Overview Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a diagnostic imaging test that allows doctors to see the different organs and structures inside an individual's body. In most cases, clear and detailed images can be obtained that reflect the structures inside the body. A magnetic resonance imaging scan does not cause a patient pain and is non-invasive. Patients will need to stay still during the scan and may be asked to perform specific breathing patterns. Magnetic resonance imaging scans usually take between fifteen minutes up to an hour and a half to complete. Once the scan is complete, the images are sent to a radiologist, a doctor who specializes in interpreting medical images. The radiologist will write up and sign a report that is then sent to the doctor who ordered the scan.
Magnetic resonance imaging is incredibly useful. These scans can help doctors diagnose a myriad of conditions, including brain tumors. The images can help with brain tumor treatment and allow doctors to better plan brain tumor surgery. These scans can also dictate the need for other treatments, such as chemotherapy for cancer. Of course, patients need to understand MRI scans first.
How The Scan Works
The three main components that allow a magnetic resonance imaging machine to produce images of the organs and structures inside an individual's body are radio waves, a large magnet, and a computer. A patient having a magnetic resonance imaging scan lays still on a table that slides into a large, cylinder-shaped machine that contains considerable-sized magnets within it. When a patient is moved inside the machine, the water molecules in their body are temporarily realigned by the magnetic field created by the magnets. Radio waves are then used to induce faint signals from the realigned water atoms, which is what also produces the images in magnetic resonance imaging.
The images are taken in a cross-sectional manner, similar to the slices that make up a loaf of bread. The magnetic resonance imaging machine's computer compiles all of these cross-sectional images into the detailed images doctors view. The computer can also produce three-dimensional images of the structures and organs inside an individual's body out of the cross-sectional images.
Keep reading to learn about when magnetic resonance imaging scans are used next.
When MRI Scans Are Used
Magnetic resonance imaging scans are used for the diagnosis and evaluation of countless conditions and diseases. Some of the most common uses for magnetic resonance imaging are to see anomalies of the spinal cord and brain, identify cysts or tumors, screen for breast cancer, and see joint abnormalities or injuries. Other uses include searching for certain heart issues, identifying diseases in the liver or other abdominal organs, searching for endometriosis or fibroids, and looking for uterine abnormalities. These scans are also commonly used to help diagnose cerebral vessel aneurysms, inner ear and eye disorders, stroke, and traumatic brain injuries.
Magnetic resonance imaging can show a doctor the size of a patient's heart chambers and how they are functioning as well as the movement and thickness of the walls of the heart. These scans can also show the degree of damage produced by heart disease or a heart attack, inflammation and blockages in the blood vessels, and structural issues with the aorta. Magnetic resonance imaging can also evaluate the prostate, bile ducts, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, and ovaries.
Reveal the various types of magnetic resonance imaging next.
Types Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scans
There are quite a few different types of magnetic resonance imaging scans. Doctors will order the one that is the most suitable for each of their patients. For instance, many patients will need a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan, often called an fMRI, to diagnose a stroke. It is capable of this because this scan tests an individual’s brain activity. This type of magnetic resonance imaging also helps map the patient’s brain. Brain mapping is crucial for diagnosing epilepsy and tumors as well as for brain surgery.
Another form of magnetic resonance imaging is a breast scan. Doctors often order an MRI of the breast for patients who are at a high risk of developing breast cancer. Thankfully, this is not invasive, though it often requires a needle biopsy of the breast. Another form of magnetic resonance imaging is a scan that examines the patient’s heart and surrounding blood vessels. This is called a cardiac MRI and helps determine how well the patient’s heart is functioning.
Discover information on open versus closed MRI scans next.
Open Versus Closed MRI
Most patients will undergo a closed magnetic resonance imaging scan. This form has been around for longer than the open version. It is the type that involves a machine and space that resembles an enclosed capsule. The strength of the magnetic field in this form is stronger, which allows them to capture more detailed images and do so faster. A closed scan can diagnose more conditions and issues than an open scan. However, there are some disadvantages. A closed scan is often a problem for patients who experience claustrophobia. In addition, larger patients may not fit in the machine, the machine is quite loud, and patients often need to stay completely still during the scan.
An open magnetic resonance imaging scan is self-explanatory. This scan takes place in an open machine. The open machine offers several advantages, including fewer issues for claustrophobic patients, being a better fit for larger patients, and more child-friendly. An open MRI also allows the technician to tilt the machine. Evidence indicates that open scans are more cost-effective, quieter, and cause fewer side effects. However, they take longer to perform and produce less detail in their images than the closed type.
Discover information on magnetic resonance imaging with contrast next.
Scans With Contrast
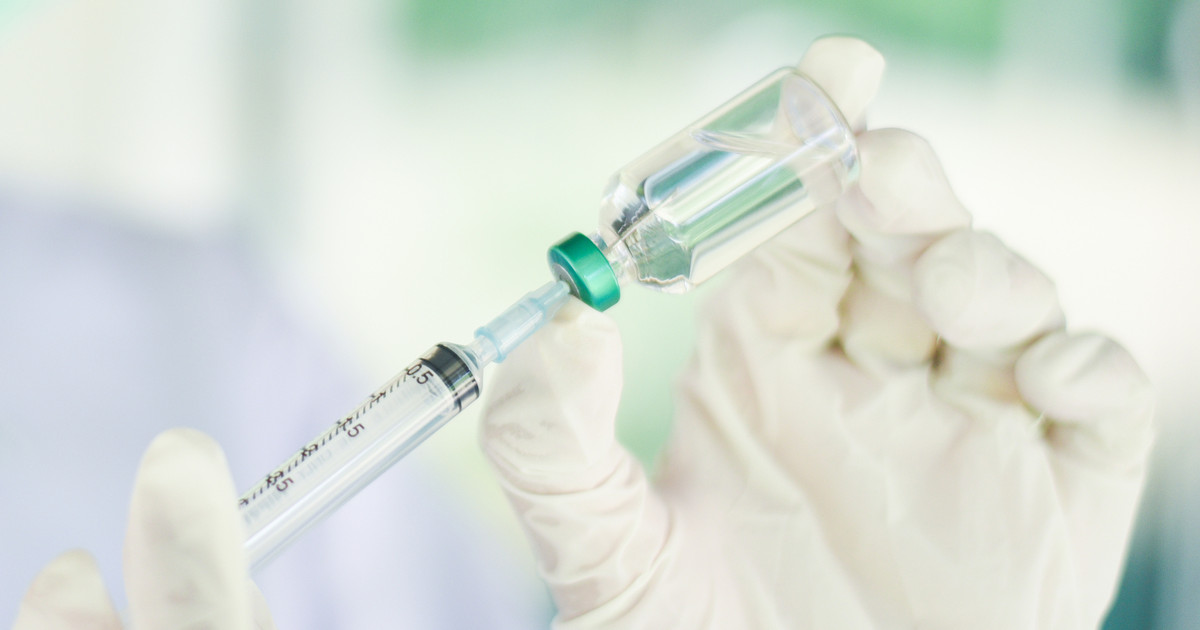
In most cases, magnetic resonance imaging does not use any contrast dye. Doctors will only order scans with contrast when they deem them absolutely necessary. The dye used in magnetic resonance imaging is gadolinium-based. Doctors will inject it intravenously. The purpose of contrast in one of these scans is to boost the quality of the image. This provides more accurate diagnoses. Contrast dye does not cause permanent organ discoloration. The patient’s body will absorb the dye or they will get rid of it through their urine. Pregnant women and those with compromised kidneys are not able to get one of these scans with contrast. The contrast medium, unfortunately, has some potential side effects as well. They include dizziness, hives, blood clots, and an allergic reaction. Thus, other patients may not be able to have the dye in magnetic resonance imaging. They include those with allergies, hypotension, and sickle cell disease.
Learn about how to prepare for the scan next.
Preparing For An MRI Scan

Patients can eat food, drink beverages, and take their medications normally before their magnetic resonance imaging scan unless their doctor informs them otherwise. When a patient arrives at the facility that will carry out the scan, they are usually asked to change into a gown. They will also be asked to remove any jewelry they have on, hairpins or hairclips, eyeglasses, watches, and wigs that contain metal. Patients have to remove any dentures, take off any hearing aids, and wash off cosmetics that may contain metal fragments as well.
An individual who has discussed concerns regarding feeling claustrophobic or very anxious during the scan may receive oral or intravenous medication to help make them comfortable during the procedure. Patients sensitive to loud or repetitive noises are provided with earplugs so that they do not hear the tapping, thumping, and other noises made by the machine. Some patients will have gadolinium injected into a vein to act as a contrast agent.
Continue reading to learn about what to expect during a scan next.
Expectations During The Scan
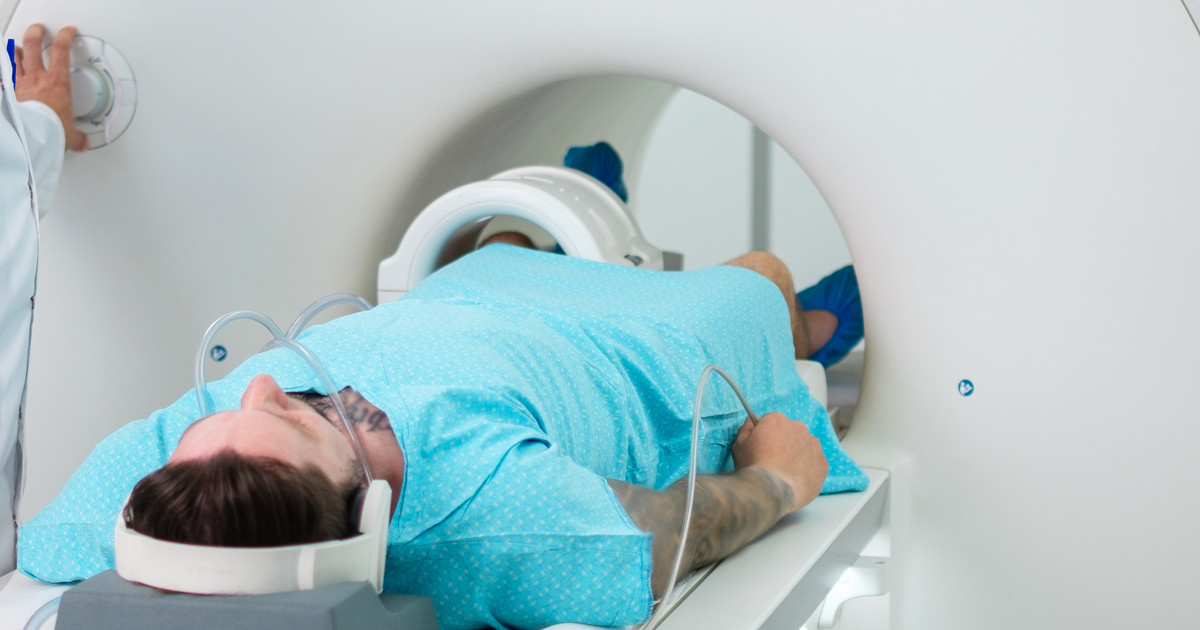
During a magnetic resonance imaging scan, patients can expect to hear some noises coming from the machine and its magnets. However, they may also ask their doctor for some earplugs or headphones to help distract them from this noise. Patients often have to remain still for the duration of a magnetic resonance imaging scan, which can span from fifteen minutes to one hour.
However, it is worth noting that there is an exception to staying still during this type of scan. Patients who are undergoing a functional magnetic resonance imaging scan are able to move. Of course, it is for a specific purpose. The technician will ask them to perform specific actions, such as tapping their fingers together or answering simple questions. The purpose of this is to determine what parts of their brain control these actions.
Compare magnetic resonance imaging to other imaging tests next.
Compared To Other Imaging Tests
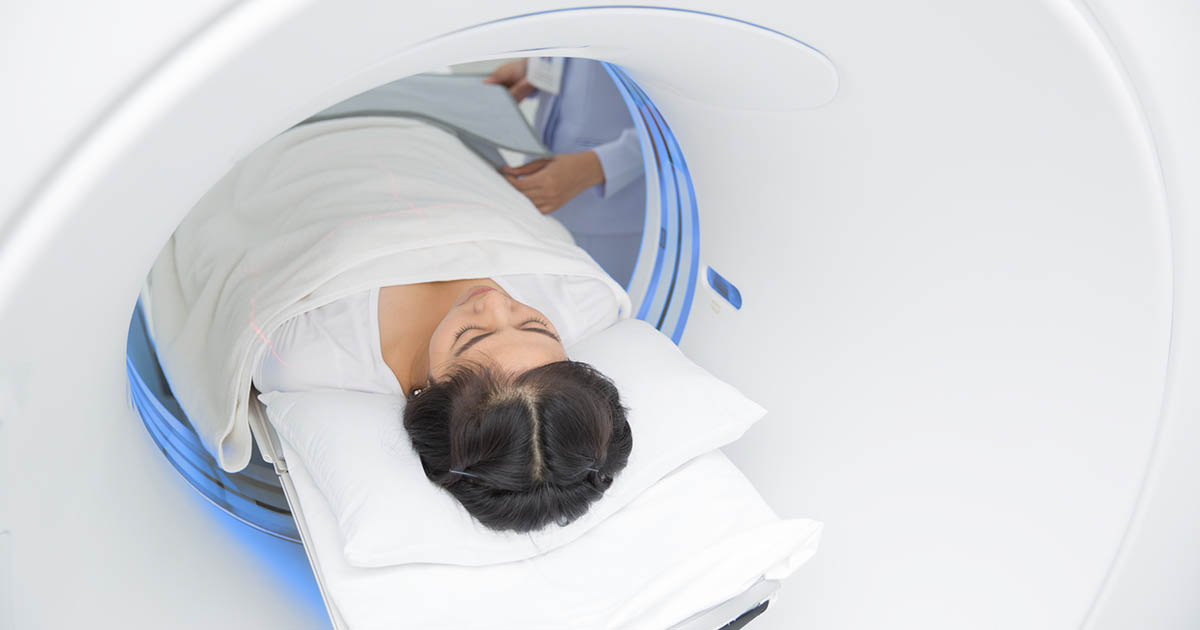
Magnetic resonance imaging does not use the same mechanisms x-rays and computerized tomography scans use to produce images of the body's structures and organs. This difference means magnetic resonance imaging scans do not use any of the potentially harmful ionizing radiation used by a computerized tomography scan. However, magnetic resonance imaging does use magnets within the machine that can produce problems if certain patients do not prepare for the scan properly.
Another difference between magnetic resonance imaging and other diagnostic imaging techniques is that the MRI machine has a much smaller opening into which the patient can slide. Some patients who undergo magnetic resonance imaging may need to be lightly sedated due to feeling claustrophobic inside the machine. Magnetic resonance imaging scans usually take longer than the typical x-ray or computerized tomography scan. A doctor decides which medical imaging technique to use based on the medical reason for the scan, the amount of detail needed, and any factors that may make certain scans intolerable.
Discover the risks linked to magnetic resonance imaging next.
Risks Of An MRI Scan
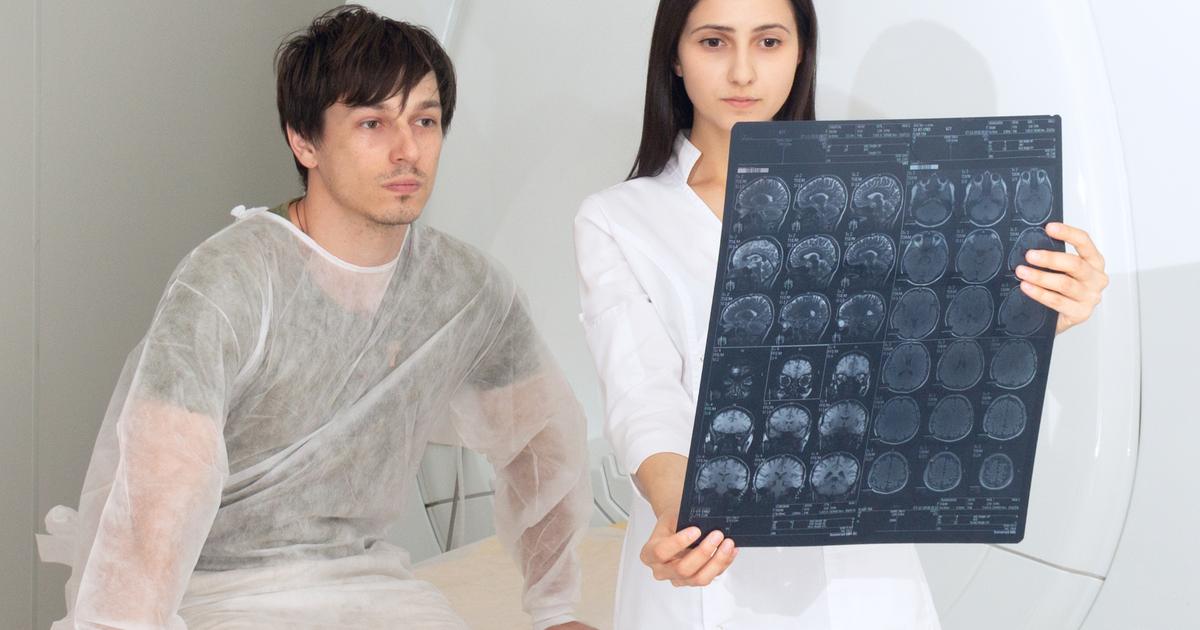
A magnetic resonance imaging machine uses strong magnets to produce detailed images of the inside of a patient's body. The presence of magnets in the machine poses risks for individuals who have certain medical devices implanted into their bodies that contain metal. Metals inside the body can be attracted to the magnets in the machine, making it a safety hazard. Metal objects in a patient's body that are not attracted to the magnets in the machine can distort the image produced by the magnetic resonance imaging scan.
The medical devices and objects that may pose a risk with magnetic resonance imaging include artificial heart valves, implanted drug infusion pumps, pacemakers, metal pins, metal screws, metal stents, and surgical staples. Other examples are metal plates, metallic joint prostheses, implantable heart defibrillators, implanted nerve stimulators, metal clips, cochlear implants, and intrauterine devices. Any non-removable metal piercings can also pose a risk to a patient if they have a magnetic resonance imaging scan.
Reveal information on MRI scans and pregnancy next.
MRI Scans And Pregnancy

Pregnant women or those who suspect they are pregnant must talk to their doctor before getting a magnetic resonance imaging scan. Many researchers say that there is no proven negative effect on unborn babies. Their claim is backed up by thirty years of pregnant women undergoing these scans with no negative effects directly linked to the scan. However, others claim that the effect is not clear. What doctors can agree on, though, is that pregnant women should not avoid getting necessary tests done. In addition, magnetic resonance imaging is preferred over computerized tomography scans for pregnant women as they do not involve the same radiation.
