The Different Body Parts Insulin Stimulates
Insulin is a hormone or a chemical messenger produced by the pancreas that is responsible for regulating blood glucose levels. As an important part of the metabolism process, insulin prevents blood sugar levels from getting too high or too low by allowing the body to utilize dietary carbohydrates for instant energy or to store glucose for later use. When most people think of insulin, they think of diabetes; however, insulin does more than just regulate blood sugar levels. Here are the different body parts insulin affects.
8. Glucose Regulation
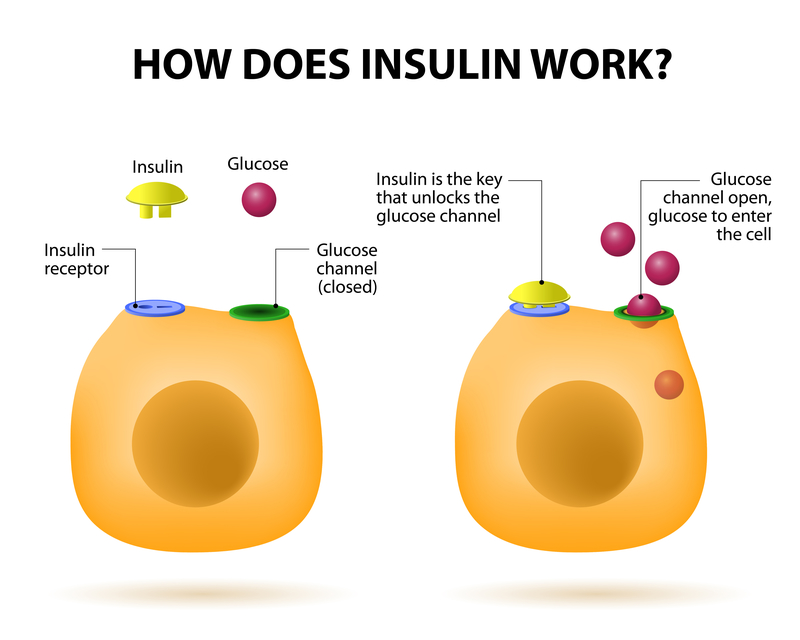
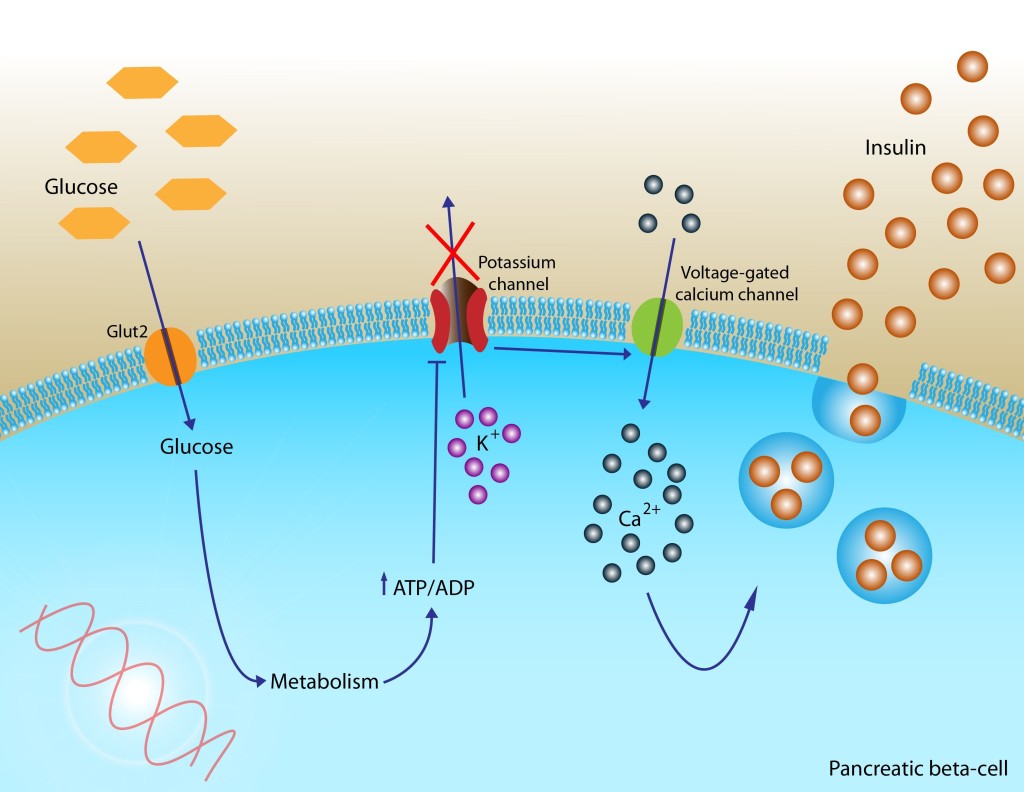
Insulin’s primary job is to control blood glucose levels. Without insulin, the body is unable to utilize carbohydrates for energy, resulting in high blood sugar, which occurs when the glucose remains in the bloodstream. A lack of insulin may cause the body to rely on fat as its sole source of energy. Breaking down fats to be utilized as energy produces releases ketones into the bloodstream, which can lead to a severe condition known as ketoacidosis. When high blood sugar is left untreated, it can result in damage to the eyes, nervous system, kidneys, and extremities.
7. Synthesis Of Lipids
According to a 2011 study, insulin plays several roles in lipid metabolism by decreasing the rate of lipolysis in fatty tissue, which lowers the level of fatty acids in the blood. It also stimulates fatty acids to be converted into triglycerides in tissues. Insulin increases the uptake of triglycerides into fatty tissue and muscle from the blood and decreases the rate of oxidation from fatty acid in the liver and muscle tissue.
