Important Facts About Ovarian Cancer All Women Should Know About
One out of every seventy-three women will develop ovarian cancer in their lifetime. It has become the fifth most common cancer found in women. Each year, approximately 20,000 women in the United States are diagnosed with ovarian cancer, with 14,000 dying from the disease, most of whom are over the age of sixty. Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries and fallopian tubes, but without detection and treatment, can spread to other organs in the pelvis and lower abdomen. If found in the early stages, ovarian cancer can be treated with surgery and chemotherapy, which improves the health and life expectancy of the patient.
Types Of Ovarian Cancer
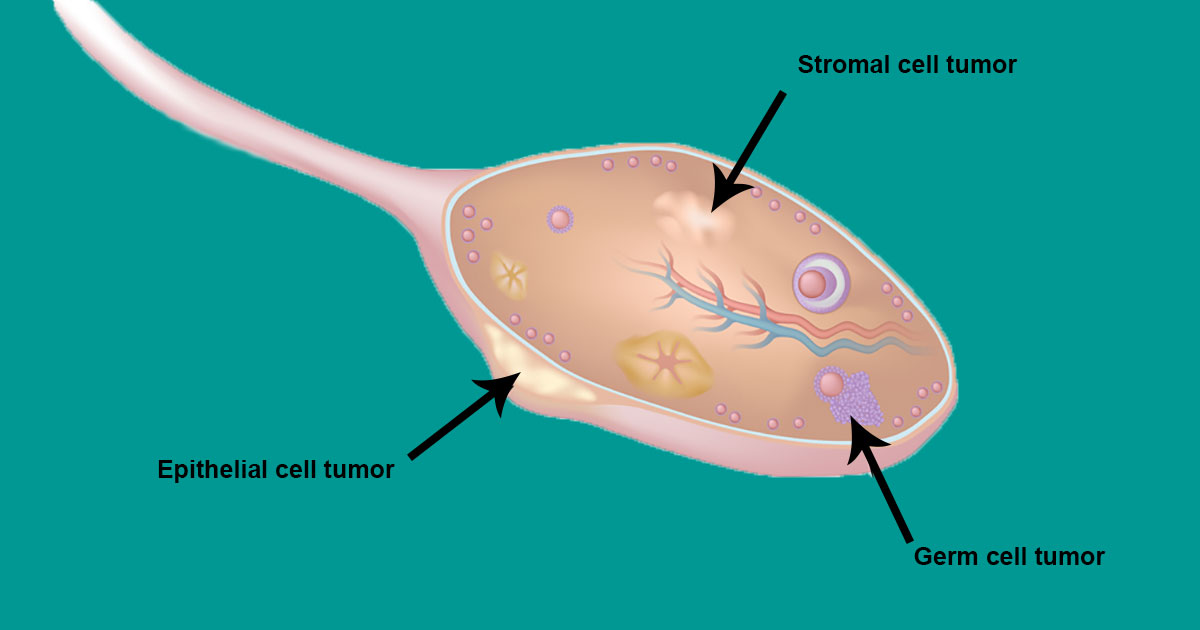
The different types of ovarian cancer are classified by the type of cell they originated from. The most common tumor is the epithelial tumor, which accounts for approximately ninety percent of all ovarian cancers. The surface epithelium is the cells that make up the outer lining of the ovaries. Stromal cell tumors account for seven percent of ovarian tumors, beginning in the stromal cell, which are the cells that produce and release hormones. The last of these common cancerous tumors start in the germ cells – the cells that make or form eggs. Other less common types of ovarian cancer include; ovarian sarcoma, Krukenberg tumors, and ovarian cysts.
