Symptoms Of Enlarged Adenoids
The adenoids are soft tissue located in the nose and help create a layer of defense against invading infections and viruses. They are considered a vital part of the immune system. While all human beings are typically born with adenoids, they generally tend to shrink as individuals age and vanish during the adult years. For some individuals, however, this is not the case. Instead of shrinking, the adenoids may swell and become enlarged. Treatment for enlarged adenoids varies, depending on the cause and severity of the swelling. There are various symptoms of enlarged adenoids. If an individual encounters these symptoms, they should visit their physician for further evaluation.
Otitis Media With Effusion
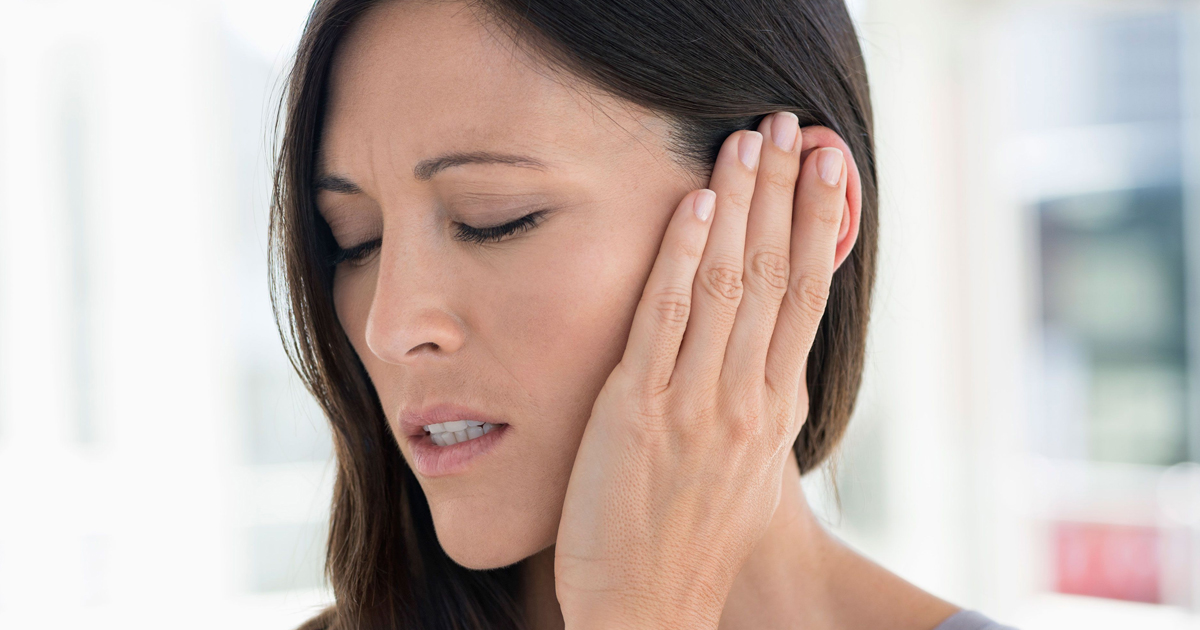
One symptom of enlarged adenoids is otitis media with effusion, which occurs when fluid collects in the middle ear. The system of the ears, nose, and throat are all connected and require passages to remain unobstructed and free-flowing to function properly. When the adenoids become enlarged, it creates a blockage and prevents the eustachian tube, which links the middle ear to the throat, from draining fluid.
Without proper drainage, the fluid may build up behind the eardrum, causing pain, loss of balance, and hearing difficulties. Usually, otitis media with effusion resolves itself after four to six weeks. Recurring bouts or instances of this condition that don't resolve on their own may be an indicator the adenoids are enlarged, and additional treatment may be needed to decrease swelling and encourage proper fluid drainage.
