Risky Complications Of Mononucleosis
Mononucleosis, commonly referred to simply as mono, is a very common illness with a reputation for striking teenagers and young adults. Nicknamed the 'kissing disease,' mono can be spread through contact with an infected individual's saliva. For example, individuals can get it by sharing a drink with an infected patient, even if they are asymptomatic. Mono can be a horrible experience, but it does not usually lead to severe complications. After several weeks of rest, the patient usually gets better and can return to normal activities. However, a small percentage of cases can lead to further health issues, some of which are quite severe.
Jaundice
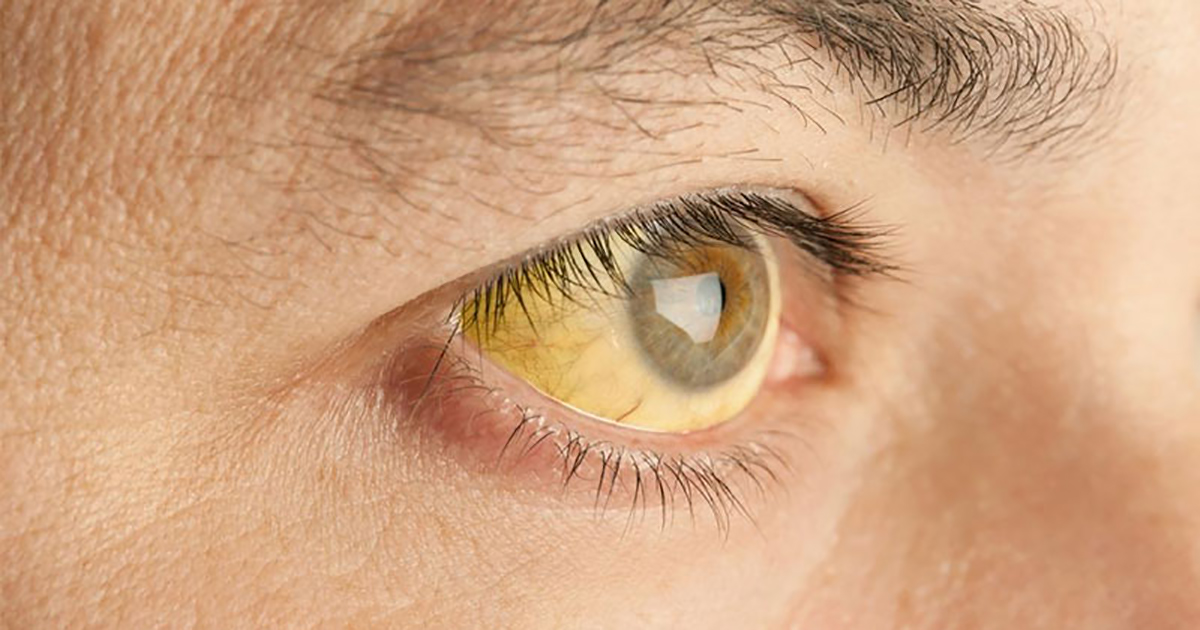
The main symptom of jaundice is a yellowish appearance of the skin, especially around the eyes. Sometimes the skin is more green than yellow, and sometimes it is itchy. Jaundice is caused by excessive amounts of bilirubin in the blood; bilirubin is a compound released by the breakdown of red blood cells. This condition is very common in babies, but in older children and adults, it often indicates serious problems with the liver. Mono typically affects the liver, but it only leads to serious liver issues in rare cases. If the skin of a mono patient turns yellow, they should go to the doctor to get blood tests for liver enzymes.
Anemia

Anemia is a lack of hemoglobin in the blood. It can cause fatigue, a fast heart rate, and shortness of breath. It is often caused by a lack of iron in the diet or blood loss. Anemia is typically diagnosed through a blood test called a complete blood count. This test shows the concentration of red blood cells, white blood cells, hematocrit, hemoglobin, and platelets in a patient's blood. Mono can cause a loss of red blood cells and hemoglobin. This complication is very uncommon, but it can happen. Someone who recovers from mono but has ongoing fatigue or dizziness should see a doctor to ask about getting blood tests done.
