How To Treat Hypovolemic Shock
Hypovolemic shock, otherwise known as hemorrhagic shock, is a condition in which the body loses a large amount of blood, causing low blood flow to organs, and as a result, these organs stop functioning. Symptoms of hypovolemic shock can be mild or severe. Victims may produce a tiny amount of urine. This effect may be accompanied by fatigue, dizziness, and sweating with mental distress. In some cases, patients wind up with cold, clammy skin. Several of the more severe symptoms are increased heart rate and difficulty breathing. Hypovolemic shock is a life-threatening condition, so the effects aren't to be taken lightly. Fortunately, there are ways you can treat the condition.
Control Or Stop Blood Loss
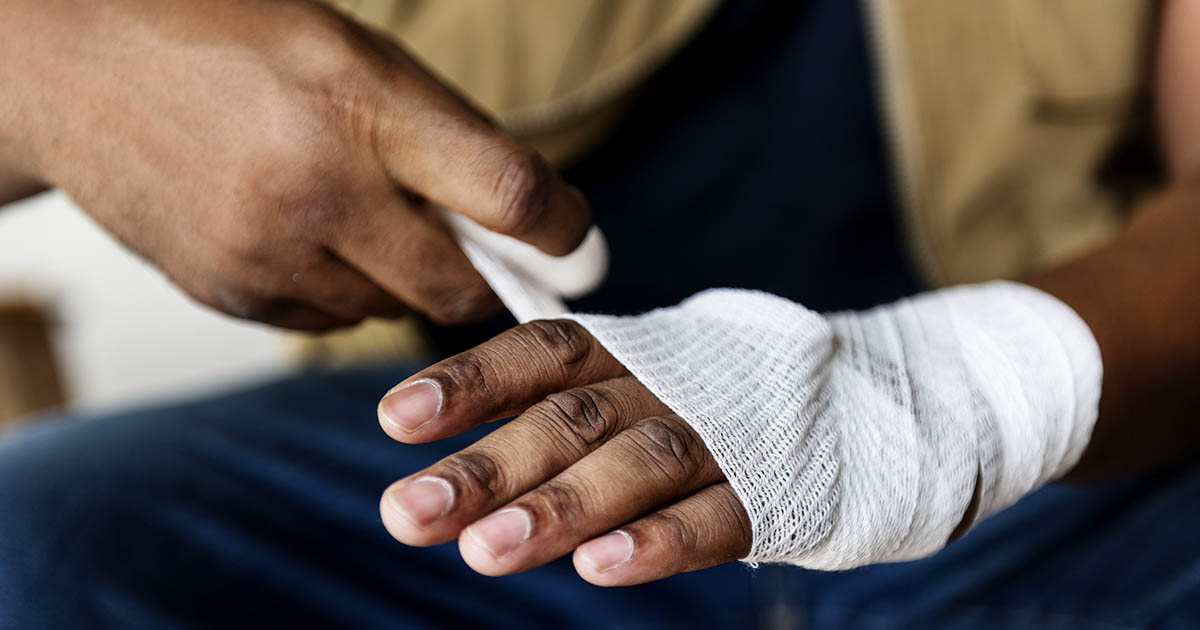
Blood loss commonly happens due to a person experiencing injuries such as burns, cuts, and wounds. In addition, blood can be lost through complications from pregnancy as well as diarrhea and vomiting. Hypovolemic shock will be diagnosed when the patient has lost up to twenty percent or more of their blood supply. In cases of hypovolemic shock, the victim needs to control or stop blood loss. Blood is needed for transporting oxygen and nutrients to organs throughout the body. Losing too much can cause many problems, including the development of anemia, a disease that occurs when the loss of red blood cells exceeds red blood cell production.
Get As Much Oxygen As Possible
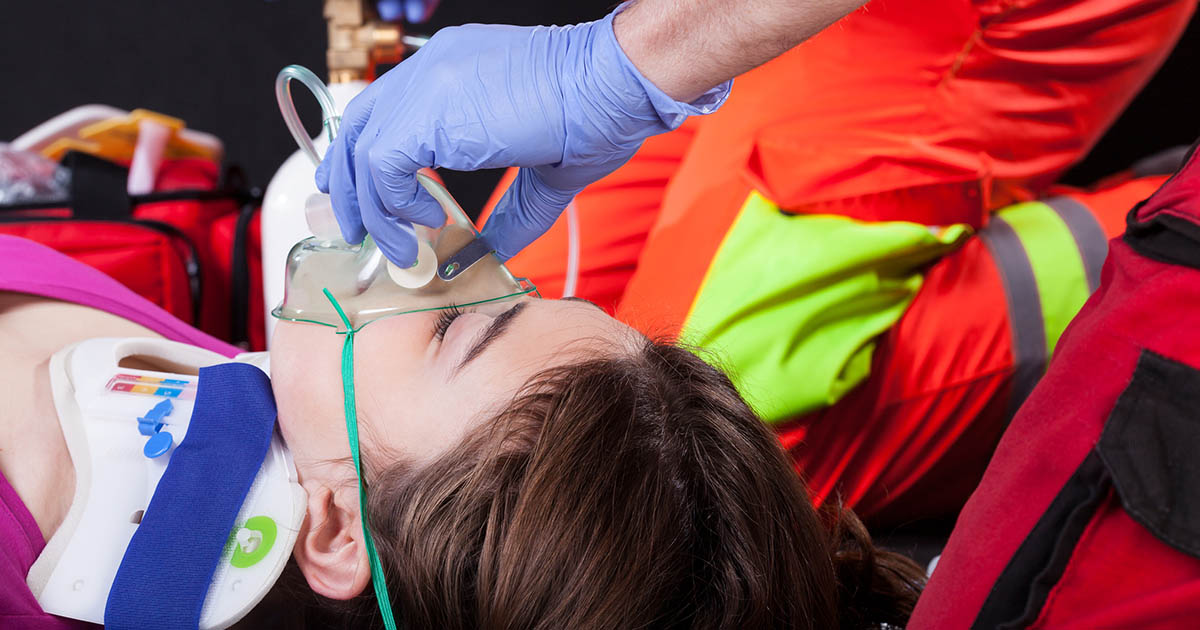
Another way to treat hypovolemic shock is to get as much oxygen as possible. This typically happens when the patient is on the way to the emergency room and involves an oxygen mask given to the patient by the paramedics. Before this, however, it's essential for anyone else around the patient to remind them to breathe as deeply as possible to increase their oxygen intake. Concerning ongoing treatment after the initial shock has passed, oxygen is still important, as the patient has still lost a lot of blood. When the body is ready, exercise and fresh air are both keys to getting oxygen. Also, some plants may improve the air quality of your home. Don't forget to drink more water as well.
Start eating more foods that increase oxygen in the blood. Foods high in nutrients like iron and vitamin C can help. Iron is used by the body to make a protein called hemoglobin, which is formed in red blood cells and is responsible for helping carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues. Foods rich in iron include lentils, chicken, turkey, spinach, whole wheat bread, and sweet potatoes. According to sources, vitamin C may help improve the body's absorption of iron. Good sources of vitamin C include broccoli, kale, oranges, and bell peppers.
