Potential Side Effects Of Skipping Breakfast
There is the saying that breakfast is just as important as lunch and dinner. After all, this meal starts the day off. Breakfast is what allows us to put in some essential nutrients before proceeding to our daily routine. Despite how necessary a morning meal can be, a shockingly high number of individuals tend to skip eating breakfast. Individuals skip eating breakfast for a variety of reasons. For instance, some use omission as a tool for weight loss. Another reason for skipping breakfast is because of a bizarre notion it is not really that important.
Skipping breakfast may not seem like a big deal to the many individuals who simply do not feel like eating. However, it can cause problems related to health.
Increased Risk Of Type 2 Diabetes
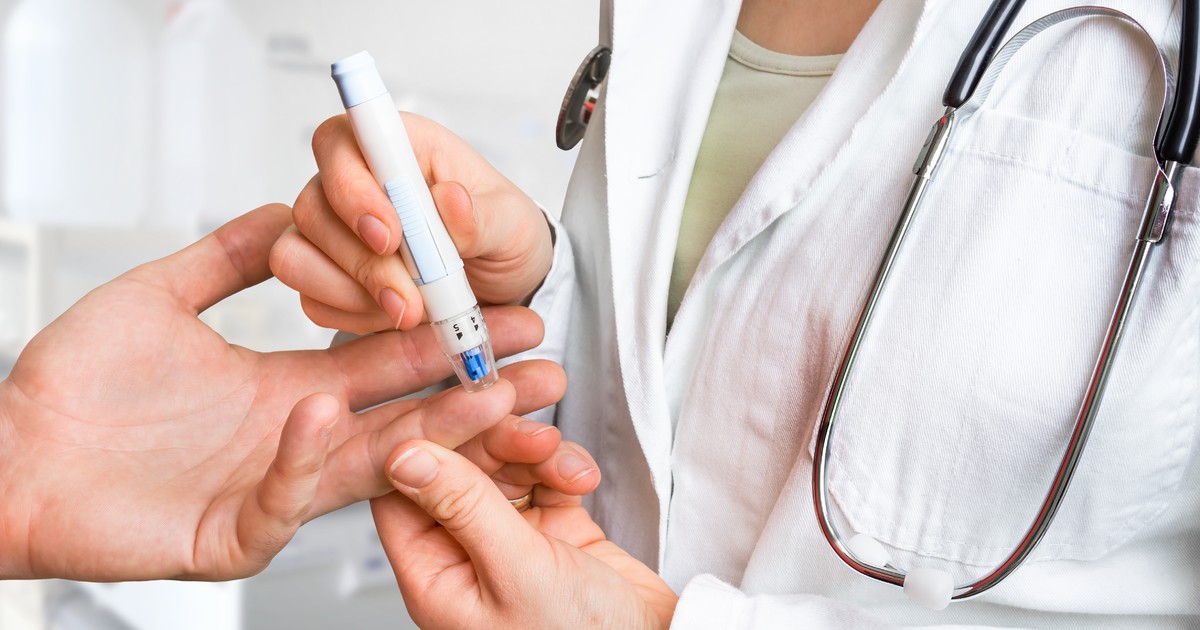
Skipping breakfast is widely linked to increased risk of type 2 diabetes. In fact, a number of studies have shown the irregular consumption of breakfast can have a significant negative impact on blood glucose. One study based in Japan focused on 4631 male and female participants for 8.9 years. Those who consumed breakfast three to five times or less weekly were associated with greater risk for developing type 2 diabetes. In a separate study for English youth, researchers found the daily consumption of breakfast, especially if it was high fiber cereal, tied to lower insulin resistance. Children who were reported not to have breakfast on a daily basis had greater triglycerides and fasting insulin.
A medical review recently published in January 2019 has also exhibited the link between skipping breakfast and type 2 diabetes. The reviews mention several studies in which participants are shown to have increased risk for type 2 diabetes upon skipping breakfast for a number of days.
Learn more about the side effects of skipping breakfast now.
Reduced Mood And Energy
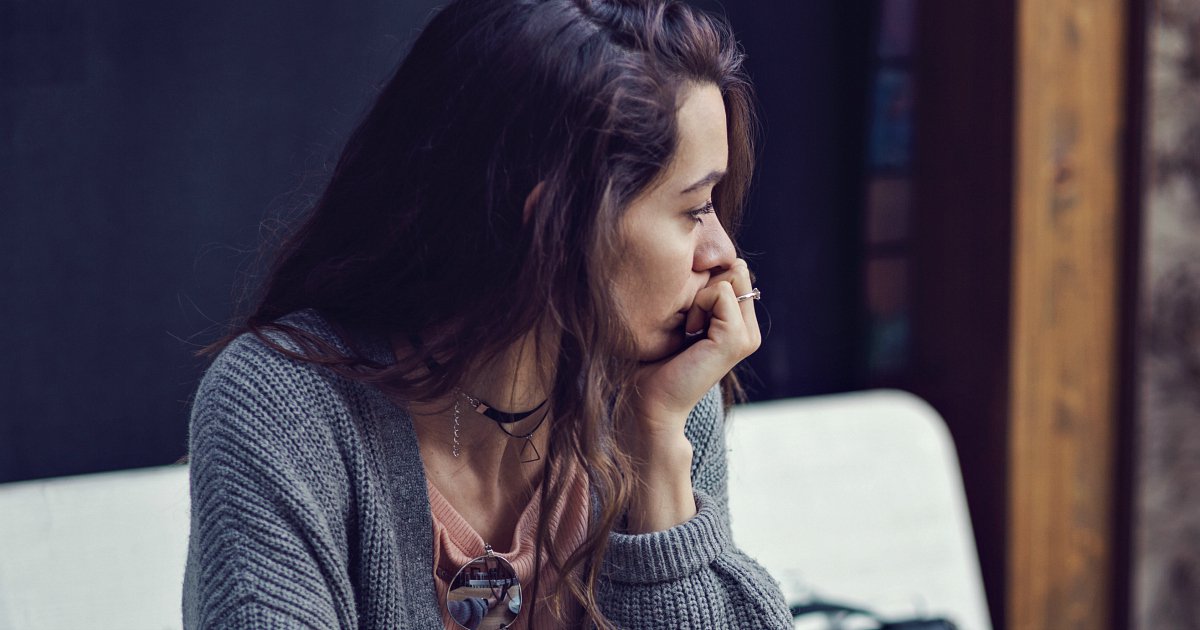

A study published in 2010 suggested eating breakfast could boost morning relaxation and happiness in participants. The participants reported being in better moods compared to not eating at all. Earlier studies show eating breakfast helped improve mood in schoolchildren. However, these effects were not long-term. The effects of breakfast omission on energy are shown in a study published in 2015 that featured healthy female participants that habitually ate breakfast. The study suggested skipping breakfast caused less energy intake and physical activity.
Some research even indicates not eating breakfast omission may have a link to mental disorders such as depression and anxiety. A 2017 medical review mentions a study that surveyed over 200,000 Korean adults. This study demonstrated adults who ate breakfast on a daily basis were less impacted by symptoms of depression than those who did not.
Continue reading to reveal more potential side effects of skipping breakfast now.
