Symptoms Of Septicemia
Septicemia is a type of serious infection in the bloodstream, and in some cases, it's also known as blood poisoning. This infection occurs when a bacterial infection in some other area of the body enters the bloodstream. The toxins and bacteria are then carried to the entire body. Septicemia can become life-threatening if not treated right away, and treatment must occur at a hospital. Not treating septicemia can lead to sepsis.
Many different symptoms point to septicemia. Individuals may also have elevated risk factors depending on your wounds, age, and whether or not you have a compromised immune system.
Nausea and Vomiting

Nausea and vomiting are common signs of septicemia. Vomiting refers to a reflex in which stomach contents are expelled through the mouth. Nausea refers to feeling as though you may vomit, even if you haven't actually vomited. Vomiting and nausea are both common symptoms across many different ailments, so experiencing these symptoms isn't an immediate guarantee of septicemia. Both children and adults can experience these symptoms. If you're pregnant or undergoing cancer treatment, you may have vomiting and nausea symptoms that have nothing to do with an overarching condition. Other common causes of nausea include intense pain, emotional stress, food poisoning, indigestion, and motion sickness. Individuals also frequently experience nausea when they have gallstones.
Learn about more signs of septicemia to watch for now.
Fever And Chills
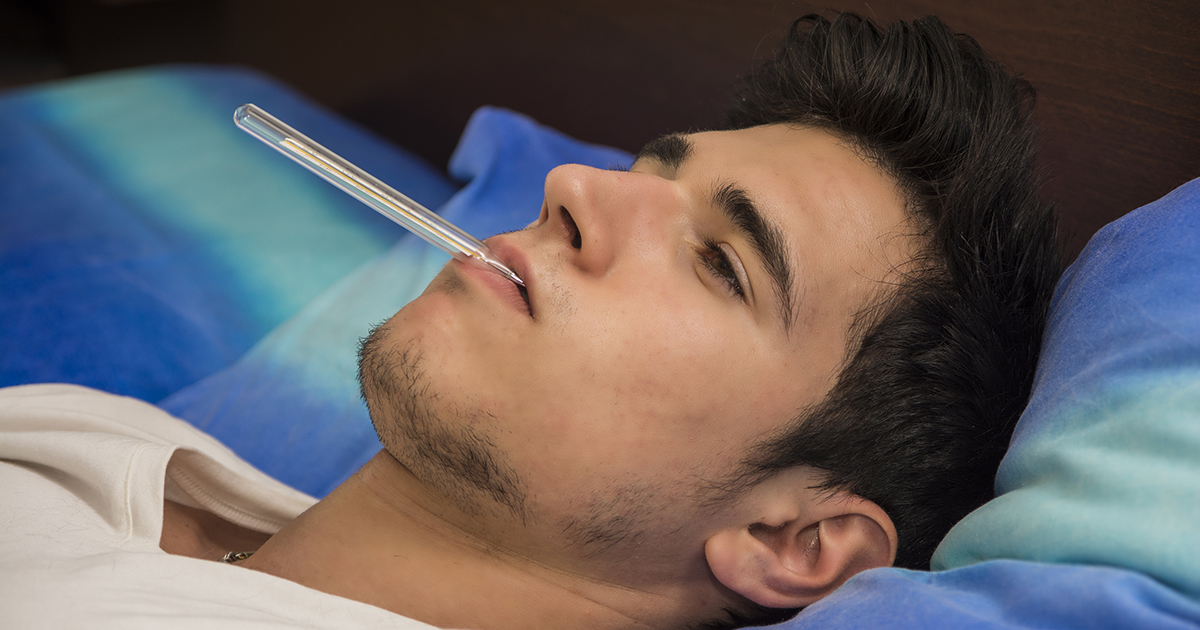
A fever and chills are some of the most common initial symptoms of septicemia. Septicemia symptoms begin very quickly and tend to have an intense onset. Even when it's the beginning stage of the sickness, individuals often look extremely sick. You may experience this fever after having an injury, localized infection, or surgery. The fever occurs when your immune system raises your body's temperature as it attempts to fight off the infection. Chills happen alongside the fever. Since your body is putting so many of its resources into fighting the illness, it doesn't have enough energy left over to keep you warm. Individuals have 'chills' when they're cold for no apparent reason.
Keep reading to reveal more septicemia symptoms.
