Causes And Symptoms of STDs In Males
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are transmitted through any type of sexual activity. Some are specific to a man or woman, but many are common to the two sexes. The symptoms, if any, are also sometimes different and men should not assume they are free of any infections if they are not showing signs. Men should be alert to any changes and be aware of some symptoms which might appear similar to other conditions.
10. Proctitis

Proctitis is a condition resulting from sexually transmitted diseases, including gonorrhea, syphilis, herpes, anal warts, and chlamydia. Prevalent among gay men and those who practice anal and oral sex with multiple partners, it causes an inflammation of the anus and rectum lining. An affected person will show signs of pain and cramping during bowel movements and possibly bleeding and other discharge.
9. Zika Virus
Zika virus is transmitted through mosquito bites or sex. Men can carry the virus in their semen and transmit it to a female partner, who, if she becomes pregnant, will risk delivering a baby with congenital disabilities. Sexually, it is transmitted vaginally, anally, and orally and it has been suggested contact with sexual toys can cause a person to become infected. Research shows saliva does not contribute to its spread.
8. Chlamydia

Common in both men and women, chlamydia often has a delayed onset of symptoms. It is caused by a bacteria transmitted through anal, oral, or vaginal sex. It could be weeks after contact when an infected man might experience unusual discharge, painful urination, and swollen and sore testicles. If the infection is in the rectum, there will be pain, bleeding, and discharge. Widespread in the US, there were 1,401,906 cases reported for both sexes in 2013.
7. Gonorrhea

Gonorrhea is caused by a bacteria transmitted through sex. It is an ancient STD affecting both men and women. Unlike women, who may not experience any symptoms, men may have a discharge from the penis with simultaneous burning and itching of the area. Delaying treatment can result in complications, including further infections and infertility. Down the road, valves of the heart can become inflamed, and an infected person can develop arthritis or eye problems.
6. Hepatitis B
Caused by the hepatitis virus, HBV, a man with hepatitis B may not be aware he has been infected. There are often little to no visual signs on the genitals, and instead, the infection affects the liver. The liver will become inflamed and may be accompanied by symptoms common with other ailments like loss of appetite, fatigue, fever, aching muscles and joints, nausea, vomiting, and jaundice skin. It is transmitted through blood and body fluids.
5. Herpes
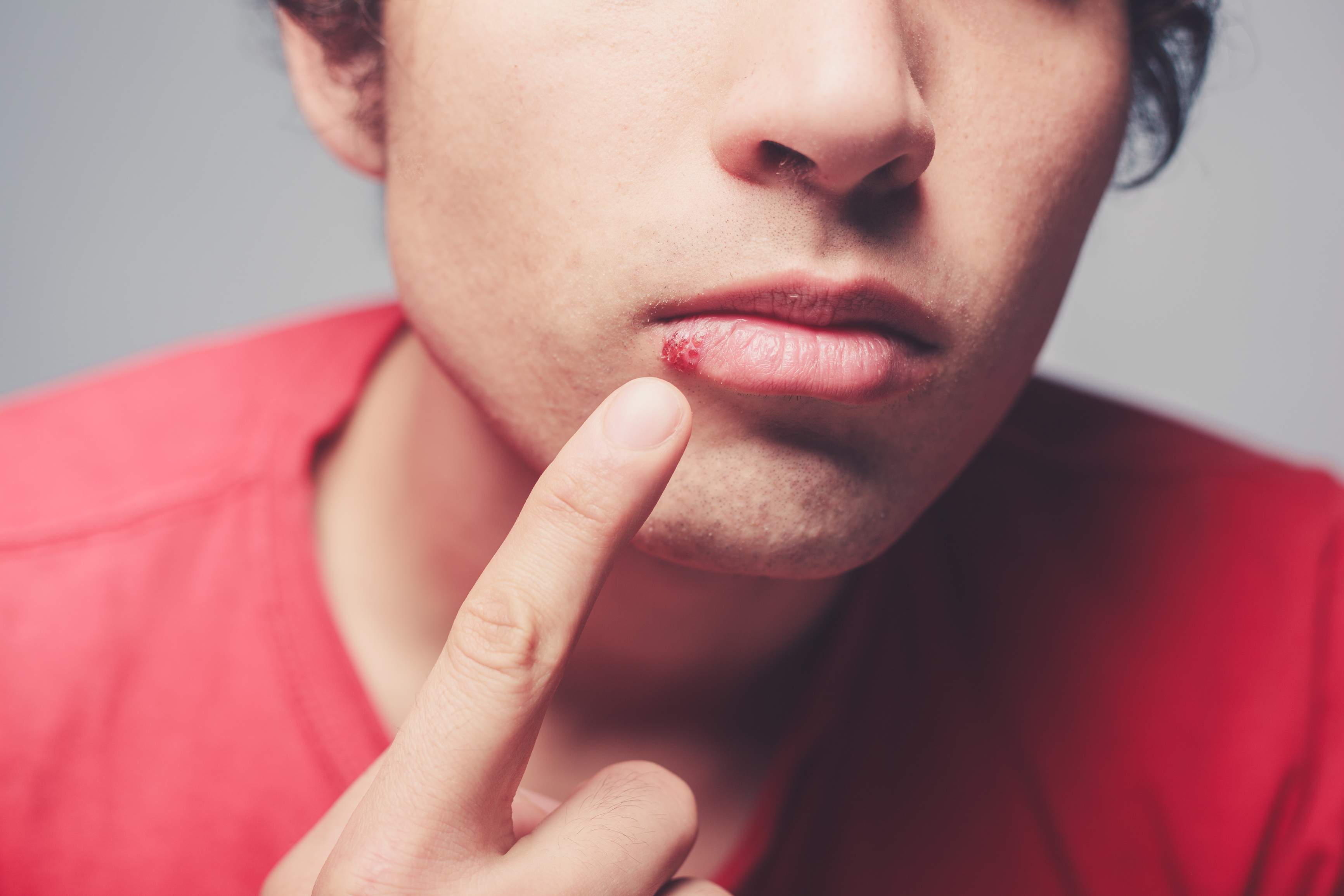

The viral infection, herpes, is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). There are two types; oral herpes affecting the mouth and genital herpes affecting the genitals. Both types are spread through contact with an infected person. Often there are no symptoms, or they may be delayed from two days to two weeks after contact. Symptoms in men include blisters, which may be painful, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, loss of appetite, fever, and a general feeling of malaise.
4. Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
One of the most common STDs, Human Papillomavirus, contains more than 150 strains of the virus. Of those, about forty are more serious and can pose harmful complications. Warts on the genitals or in the mouth are a symptom of low-risk strains, but some can cause anal, throat, or penis cancers. The main transmission is through sex, but HPV is also one STD which has two preventable vaccines to help avoid both low and high-risk strains.
3. Syphilis
Syphilis dates back to the 1400s but is still prevalent in today’s culture. In recent times, it has been connected to HIV so it is one of which men should be aware. It is caused by a bacteria transmitted through anal, oral, or vaginal sex. There are four stages involved including primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Symptoms vary for each but generally include a rash, fatigue, a sore throat, a headache, and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment with antibiotics sometimes produces a fever or aches.
2. When To Call A Doctor

Diagnosis and treatment vary depending on the type of infection. Some require a blood test while others do not require any tests. Unusual discharge is often examined for gonorrhea and chlamydia. If a man expects he was in contact with someone with an STD or if he is displaying any symptoms, a visit to the doctor is required to prevent further transmission and complications. Immediate attention is needed if the problem worsens or is accompanied by a fever.
1. Preventing STDs

The only way of completely avoiding contracting an STD is abstinence. Practicing safe sex by wearing a condom, knowing sexual partners and their backgrounds, and using dental dams and barriers during oral sex are some best practices for preventing the spread of infections. Limiting relationships to monogamous are safer than engaging in sex with more than one partner. Having open conversations and being honest about sexual health protects both partners.
