What Causes And Increases The Risk Of Uveitis?
Uveitis is a condition that develops when the uvea, the middle layer of the eyes, becomes inflamed. The disease can lead to pain in the eye, and it can also cause changes to an affected individual's vision. Symptoms patients experience include sensitivity to light, redness in the eyes, dull aches and pain in the eye, seeing small shapes move across their field of vision, cloudy or blurred vision, and loss of peripheral vision. These symptoms can present gradually or develop quite suddenly. They can also be experienced in either one or both of the eyes. Though most cases will improve with treatment, uveitis can sometimes lead to further complications, such as glaucoma and cataracts. When symptoms present, it's best to seek out medical assistance immediately.
Get to know what causes and increases the risk of uveitis now.
Eye Injury
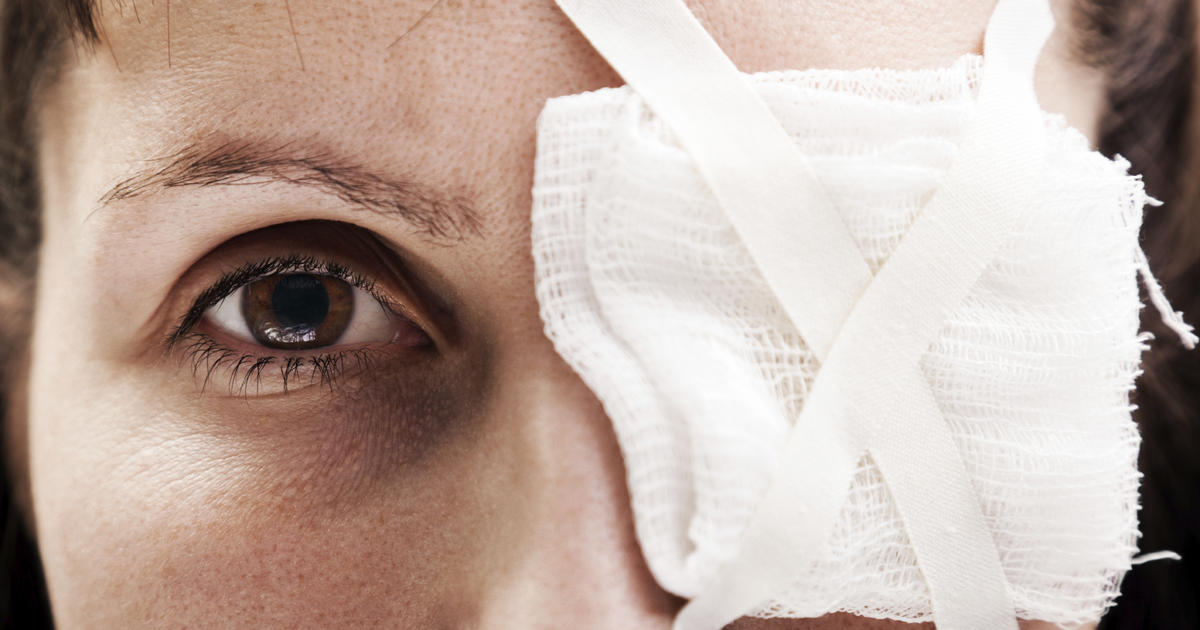
Uveitis is sometimes caused as a result of an eye injury, which can occur when the eye experiences trauma, such as a puncture or hard impact or blow. Scratches and abrasions from the fingers or other foreign objects will introduce bacteria to the eye, which, after being injured, cannot adequately protect itself. Foreign bodies, such as small bits of wood, metal, or toxic chemicals, can also lead to an eye injury and the development of uveitis. Uveitis can also develop after the eye is injured during a surgical procedure, or even as a result of wearing dirty or old contact lenses. Eye injuries can occur across many settings, but they need to be taken seriously, no matter how minor they may seem.
Continue to learn about the next common cause of uveitis.
Autoimmune Disorders

There is also quite a bit of evidence linking autoimmune disorders with the development of uveitis. The immune system acts as the body's main defense system, keeping it healthy and fighting off illnesses. Sometimes, and for unknown reasons, the immune system can go into overdrive and be overactive in the eyes. When the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the eye, believing it to be a foreign substance, the area is weakened. The autoimmune conditions most commonly found to cause uveitis include reactive arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, bowel inflammation, psoriasis, Behcet's disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Keep going to uncover another cause of uveitis.
