Guide To Treating Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome
Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome is best described as an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks healthy nerve cells located in the neuromuscular junctions. These junctions are where the muscles connect to nerves, which are responsible for communicating with the muscle cells that cause the muscles to move in a certain way. Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome interferes with the process of communication, and it does so by using antibodies to attack these nerve cells. The antibodies inhibit the nerve cells from producing sufficient amounts of a chemical called acetylcholine, which is responsible for the transmission of impulses between muscles and nerves. A lack of it results in problems with being able to move the muscles normally. Common symptoms associated with Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome include muscle weakness, difficulty walking, tingling in the feet or hands, difficulty breathing, changes in the bladder and bowel, and excessive fatigue.
Learn about the options for treating Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome now.
Potassium Channel Blockers

Because there is no current cure for Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome, no known method can inhibit the immune attack that causes interference in the nerve to muscle communications. Even though nothing can be done about that specifically, alterations can be made to the electrical activity passing through the affected areas. Potassium channel blockers are able to increase the duration of the electrical activity when it passes through the neurotransmitter junction. This increases the release of acetylcholine and the influx of calcium into the ending of the nerve. Due to the fact Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome acts to stop the production of acetylcholine, the use of potassium channel blockers can help neutralize that effect by stimulating the release of larger amounts of acetylcholine. Ultimately, the result of this neutralization is neuromuscular transmission is enhanced, and muscle weakness is reduced. This type of channel blockers can also help reduce other symptoms, including tingling in the hands and feet, problems walking or breathing, and excessive fatigue.
Uncover details on more treatments for Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome now.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin
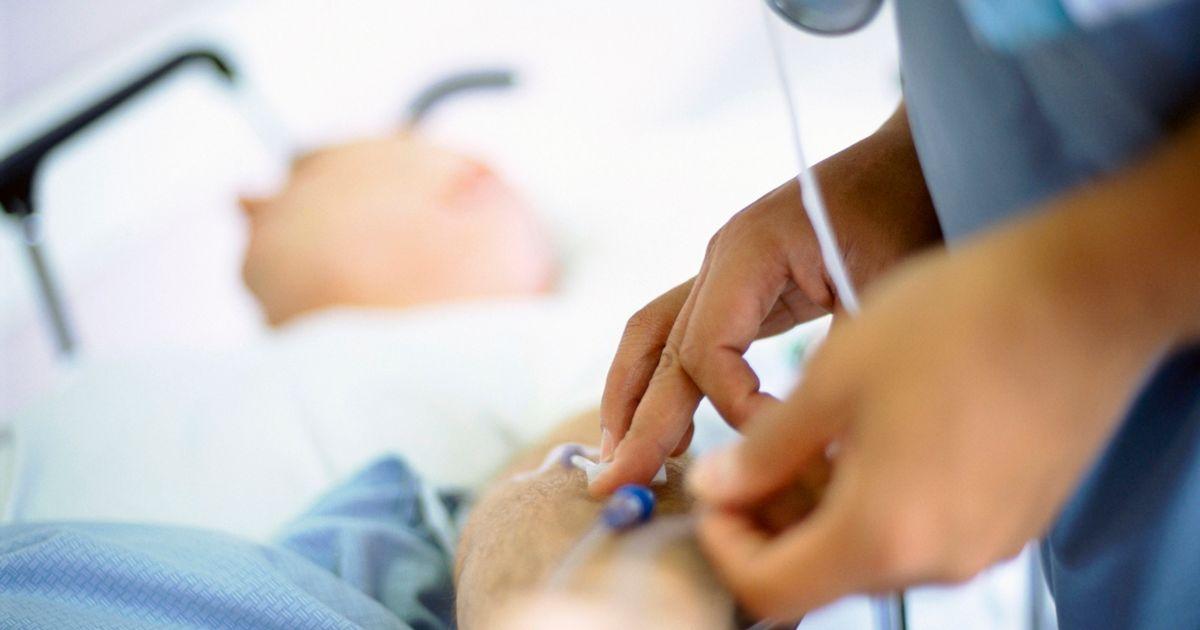
Intravenous immunoglobulin helps modulate the immune system to where it temporarily stops attacking the nerve cells. Immunoglobulin therapy is a way in which the physician can help manipulate the defective immune system into deactivation of the mechanisms acting on the neuromuscular junctions. There are, however, limitations of intravenous immunoglobulin when it comes to autoimmune disorder treatment such as in Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome. This type of therapy will remove the harmful antibodies the immune system is producing that interfere with nerve communications. However, it will not stop the immune system from its abnormal production of such antibodies. This is most likely the reason why intravenous immunoglobulin is considered a temporary solution. It is also a treatment often used in conjunction with other methods for optimal effectiveness.
Continue reading to reveal more Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome treatments now.
