Opioids - What Are They And What Do They Do?
Opioids can be both synthetic and natural, acting as a potent painkiller. Derived from the poppy plant, an 'opiate' applies to natural medications derived from opium. Opioids, on the other hand, are generally artificially made. When used short-term, opioids such as morphine, can alleviate significant amounts of pain. Unfortunately, prolonged use increases one's risk of abuse and addiction.
How Do Opioids Work?
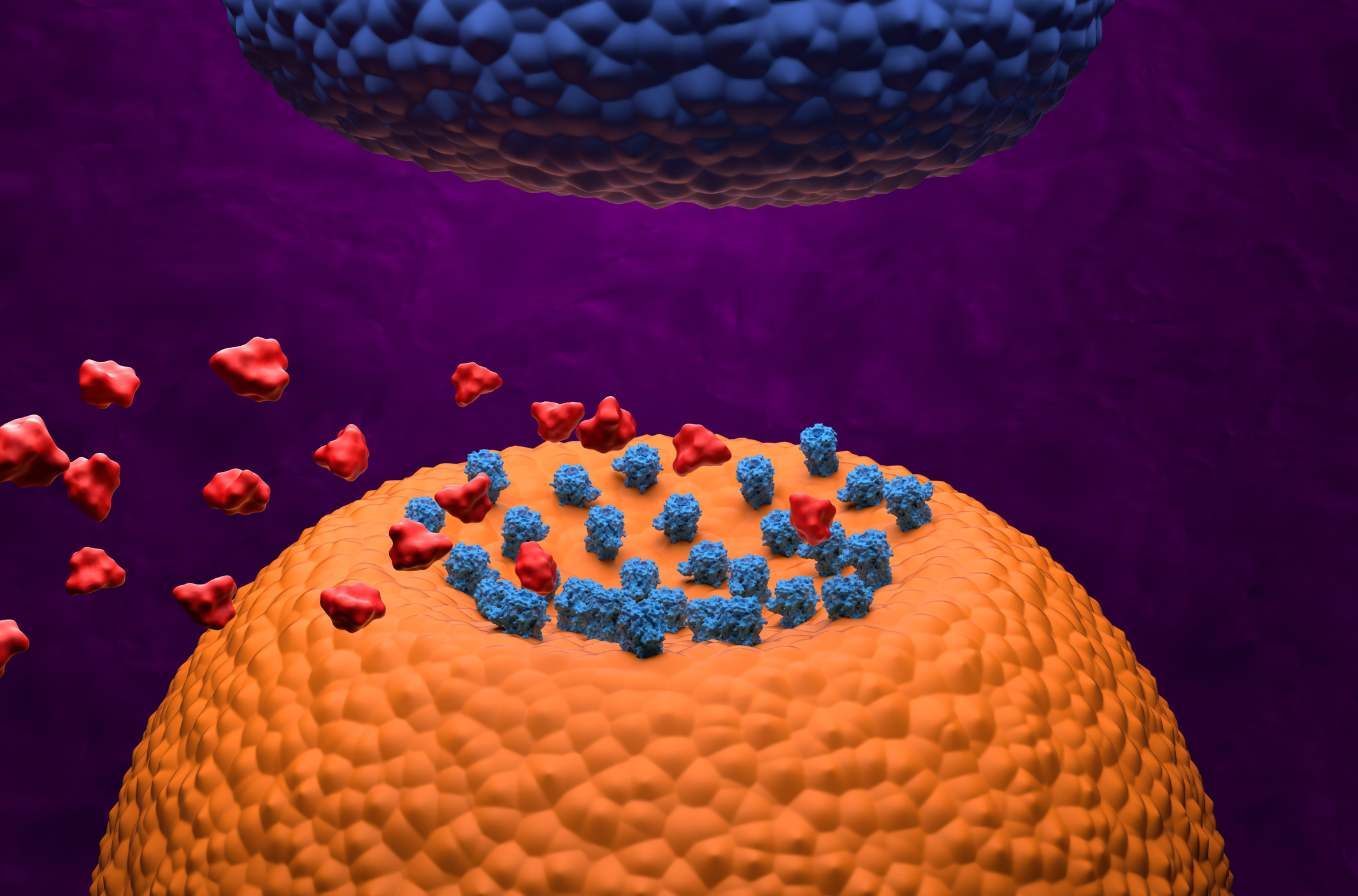
Once an opioid molecule is present in the bloodstream, it travels to the brain, where it attaches itself to specific receptors. These receptors are also found in the spinal cord and other areas of the body. It is then able to mimic neurotransmitters based on its structure, activating certain cells. Think of an opioid and its targeted receptor as a lock and key, as it initiates a chemical response in the brain's reward center.
Working differently than a natural neurotransmitter, opioids do not activate nerve cells in the same manner. As opioids take effect, the reward center is flooded with dopamine, supporting movement, emotion, cognition, motivation, and pleasure. It is the stimulation of this circuit that places individuals at-risk for drug abuse and a potential dependence. Based on its rewarding properties, individuals must follow all instructions carefully and continually review their dosage with a physician.
Next, discover what opioids exactly do to the human body.
How Are Opioids Used?

Commonly prescribed for pain, opioids can be used in a wide range of clinical settings. After a patient is out of surgery, for instance, opioids may be given to help control pain levels. The same is true for those who have experienced a significant injury, are enduring cancer-related pain, or require relief from a chronic, degenerative disorder.
The human body actually produces its own opiate-like substances, such as endorphins. Unfortunately, our body’s natural defense system is not effective against immense levels of pain. Considering pain is the body’s way of letting a person know that something is abnormal, powerful opioids are generally used to combat pain levels.
Keep reading to learn about the short-term effects of opioids.
Short-Term Effects

There are various short-term effects that opioids can have on an individual’s body, and can affect both their physical and mental well-being. Some of the short-term physical effects of opioid use include drowsiness, constipation, nausea and vomiting, and difficulty breathing, which can also worsen sleep apnea. Male patients may also experience impotence due to using this medication, even for a short period of time. Mental effects of opioid use include experiencing feelings of euphoria or feeling high, as well as headaches, dizziness, and confusion, which can cause an individual to lose their balance and fall, resulting in possible fractures or other injuries.
Continue reading to find out what the long-term effects of opioid use can do to the body.
Long-Term Effects

The long-term effects of using opioids can also include an increased tolerance to it, substance use disorder or dependence, liver damage, infertility in women, worsening pain also known as opioid-induced hyperalgesia, and life-threatening withdrawal symptoms in infants born to addicted mothers. Even when opioids are prescribed by a physician for pain management and relief, some of the serious side effects include a physical dependence, substance use disorder, and the possibility for the patient to overdose. Individuals who end up dealing with an opioid dependence problem are likely to experience intense withdrawal symptoms when they lower their dosage quickly or suddenly stop using the medication. If a patient wants to lower their dosage, they should do so with the help of a healthcare provider.
Next, discover the various types of opioids that are used for pain relief.
Opioids For Pain Relief

When taken as prescribed, an individual will experience temporary pain relief and reduced anxiety. When administered in higher doses, intense feelings of euphoria are reported. They are also prescribed in cases relating to irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). If a person is experiencing chronic pain, it is suggested that they try other options before resorting to opioids, as a long-term use is not recommended, and that they also consult a physician when it comes to taking opioids for pain relief.
Some of the most common opioids are codeine, fentanyl, hydrocodone, methadone, and oxycodone. Often prescribed on an ‘as needed’ basis, it is important to regularly check in with a doctor if someone is taking these potent medications. If an individual has been taking opioids for an extended period of time, they should speak with their doctor before fully discontinuing use, as they may experience symptoms of withdrawal.
