The Different Complications Of Jaundice in Newborns
Babies born with a yellowish hue to their skin likely have jaundice. The fairly common condition in newborns and infants is caused by an abundance of bilirubin in their blood. Bilirubin, found in the red blood cells, is a yellow pigment which is flushed through the liver. Appropriate levels are maintained by being eliminated in the urine and feces. When jaundice is not successfully treated, two main complications arise: Acute bilirubin encephalopathy and kernicterus.
10. What To Expect
If parents are concerned about the level of jaundice or additional symptoms their baby is displaying, it is important to make a note of issues to discuss with a doctor. He or she will ask if the baby is feeding well and whether feeding is through breast milk or formula; if there has been any abnormal elimination; how easily the baby wakes; and if he or she appears ill or has muscle weakness. Changes in skin color and any spread of it to other body parts should be noted.
9. Phototherapy
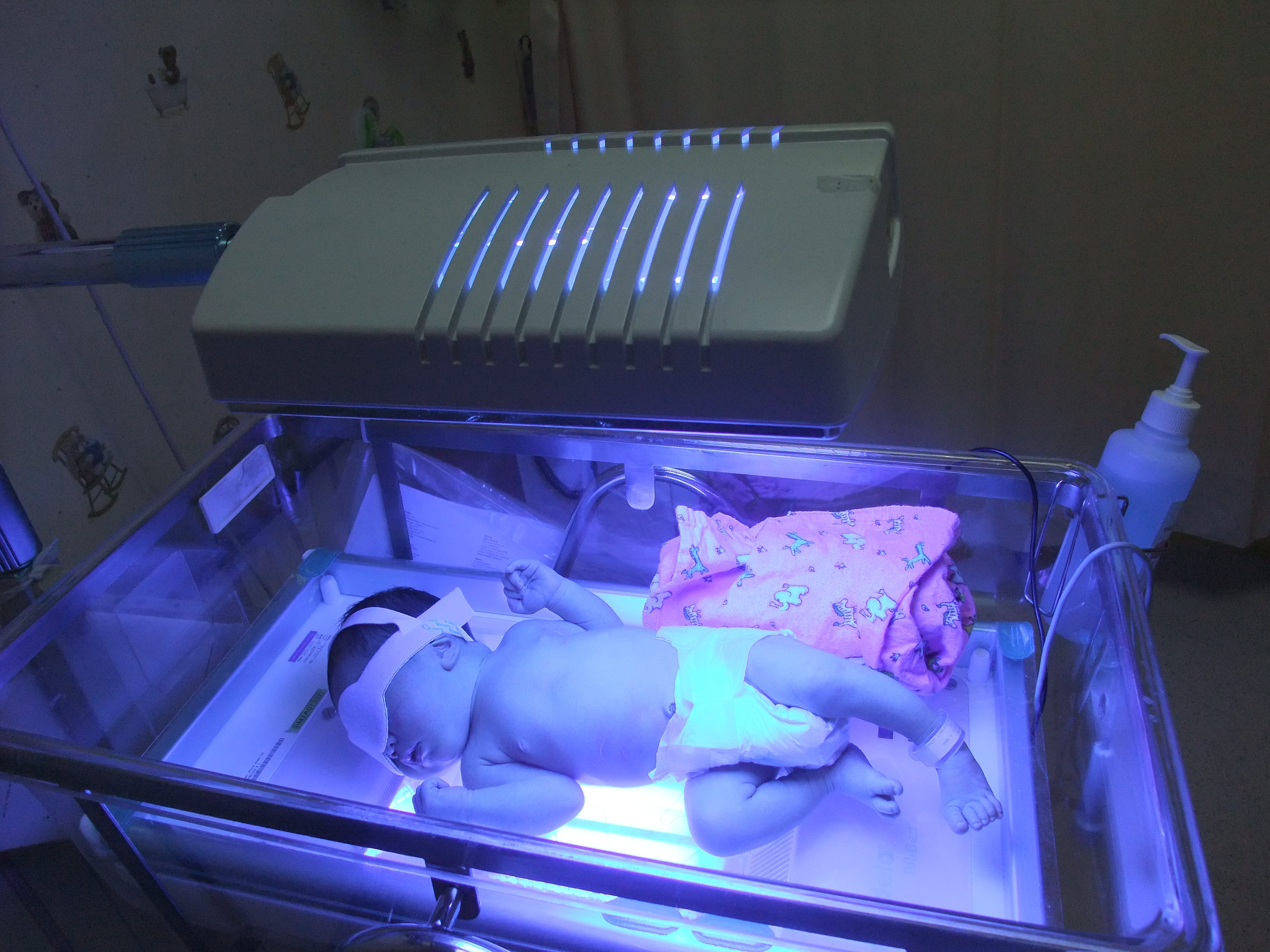

A form of treatment for jaundice using light is called phototherapy. Photo-oxidation is a procedure used to lower bilirubin levels in babies through the addition of oxygen. The liver has an easier time removing the bilirubin because it is now able to dissolve in water. Two main types, conventional phototherapy and fibreoptic phototherapy, aim light on a baby’s skin. Fibreoptic is used on premature babies, but conventional is usually the first method attempted in most cases.
