Serious Symptoms Of Ear Cancer
Ear cancer is a term used to describe a malignancy that develops in the cells that form the tissues of the outer ear, ear canal, middle ear, or inner ear. The cause of ear cancer is not known due to its low prevalence, but several factors are known to increase an individual's risk. An ear cancer diagnosis is made with a physical examination, MRIs, CT scans, and a biopsy of the affected tissue. Ear cancer treatment options are based on the size and exact location of the tumor in the ear. The first line of treatment of ear cancer is surgical excision, and many cases require subsequent reconstructive surgery. Severe cases may require removal of the entire eardrum, ear canal, and surrounding bone. Ear cancer that affects the temporal bone or ear canal often requires radiation therapy following surgical excision.
Scaly Patches Of Skin
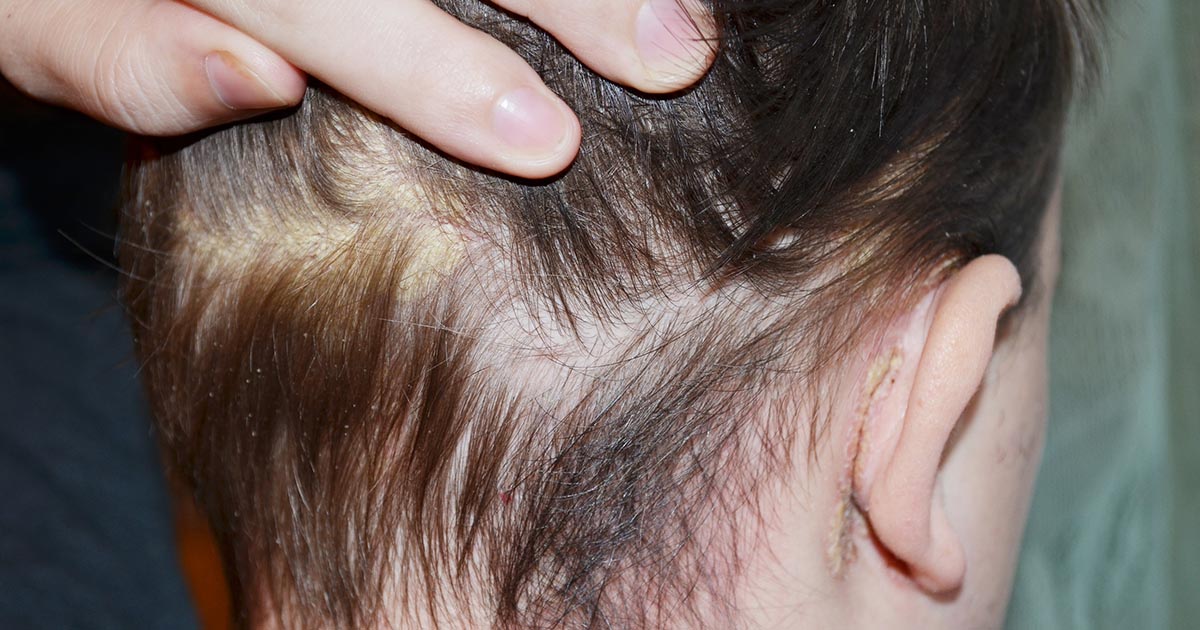
An individual who experiences the development of scaly patches of skin around or on the skin of the outer ear may be affected by ear cancer. The outer ear is the part of an individual's ear that can be seen from the outside. The primary functions of the outer ear are to help focalize and collect sound while protecting the rest of the ear. The outer ear has three different parts: the eardrum, ear canal, and ear flap. Ear cancer usually starts as a malignancy of the skin on the outside of the ear. The most prevalent types of skin cancers to appear on the outer ear, skin around the ear, and ear canal are referred to as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Basal cell carcinoma is the type more likely to produce scaly patches of skin upon the initial manifestation of the malignancy. The scaly patch is resistant to the effects of creams, moisturizers, lotions, and gels. As the tumor progresses, the scaly patch will gradually develop a pearly white colored bump underneath it.
Skin Ulcers
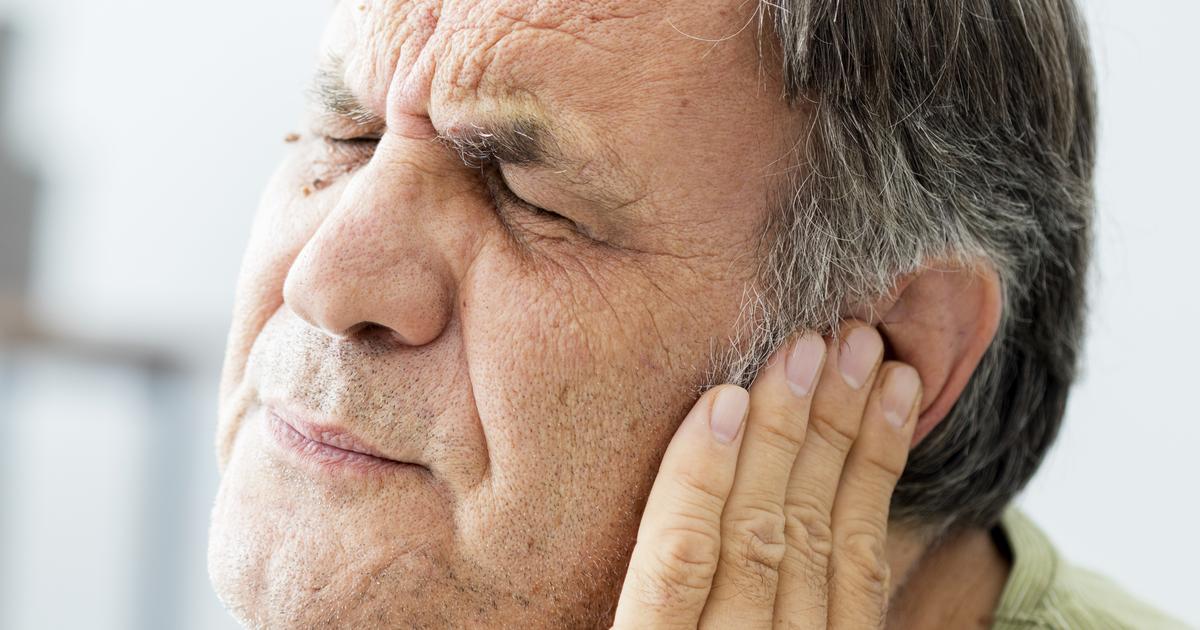
The development of skin ulcers on the region of skin that surrounds or makes up an individual's outer ear may indicate they are being affected by ear cancer. A sore around or on the outer ear that is chronically inflamed and does not resolve without treatment within four weeks is of considerable concern in regards to ear cancer. A sore or ulcer that does not heal is considered one of the most common symptoms that occur in affected individuals. A skin ulcer caused by ear cancer may spread from the face to the ear. A skin ulcer from ear cancer may crust over and begin to bleed with touch as it progresses. Squamous cell cancers can cause the development of cancer in or on the ear and have a cauliflower-shaped and or ulcerated appearance. Malignant melanoma may develop on the outer ear, and most commonly originate conspicuously in a hyperpigmented freckle, mole, or spot that begins to change shape, color, and consistency in borders. This pigmented spot continues to grow, may form a blister, may become itchy, and can ulcerate.
