Most Common Illnesses And Infections In Children
Children are typically much more susceptible to illnesses and infections than healthy adults. For the first six months of a child's life, they are protected to a certain extent by the biological immunity passed down from their mother. At around six months of age, it is common for children to start getting more frequent colds and other ailments. A child's immune system is not fully developed, and children are exposed to a significant amount of viruses and bacteria at daycare and school. In addition, children frequently put their hands in their mouths, and they are often unable to practice healthy hand washing habits. This combination can allow dangerous viruses and bacteria to enter the body and cause illness. Many childhood illnesses can be diagnosed with a physical exam alone, and blood tests may sometimes be needed.
Hand, Foot, And Mouth Disease
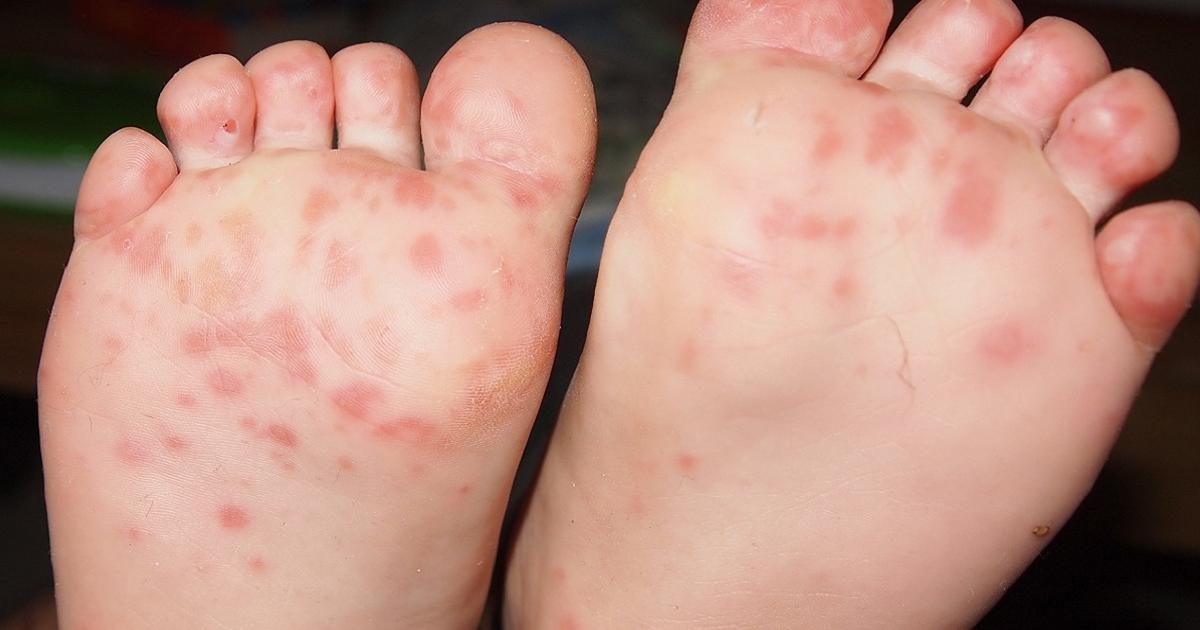
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a viral condition that most often develops due to a coxsackievirus. Symptoms usually begin within three to six days of infection, and a fever is normally the first symptom. Patients may also develop a sore throat, and a rash on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet is common. Although the rash does not generally itch, it may cause discomfort and blistering. Painful sores on the inside of the mouth are frequently present, and some children with this condition may be irritable and experience a loss of appetite. This ailment usually resolves on its own within ten days, and there is no specific treatment for it. Doctors recommend using a topical numbing gel to relieve the pain from mouth sores, and acetaminophen is recommended for relieving generalized discomfort.
Chickenpox
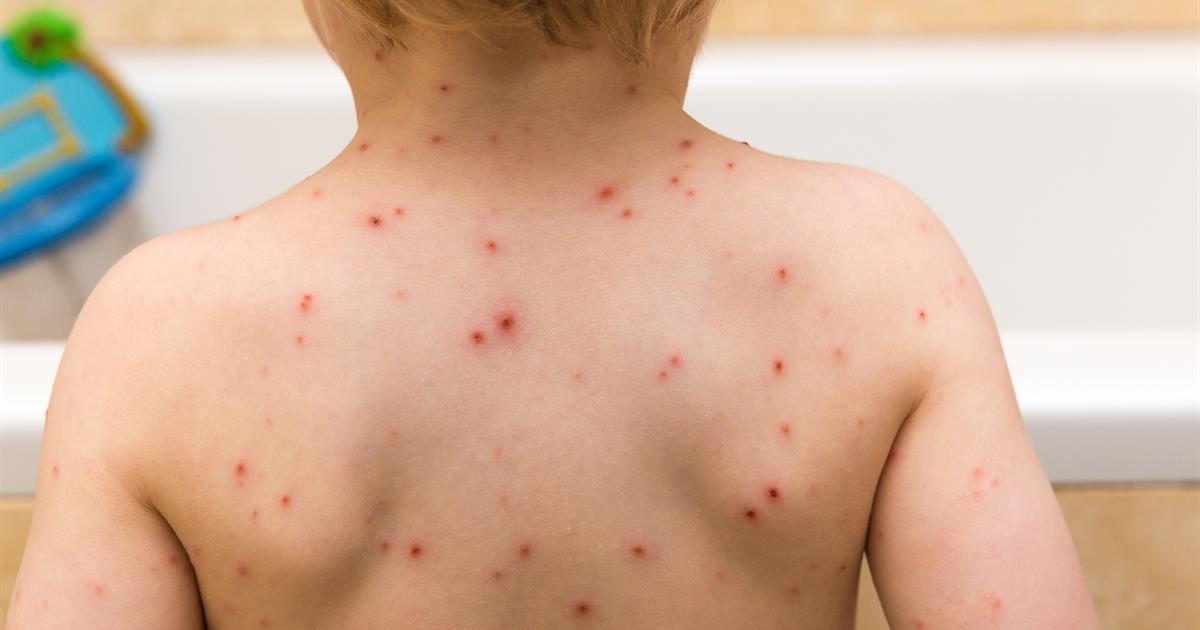
Chickenpox is a highly contagious infection caused by a virus known as varicella-zoster. Children younger than two years old are at an especially high risk of chickenpox, and a vaccine is available that can prevent this condition. Patients with this ailment develop symptoms within ten to twenty-one days of infection. In the early stages of this condition, the patient might experience a fever, body aches, headaches, fatigue, and a loss of appetite. After one or two days, an itchy, raised rash will normally develop over large areas of the body. Some patients may have as many as five hundred raised bumps. The spots turn into blisters, and these begin to leak after a day or so.
At this time, the rash will form scabs, and new spots may also appear. While many cases of chickenpox are mild and resolve on their own, patients are considered contagious until the entire rash has formed scabs. Medical treatment should be sought if a patient with this condition develops a fever of more than 102 degrees Fahrenheit and if they experience dizziness, vomiting, shortness of breath, or loss of muscle control. These may be signs of serious complications.
