporating anti-inflammatory foods, staying hydrated, and managing stress can enhance both gut and skin health, offering a holistic approach to beauty and well-being.
6. Weight Management and Metabolic Health

The gut microbiome influences weight management and metabolic health, affecting how the body processes food and stores fat. Certain bacteria can extract more calories from food, contributing to weight gain and metabolic disorders such as obesity and diabetes. Dysbiosis can also lead to insulin resistance and altered lipid metabolism, exacerbating these conditions. By promoting a balanced microbiome through diet and lifestyle changes, individuals can support healthy weight management and metabolic function. Regular physical activity, mindful eating, and adequate sleep further enhance metabolic health, fostering a balanced and thriving microbiome.
7. Hormonal Balance and the Gut

Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions, and the gut microbiome plays a role in hormone metabolism. An imbalanced microbiome can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to issues such as irregular menstrual cycles, mood swings, and thyroid dysfunction. The gut-liver axis is particularly important, as the liver processes hormones and the gut microbiome influences liver function. By supporting gut health, individuals can promote hormonal balance, enhancing overall well-being. Strategies such as consuming hormone-supportive foods, reducing toxin exposure, and managing stress can optimize hormonal health, contributing to a balanced microbiome.
8. Chronic Inflammation and Gut Health

Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many diseases, and the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses. Dysbiosis can lead to an overactive immune response, perpetuating inflammation and increasing the risk of conditions such as arthritis, cardiovascular disease, and inflammatory bowel disease. By addressing gut health, individuals can reduce systemic inflammation, supporting overall health and longevity. Anti-inflammatory diets, rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber, can help modulate inflammation and promote a balanced microbiome, enhancing quality of life and disease prevention.
9. Sleep and the Microbiome

Sleep is essential for health, and the gut microbiome influences sleep quality and circadian rhythms. An imbalanced microbiome can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia and fatigue. The production of sleep-regulating hormones, such as melatonin, is influenced by gut bacteria. By nurturing a healthy microbiome, individuals can improve sleep quality, supporting physical and mental rejuvenation. Establishing a regular sleep routine, minimizing screen time before bed, and consuming sleep-supportive foods can enhance both sleep and gut health, promoting a harmonious balance between rest and activity.
10. Personalized Approaches to Gut Health

Every individual's microbiome is unique, and personalized approaches to gut health can yield the best results. Genetic factors, lifestyle, and environmental influences all shape the microbiome, necessitating tailored strategies for optimal health. Testing and analysis of the gut microbiome can provide insights into specific imbalances, guiding personalized interventions. By understanding individual needs, individuals can adopt targeted dietary and lifestyle changes, promoting a balanced and thriving microbiome. Collaboration with healthcare professionals and nutritionists can further enhance personalized approaches, supporting long-term health and well-being.
Embracing a Healthier You
Spotting the subtle clues of gut microbiome imbalance is the first step towards a healthier you. By understanding the intricate relationship between the gut and overall health, individuals can make informed choices to restore balance and vitality. From diet and lifestyle changes to personalized interventions, there are numerous strategies to support a healthy microbiome. Embracing these approaches can lead to improved digestion, enhanced mental well-being, stronger immunity, and overall better health. As we continue to explore the fascinating world of the gut microbiome, we empower ourselves to take charge of our health, fostering a vibrant and balanced life.
