How To Treat Neuroendocrine Tumors
Neuroendocrine tumors are tumors that grow inside the cells that generate hormones. There are multiple places neuroendocrine tumors can grow including the glands, pancreas, lungs, intestines, and stomach. Not all neuroendocrine tumors are cancerous, but some are. Cancerous tumors may spread cells throughout the rest of the body. Benign tumors don't move. Neuroendocrine tumors tend to develop over a span of years, taking longer to form than many other tumors. Neuroendocrine tumors are a wide category of tumors, and there are many specific kinds. Because of this, everyone's circumstances regarding neuroendocrine tumors will be unique. Different treatments have been developed to shrink and remove the tumors, and as such, it's important to talk to a medical professional about the best course of treatment.
Surgery To Remove Tumor
When the neuroendocrine tumor is a pheochromocytoma or a presentation of Merkel cell cancer, the main treatment is surgery to remove the tumor, where a surgical oncologist will remove the tumor and some of the surrounding healthy tissue. The healthy tissue is a margin to make sure the surgeon gets all the cancer cells. Surgical oncologists are surgeons who specialize in treating cancer through surgery.
A less invasive surgery called laparoscopic surgery might be possible for patients who have pheochromocytoma. Rather than using a single large incision, a few smaller incisions are used. The surgeon inserts a camera and surgical tools through the opening to guide them through the surgery process. Prior to any surgery, it's important for patients to be informed of the risk factors and possible side effects. If it's not possible to surgically remove the tumor, another method of treatment must be used.
Continue reading for more details on how neuroendocrine tumors are treated.
Embolization
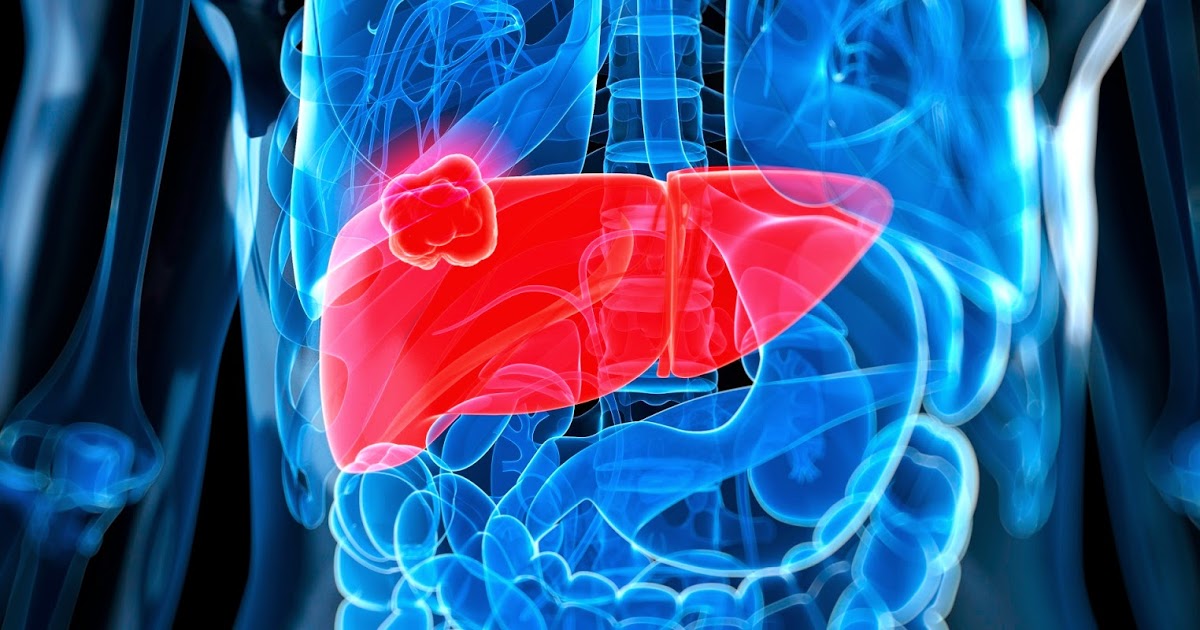
It's extremely common for a neuroendocrine tumor to metastasize into the liver. Liver metastasis is an important factor when determining the prognosis for a patient, and patients with liver metastasis may have a severely impaired quality of life. Embolization is a therapy used in patients whose neuroendocrine tumors have metastasized to the liver and is employed when patients cannot undergo surgery. Trans-arterial embolization is a common technique that selectively infuses particles into whatever artery branch is feeding the tumor's lesions. This technique has been shown to reduce the size of tumors and hormone output.
Learn more about treating neuroendocrine tumors effectively now.
