Serious Warning Signs of Cataracts
Cataracts refer to a medical condition that occurs when the lens of the eye becomes opaque, which results in blurred vision. Approximately seventy percent of individuals over the age of seventy-five have cataracts. Glaucoma and other age-related macular degenerations are associated with cataracts. They are formed when clumps of protein gather in the lens and cause it to become cloudy. This clouding affects the amount of light that reaches the retina. Aside from developing as individuals age, cataracts have also been linked to previous eye surgeries, the long-term use of steroid medication, as well as other medical conditions, like diabetes.
Cloudy or Blurred Vision
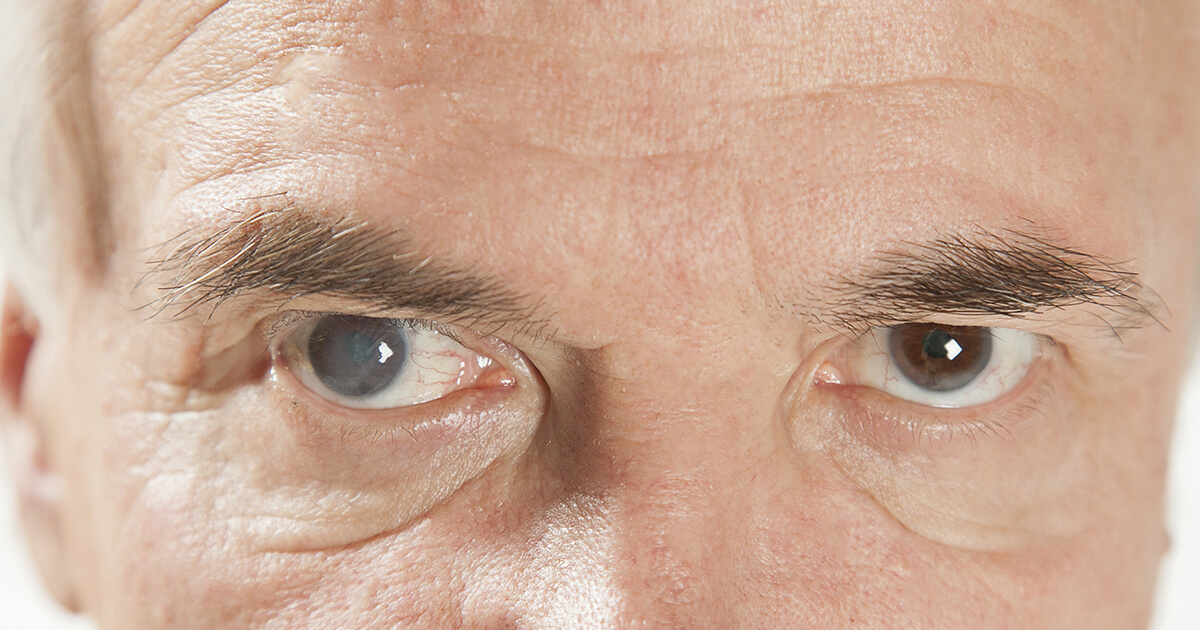

The most identifiable sign of cataracts is cloudy or blurred vision. Cataracts start small and increasingly cloud the eye, so the progression is slow in most cases. There are three different types of cataracts, and they affect different parts of the lens.
Posterior subcapsular cataracts are the most common in individuals with diabetes or those who are taking steroids. Posterior subcapsular cataracts affect the back of the lens, nuclear cataracts affect the center of the lens, and cortical cataracts affect the side of the lens. Individuals with nuclear cataracts may find their vision clearing up at one point, which is known as second light.
Darkening Of The Eye
At first, cataracts may not affect an individual's vision too much, including only lightly affecting one portion of the eye. In fact, some patients may be unaware of any vision loss when a cataract first develops. However, as cataracts grow, it is important to note they can result in a darkening of the eye. This is because advanced cataracts tend to appear darker than newly formed cataracts. The darkening of cataracts also affects a patient's night vision, which can make it hard to drive at night. Research shows patients who were in the process of treating their cataracts decreased their risk of vehicular accidents by roughly thirteen percent.
