What Are The Types Of Surgery?
Surgery is a medical specialty that involves opening the body to treat acute illnesses and chronic conditions. Surgery may be performed to relieve pain and to remove, change, or reshape body tissues. Since surgery is an invasive procedure performed inside the body, it typically requires the use of anesthesia. Patients may be given local anesthesia to numb a small area or region of the body for minor procedures. For longer or more complex procedures, general anesthesia is used so patients are unconscious for the procedure and cannot feel any pain. Some surgeries are performed at outpatient surgery centers, and longer procedures such as organ transplants or heart operations are done in hospitals. Before having surgery, patients will have blood tests, and their vital signs will be measured; some patients might also have an electrocardiogram. These tests are performed to ensure the patient is healthy enough to undergo the surgery.
Some of the most common overarching types of surgeries are discussed below.
Open Surgery
Open surgery is the oldest, most conventional form of surgery. Unlike newer procedures, open surgery involves making a single, large incision to open an area of the body for visualization and repair. Generally, the incision for open surgery is at least three to four inches in length, and many surgeries require even larger incisions. Open surgeries carry a higher risk for infection, blood loss, and other complications, and patients have a longer recovery time with these types of procedures.
However, certain types of surgeries, including organ transplants, must always be performed as an open procedure. Open procedures are frequently necessary for hernia repair operations that require the insertion of mesh into the body. Open surgery is also needed in cases where it is the only way to provide sufficient visual information to diagnose a condition or remove tissues, and it is beneficial for some types of repairs that cannot be made using current minimally invasive techniques. Surgeons will discuss all of the procedure options with the patient before the operation, and the patient will be advised of the risks and benefits associated with each surgical approach.
Read more about the different types of surgery now.
Keyhole Surgery
Keyhole surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique in which an operation is performed with several small incisions, each of which is normally less than one centimeter in length. A camera is inserted into one of the incisions, and this allows surgeons to view the interior of the body on a large monitor in the operating room. Surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions, and these instruments are often smaller than those used for open procedures. Keyhole surgery is most frequently used for gynecological and urological procedures, and it can also be used for certain joint replacement procedures, including knee replacements. Keyhole surgeries performed on the chest are known as video-assisted thoracoscopic procedures.
Compared to open procedures, keyhole operations are associated with a faster recovery time, reduced risk of infection, reduced bleeding, and reduced internal scarring (adhesions). Patients who have keyhole procedures typically report less pain than patients who undergo open procedures. Some types of keyhole operations are performed by inserting a camera and surgical instruments through an orifice of the body such as the mouth or nose, and these operations require no incisions.
Uncover more details on the major types of surgery out there now.
Laparoscopic Surgery
Laparoscopic surgery is a type of surgery that involves the abdominal and pelvic areas, and it is performed using keyhole methods. A laparoscopy might be performed to diagnose a condition or to take a tissue biopsy, and it is commonly carried out for the treatment of appendicitis and gynecological conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic inflammatory disease, fibroids, and ovarian cysts. Patients with undescended testes or any type of unexplained abdominal or pelvic pain may also have a laparoscopic procedure. Gallbladder removal, some types of weight loss surgery, and hysterectomies are often performed using laparoscopic methods too.
As a diagnostic procedure, laparoscopic surgery is beneficial in the diagnosis of many kinds of cancer, including cancer of the liver, gallbladder, bile duct, pancreas, and ovaries. Laparoscopic procedures used for diagnostic purposes typically last between thirty to sixty minutes, and all laparoscopic surgeries are performed with general anesthesia. Where possible, dissolvable stitches will be used. Patients who have had a laparoscopic procedure to diagnose a condition are generally able to resume their normal activities within five days. Minor laparoscopic operations such as appendix removal typically require a recovery period of three weeks, and major laparoscopic procedures such as those for ovarian cancer could necessitate a recovery time of up to three months.
Keep reading to learn about more types of surgery now.
Elective Surgery
Elective surgery refers to any operation planned in advance and not done in an emergency situation. Elective surgery includes a variety of procedures, including cosmetic procedures such as breast reduction and liposuction, as well as operations to remove the tonsils and to treat scoliosis, cardiac conditions, and ear conditions. While the term 'elective' might imply the procedure is optional, many cases of elective surgery involve major operations that can significantly improve the patient's quality of life.
Patients having an elective procedure will often be seen by their surgeon several times before the operation. During these office visits, the surgeon will explain the most effective surgical methods for the patient's needs, and the patient will also have a general health examination to help the surgeon plan for the procedure. The risks and benefits of the surgery will be explained to the patient, and they will have an opportunity to ask questions. The surgeon will advise the patient as to the anticipated recovery time, and plans will be put in place for appropriate aftercare and follow-up appointments.
Get the details on more significant types of surgery now.
Emergency Surgery
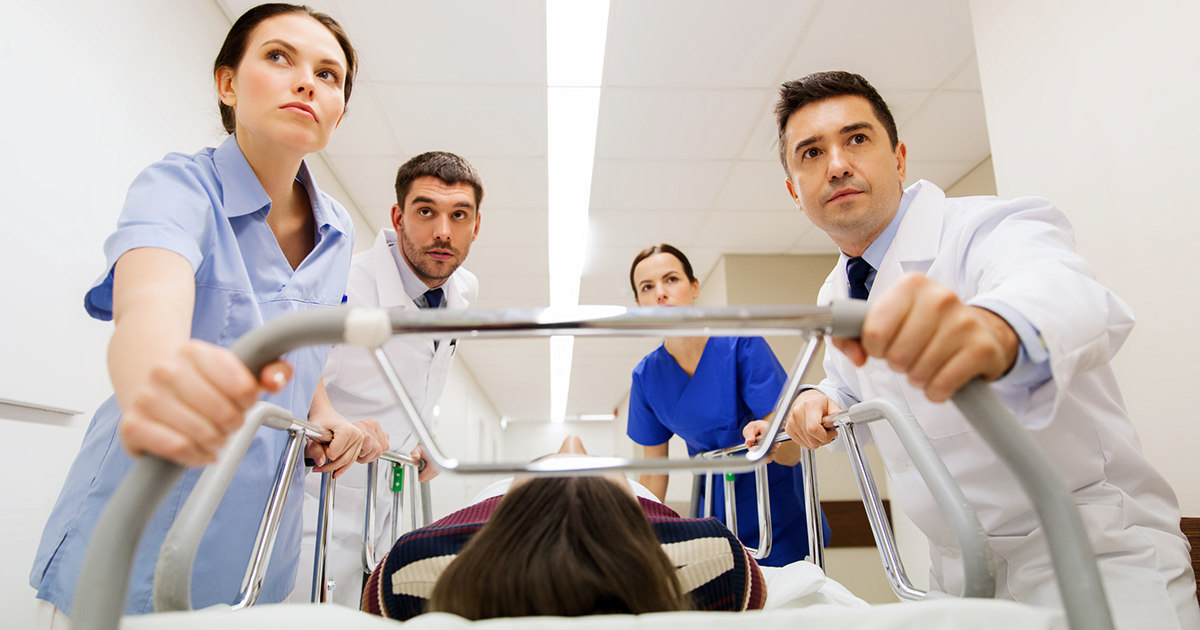

Any operation that must be performed immediately and cannot be delayed is considered emergency surgery. Emergency procedures, which typically require general anesthesia, are performed to prevent death or permanent harm to the patient. These operations are normally carried out by surgeons who work in a hospital emergency department. Before the surgery, doctors will carry out an intake assessment to record the patient's vital signs and gain intravenous access. After conducting a physical exam, patients may have blood tests, electrocardiograms, and CT scans or other imaging studies. The patient will be stabilized before being taken to the operating room.
If one hospital cannot perform a particular procedure due to a lack of staff or equipment, the patient will be transferred to another hospital (usually by helicopter) as soon as they are stable. At large hospitals, at least one trauma or general surgeon is available twenty-four hours a day, and they will often perform a pre-operative assessment in the emergency room. If possible, the surgeon will speak with the patient's family before beginning the operation. After the surgery has been completed, patients may need to be placed in intensive care, and most will need to spend several days in the hospital.
