Methods Of Treating Bulging Eyes
Eye Surgery
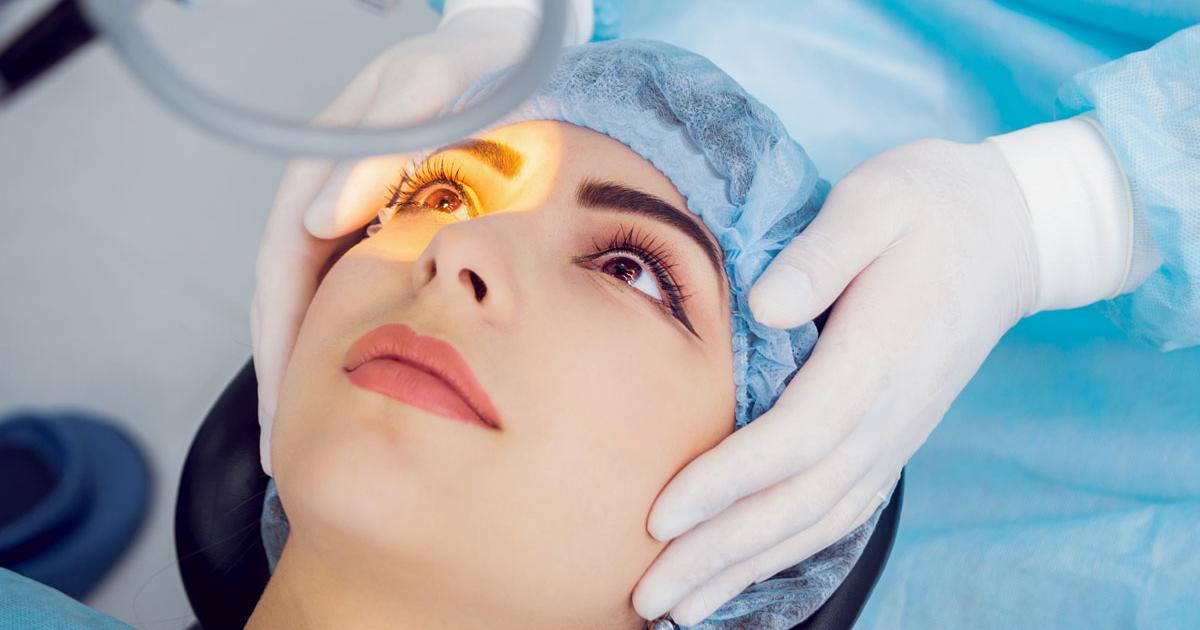
There are some more serious cases where the best treatment option for bulging eyes may be eye surgery. If the bulging is caused by a cancerous tumor, patients might need surgery or chemotherapy to help. Surgery is rarely considered as the first option for bulging eyes unless the situation is an emergency. It might help in cases where the symptoms are severe or persistent and can't be helped by less invasive treatment methods. Some patients might get cosmetic surgery to improve the appearance of their eyes if the underlying cause of the bulging has been treated, and the condition is not worsening.
Medical treatment doesn't always reverse protruding eyes. If treatment helps the underlying condition but doesn't help the existing bulging, some patients might opt for surgery. Another case where surgery is viable would be if individuals have thyroid disease that's causing severe enough bulging to threaten vision loss. If the bulging eyes are caused by issues with tissues or blood vessels behind the eyes, certain surgeries may be necessary to help repair these.
Thyroid Medication
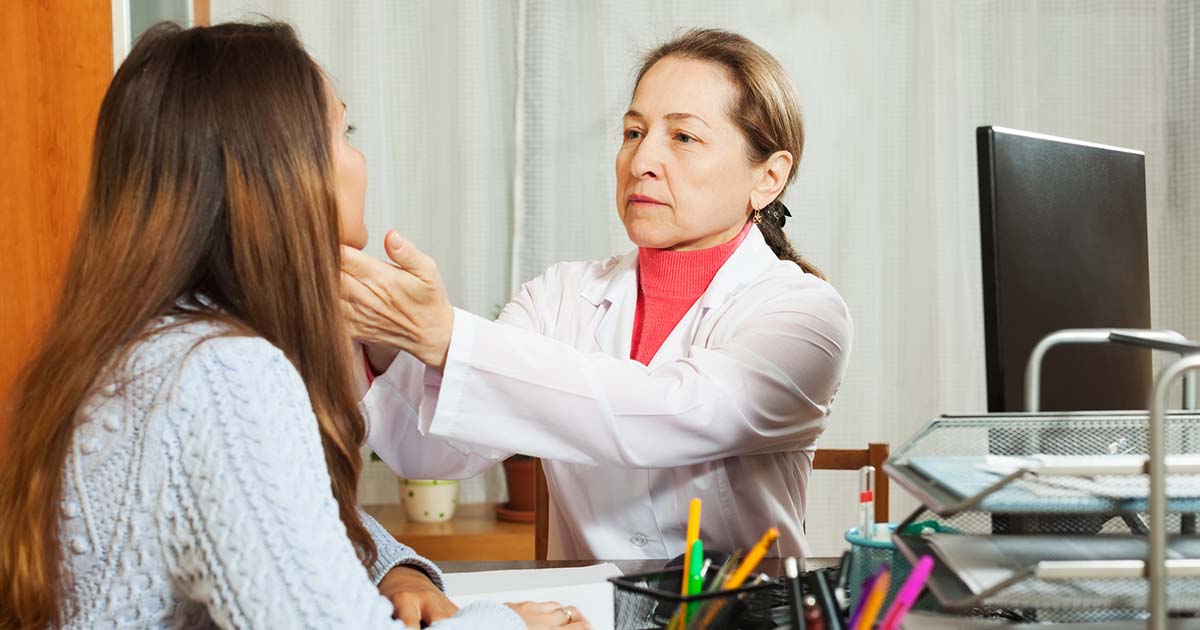

The most common underlying cause of bulging eyes is hyperthyroidism, a condition that occurs when the thyroid gland makes too much thyroid hormone, and it's often caused by an autoimmune disorder called Graves' disease. The bulging occurs when tissues around the eyes become inflamed, leading to pressure and bulging. Though anyone can have Graves' disease, the most commonly affected group is women between thirty and sixty years old. Thyroid medications are typically used to treat hyperthyroidism. There are antithyroid medications that keep the thyroid from producing as much thyroid hormone as usual.
Some beta-blockers are sometimes used for treatment. Beta-blockers help block stress hormones from affecting the cardiovascular system. This is very important in cases of hyperthyroidism, since the metabolic effects can lead to a racing or irregular heartbeat. Another less common use for beta-blockers is to treat glaucoma, which is an eye condition that can lead to blindness. If patients have surgery to remove part or all of their thyroid gland, they may need supplemental thyroid medications.
