What Causes Double Vision?
Double vision, also referred to as ghost imaging, is a condition where copies of a single image are seen through one or both eyes. Double vision in a single eye is often related to a physical defect in that eye. When light passes through the defective part, it is scattered on the retina at the back of the eye, causing the patient to see multiple images. If a patient is experiencing double vision in both eyes, it is important for them to see a doctor, as this can be a symptom of a more serious neurological condition. Depending on the cause, double vision can be temporary or a long-term condition. There are several common causes of double vision, some more concerning than others. Learn about them now.
Keratoconus
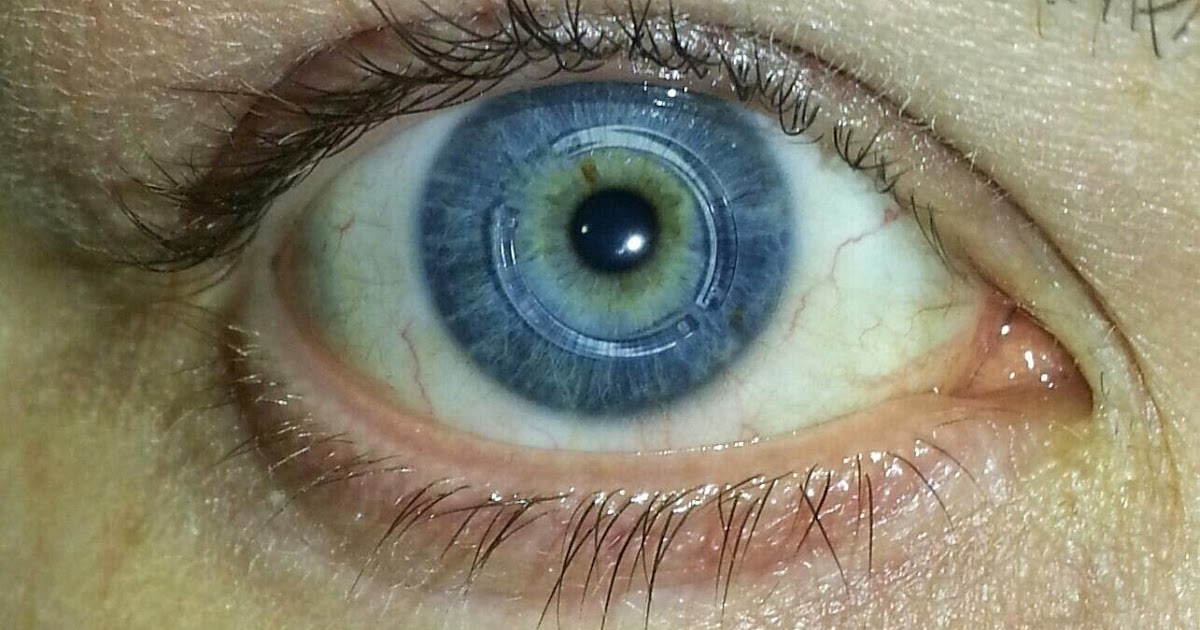
Keratoconus is the gradual transition of the cornea from its normal shape to a bulging or cone shape. The cornea is the outer layer of the eye that covers the lens and the pupil. When it is normal, it allows light to pass through the pupil to the back of the eye. If it is misshapen, it will alter the light, causing it to send multiple images to the retina. This will only cause double vision in the affected eye.
Some individuals have a genetic predisposition for this condition. Other causes include prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays and chronic eye irritation. In its early stages, double vision caused by keratoconus can be corrected through prescription glasses. As the condition progresses, it may require special contact lenses or a corneal transplant.
Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is one of the most common elective procedures done today. It is an out-patient procedure that can correct several vision issues such as nearsightedness or farsightedness. In the most common form, the doctor changes the shape of the cornea using a small laser. These changes are subtle and take some time to heal. However, any changes to the cornea affect the way light passes through.
In many cases, surgery patients experience mild double vision as they recover from the surgery. These issues normally resolve themselves within ninety days of the procedure. If a patient still experiences vision issues six months after the surgery, the doctor may recommend a second corrective procedure.
