Common Causes Of Hair Loss
Individuals who experience hair loss could notice thinning hair in certain areas of their scalp. This may progress to total hair loss. While hair loss generally occurs on the scalp, some individuals may lose eyelashes or eyebrow hair. The loss of facial hair or body hair could happen as well. Patients experiencing this symptom may want to consider seeing their doctor for a physical exam. Their doctor will assess the location and severity of the patient's hair loss. They may also order blood tests.
Thankfully, individuals have many options when it comes to hair loss treatment. Many individuals are able to achieve hair regrowth. Some patients may need to change their hairstyle, take vitamin supplements, or use a special shampoo. There are also medications for hair loss and many hair growth treatment options. However, the best treatment for hair loss depends on the cause, such as alopecia treatment including medicated creams. Thus, individuals need to understand the cause of their hair loss first.
Genetics And Aging
Male and female patients typically notice some thinning or loss of scalp hair as they age. This typically begins when an individual is in their fifties. It usually worsens as the patient enters their sixties, seventies, and eighties. Male and female-pattern baldness are two hereditary conditions that create a more pronounced loss of scalp and body hair than what occurs through the typical aging process. Both of these conditions are linked to genetic factors.
While previous research attributed hair loss to changes in a single gene, scientists now know the process is influenced by multiple genes, many of which come from the patient's mother. The genes that determine hair type and texture vary from population to population. Patients who have a first-degree relative with a potentially hereditary hair loss condition may want to consider starting medications for hair regrowth early. They may also wish to find out more about potential surgical hair replacement options.
Alopecia Areata
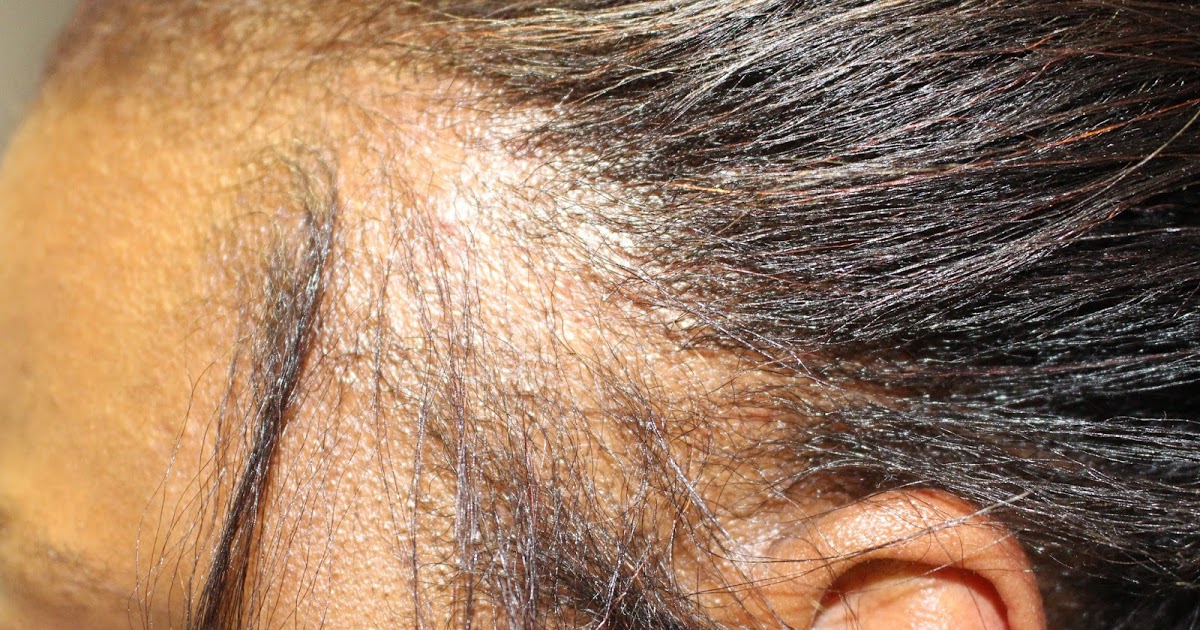
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that affects the skin and hair follicles. Patients with this condition develop hair loss on the scalp and face, and loss of body hair may occur as well. Currently, 6.8 million Americans are living with alopecia areata. The lifetime risk of developing this condition is 2.1 percent. Although symptoms can begin at any age, they typically start in childhood. There are three major types of alopecia areata, and symptoms vary by type. The patchy form of this condition is the most frequently diagnosed type. It causes multiple hairless patches on the scalp or body, which are roughly the size and shape of a coin. In alopecia totalis, patients experience a complete loss of scalp hair. Patients diagnosed with alopecia universalis have a total loss of hair from the face, scalp, and body.
Although there is currently no cure for this condition, patients may want to consider treatments to better manage their symptoms. Examples include topical minoxidil, corticosteroid injections, or anthralin cream. These medications are available by prescription.
