How To Diagnose And Treat Schwannomas
When a tumor develops in the peripheral nervous system or the cranial nerves within the Schwann cells, it is called a schwannoma. Schwann cells are responsible for the production of the protective myelin sheath around the axons of nerves. Most often, schwannomas are benign or noncancerous, and in the cases where a schwannoma is cancerous, it will be called a soft tissue sarcoma. One of the most common areas for a schwannoma to form is on the nerve connecting the inner ear to the brain. This is called an acoustic neuroma or a vestibular schwannoma. One of the most common areas where cancerous schwannomas occur is on the sciatic nerve of the leg. Schwannomas do not develop anywhere in the brain or the spinal cord. Symptoms will manifest when the schwannoma has grown large enough to put pressure on the nerves near it. The location of the tumor will be the main influence on what kind of symptoms an individual will experience.
Learn about how schwannomas are diagnosed and treated now.
Electromyogram
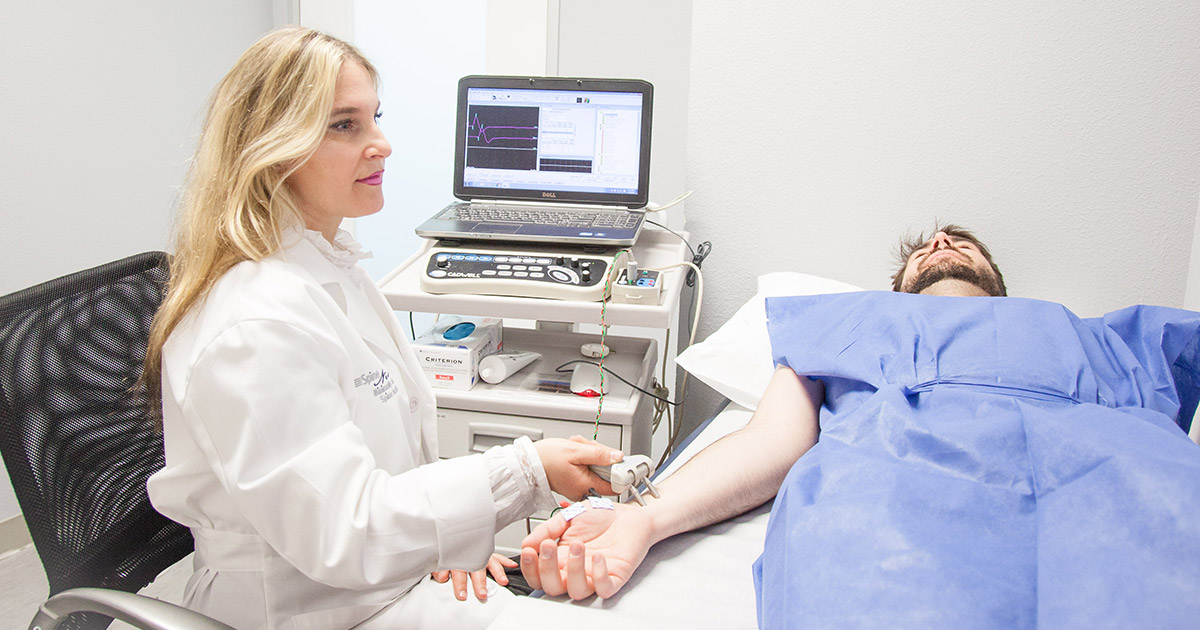
Schwannomas can be diagnosed using an electromyogram (EMG), or a test that measures the electrical impulses and activity of the muscles and nerves. This is a helpful tool because the electrical activity between nerves and muscles will be impaired when a schwannoma develops. This test measures the electrical activity when the muscles are in a forceful contraction, slight contraction, and at rest. A small needle with an electrode on the end is inserted into various muscles to perform an electromyogram. The individual having the electromyogram done will be asked to move the muscles being tested in various ways after the electrode has been placed. If an electromyogram is before a diagnostic imaging scan like an MRI or CT scan, the results may or may not prompt the use of one to pinpoint the tumor location. In addition, the results of a patient's electromyogram will determine if a biopsy on the area of concern should be performed. An electromyogram can also be used for a physician to rule out other diseases as the cause of symptoms an individual may be experiencing.
Get familiar with more ways to diagnose and treat schwannomas now.
Computerized Tomography Scan
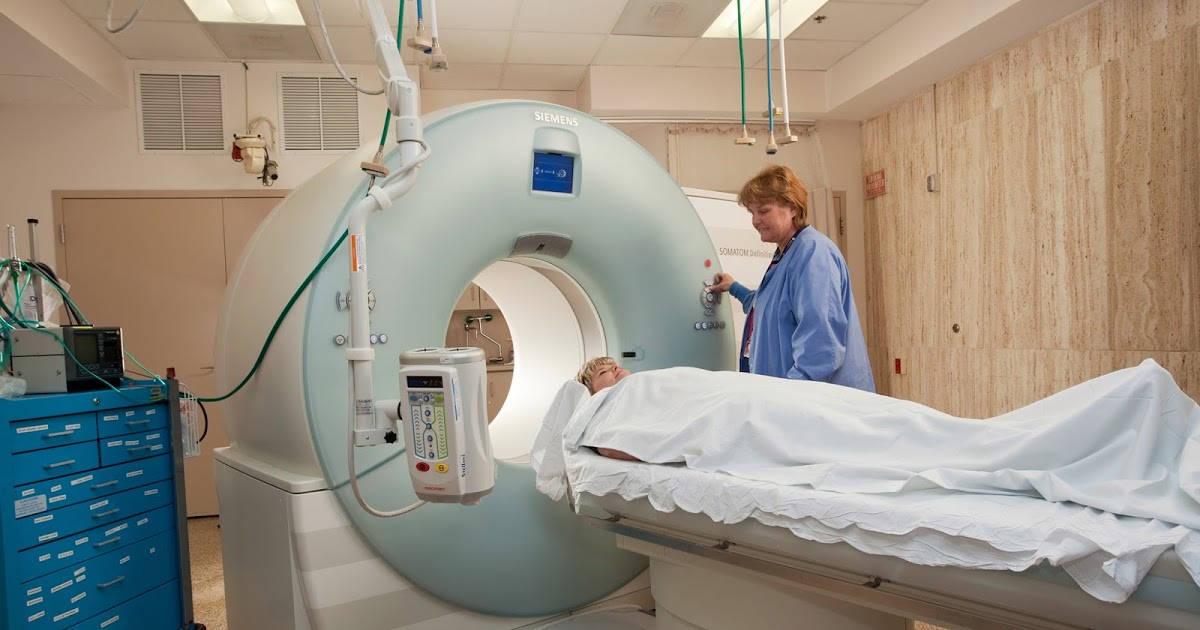
A computerized tomography scan (CT scan) will often be ordered when a physician suspects a patient may have a schwannoma. A CT scan utilizes special x-ray equipment in a procedure used to develop detailed scans or images of the targeted areas within the body. The images are formed when the CT machine takes continuous pictures in a helical fashion. Each picture developed during one of these scans will show the bones, organs, and other tissues within an individuals body. CT scans are utilized to check for thousands of possible abnormalities, one of them being the detection of abnormal growths like schwannomas. These scans are also used to determine what type of tissue damage has occurred around a schwannoma. This type of imaging test is extremely helpful for the planning of surgical procedures used to treat a schwannoma. With the administration of a CT scan, a physician can easily rule out other diseases or conditions that could be causing the same symptoms as a schwannoma.
Continue reading to learn about the methods of treating a schwannoma now.
