How To Treat Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a type of eye disease that can sometimes happen as a result of diabetes. High blood glucose levels from diabetes can harm the blood vessels in the retina. These blood vessels, located at the back of the eye, may leak or become swollen; they could also close and disrupt or stop blood flow to the retina. Occasionally, diabetic retinopathy can cause abnormal growth of extra blood vessels in the retina. In the earliest stages, the condition often has no symptoms, but as it progresses, patients may notice blurred vision, spots or floaters in their visual field, blockages or blank areas in their vision, and difficulty seeing colors. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy leads to loss of vision. The condition normally affects both eyes. Patients with diabetes are encouraged to have annual eye health exams with an ophthalmologist to prevent diabetic retinopathy and related eye conditions. The treatment methods listed below may help in the management of diabetic retinopathy.
Vitrectomy
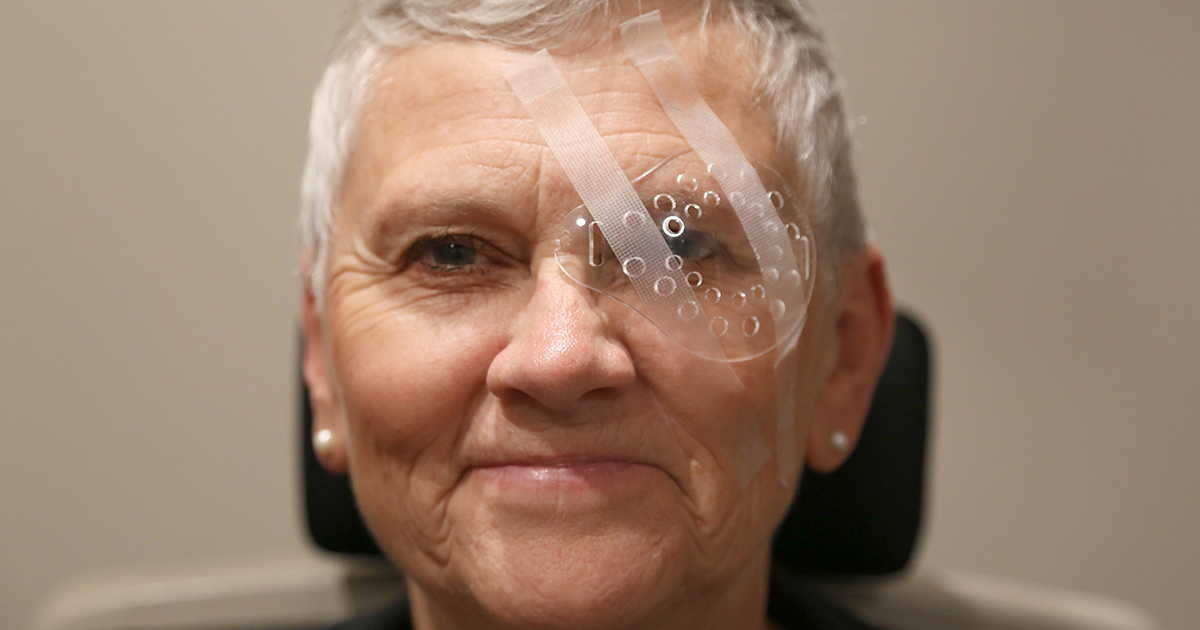

Vitrectomy is a surgery used to remove the vitreous, a type of fluid inside the eye. In patients with diabetic retinopathy, this procedure can be done to repair bleeding caused by the condition. It may also be performed to make it easier for surgeons to repair other problems with the retina. The procedure can be performed under a general anesthetic, and patients may also choose to have it done with local anesthesia instead. Patients may have the operation done at an outpatient facility, though some may prefer or need to have the procedure done in a hospital setting, and these patients often require one night of hospitalization following the surgery.
During the procedure, the surgeon will fill the eye with a special oil to replace the drained fluid. Some patients may also need to have a gas bubble injected into the eye during the surgery to keep the retina in its proper position. After surgery, the eye will be covered with a patch, and patients may need to hold their head in a particular way for a few hours or days following the procedure. Antibiotic eye drops are often recommended post-surgery, and patients typically need to use these for a few weeks.
Learn about the next method of treating diabetic retinopathy now.
Photocoagulation
This treatment is a type of laser eye surgery used to seal blood vessels in the retina that are bleeding. Depending on the extent of a patient's condition, several types of the procedure can be performed. Focal photocoagulation is done when there is minor bleeding from just a few blood vessels in the retina. The procedure is usually an outpatient operation, and it does not require general anesthesia. Anesthetic eye drops are used to numb the eye before surgery instead. The eye is dilated with additional eye drops so the surgeon can see everything in detail. The surgeon will begin by identifying the bleeding vessels over a small area and seal these off one at a time with small burns from the laser. After the surgery, patients will need someone to drive them home. Their vision will be blurry for a few days, and there may also be eye pain or headaches during this time. This operation is typically done to help preserve existing vision and prevent additional vision loss in patients with diabetic retinopathy.
Discover more ways to treat diabetic retinopathy now.
