Serious Warning Signs Of A Biotinidase Deficiency
Biotinidase deficiency develops when the body has a very low concentration of biotin, sometimes known as vitamin H. In some patients, biotin may be completely absent. This condition is inherited, and the deficiency itself is caused by the body's lack of ability to recycle and reuse available biotin. Biotin helps the body digest fats, carbohydrates, and protein. Biotinidase deficiency is equally prevalent in males and females, and the first symptoms of the condition normally develop in newborns or in babies less than three months old. In some cases, symptoms may not appear until the child is ten years old. To diagnose the condition, genetic testing can be performed, and newborn babies are routinely tested for this deficiency as part of required newborn screenings. The standard treatment for biotinidase deficiency consists of biotin supplements, and patients normally take between five and twenty milligrams of these supplements daily. While patients have to continue supplementation for life, the majority of patients treated have an excellent prognosis.
If biotinidase deficiency is not identified and treated, serious symptoms may develop. Some of the most common symptoms observed in patients with untreated biotinidase deficiency are outlined below.
Muscle And Limb Weakness
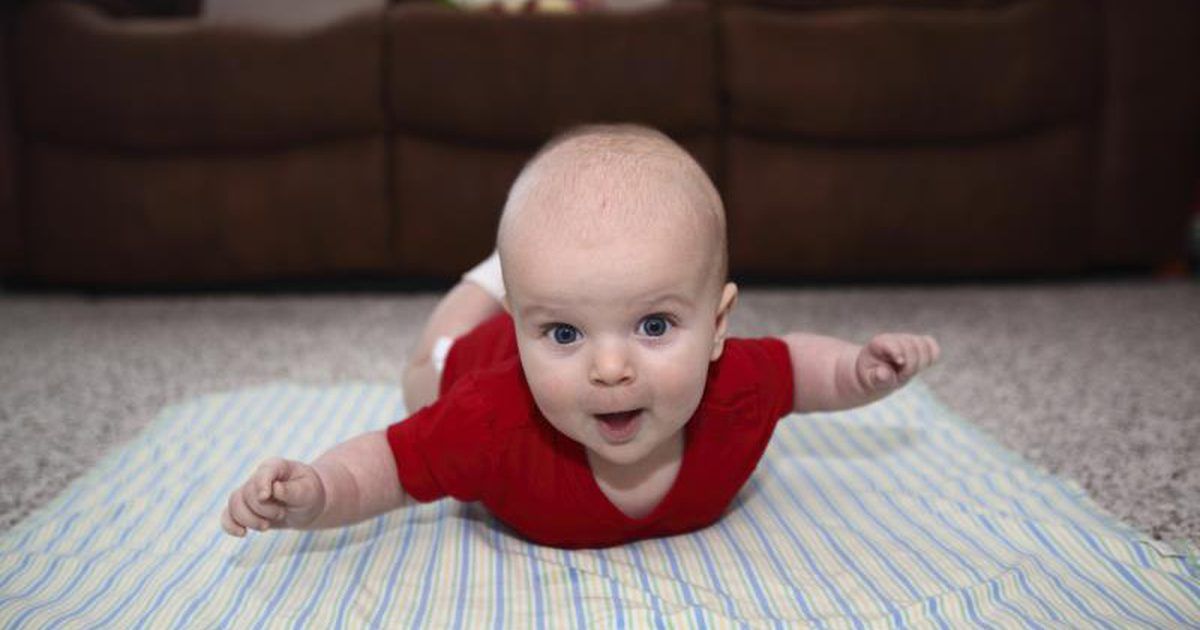

Newborn babies with this condition frequently exhibit muscle and limb weakness. Also known as hypotonia, this symptom is one of the earliest to appear. Pediatricians and neurologists typically perform assessments of newborns who present with muscle and limb weakness. To diagnose hypotonia, doctors start by performing a physical examination. This checks for overly flexible joints, weakness of the muscles in the torso, and tilting of the head when the child pulled into a sitting position. In addition to the exam, doctors may recommend the child get a CT scan or other imaging tests done. Nerve conduction studies, electromyography, or muscle biopsies may be needed for some patients. Physical therapy can help patients with muscle weakness to improve their muscle tone and function.
Learn more about the warning signs of biotinidase deficiency now.
Ataxia
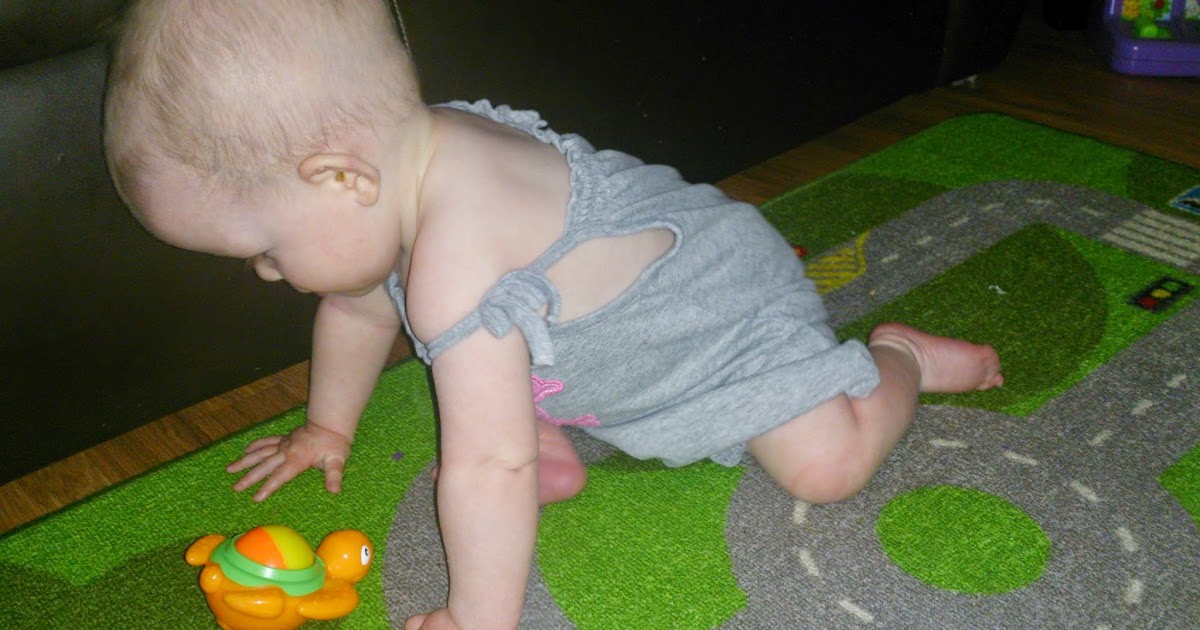

Ataxia refers to difficulties with balance and coordination, and it can manifest differently in each patient. Children who have started walking may walk with a gait that veers off to one side; the child may also walk backward, sway, or stop and start while trying to walk. This disorder can also include slurred speech, and patients may develop hand tremors. There may be abnormalities in eye movement patterns, and fine motor skills may deteriorate. Some patients may also experience heart problems. To evaluate the severity of these symptoms, doctors will check the patient's gait, and they will also test the patient's reflexes, grip strength, and range of motion. Specific tests to detect tremors will be used, and the doctor will also evaluate the patient's eye movements. These symptoms usually improve with proper treatment for biotinidase deficiency, and patients may also have speech, occupational, and physical therapy. These therapies help patients walk in a more balanced way and speak more easily. Parents of children with a biotinidase deficiency should monitor their child closely for signs of new or worsening balance, tremors, or coordination difficulties, and these should be mentioned to the child's pediatrician or neurologist as soon as possible.
Get the details on more biotinidase deficiency symptoms now.
Optic Atrophy

Optic atrophy usually occurs in older children who have a biotinidase deficiency. The condition affects the optic nerve and develops when the retinal ganglion cell axons die. These axons form the optic nerve. On examination, patients who have optic atrophy will have a very pale optic nerve, and the vision will be impaired. Patients who have mild atrophy may still have good visual acuity, but they may not be able to distinguish colors. Other symptoms include blurry vision, trouble with peripheral vision, and reduced sharpness of the patient's vision. In the most severe cases, patients may be legally blind, and they may not be able to distinguish light. Optic atrophy is normally diagnosed with a comprehensive vision examination. The doctor will check the patient's eye pressure and assess their color vision, visual acuity, peripheral vision, and the ability to distinguish contrast. A fundoscopy exam will also be completed. Since axons cannot be replaced, early detection of this condition is essential for preserving vision.
Continue reading to reveal more biotinidase deficiency warning signs now.
Seizures

Seizures are often one of the first symptoms to appear in individuals with biotinidase deficiencies. A seizure is an unexpected burst of electrical activity in the brain. Some patients may experience multiple seizures per day, and others may only have a seizure occasionally. When a patient has a tonic-clonic seizure, they may lose consciousness and start having rapid tremors of the legs and arms. Breathing may change, and patients may experience drooling or an inability to swallow. In other seizure types, patients may remain conscious and appear spacey or detached. After the seizure ends, the patient has no memory of this time, and they may feel depressed or weak. Some patients may fall asleep after the seizure, and others may feel thirsty or nauseous. To diagnose a seizure, neurologists use an electroencephalogram, which records brain wave activity, enabling the doctor to identify any seizure activity the patient experiences during the recording. Treatment for a seizure normally consists of medications called anticonvulsants, which can reduce or eliminate seizure activity in some patients. Individuals who have frequent seizure activity may need to take several anticonvulsants to gain control of their symptoms.
Uncover more information on the symptoms of a biotinidase deficiency now.
Various Skin Rashes
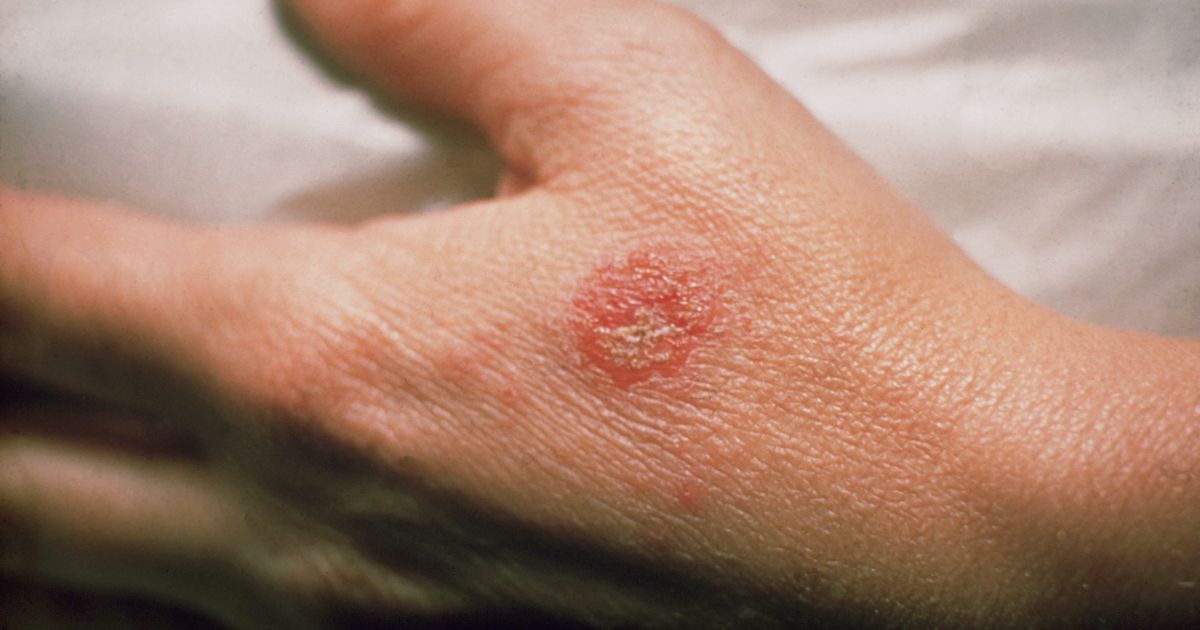
Various skin rashes may develop with biotinidase deficiency. In the early stages of this condition, patients may experience an eczematoid rash. These patches of eczema consist of red, itchy spots, and patients may have bumps that leak fluid and form a scab. Treatment for this type of rash normally involves moisturizers and steroid creams, and home remedies like oatmeal baths may help control itching. In addition to this rash, patients with biotinidase deficiency may develop fungal infections such as candidiasis, which often impacts the skin, nails, and mouth. Patients who notice any skin rash should be evaluated by a dermatologist to receive the most appropriate treatment.