Treatment Options For Acute Renal Failure
Acute renal failure, also known as acute kidney failure, is an illness that occurs when the kidneys begin to shut down and halt the process of removing waste from the bloodstream, which stems from a variety of causes. As suspected, acute renal failure requires a hospital visit, and during this visit healthcare professionals attempt various forms of treatment to get to the root cause of the acute renal failure, as treatment focuses on identifying the original cause of the damage to the kidneys.
A doctor will focus on the most effective treatments that not only avoid dangerous side-effects and complications but also develop a plan to allow the kidneys the time they need to heal properly. Learn more now about the various treatments available for patients coping with acute kidney failure.
Dealing With Dialysis
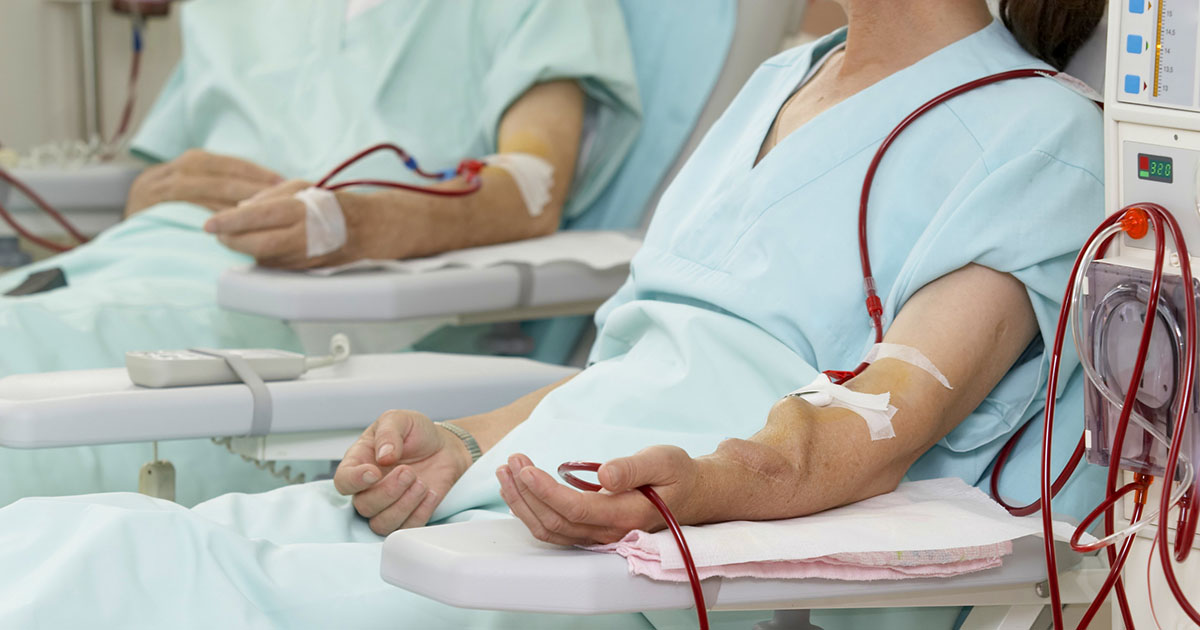
The process of dialysis is specifically used to take waste and toxins out of the blood by using a man-made device to filter the blood. How this process works is that a medical professional will provide all the necessary pretreatment to hook the patient up to a machine called a dialyzer, which is a type of artificial kidney. The dialyzer will pump blood from the body through a filter system, and then return the blood to the body with all the minerals and fluids it needs to keep it at a healthy level. For as long as the kidneys are considered unhealthy, a doctor may recommend completing the dialysis process more than once, or even on a daily basis.
Peritoneal Dialysis
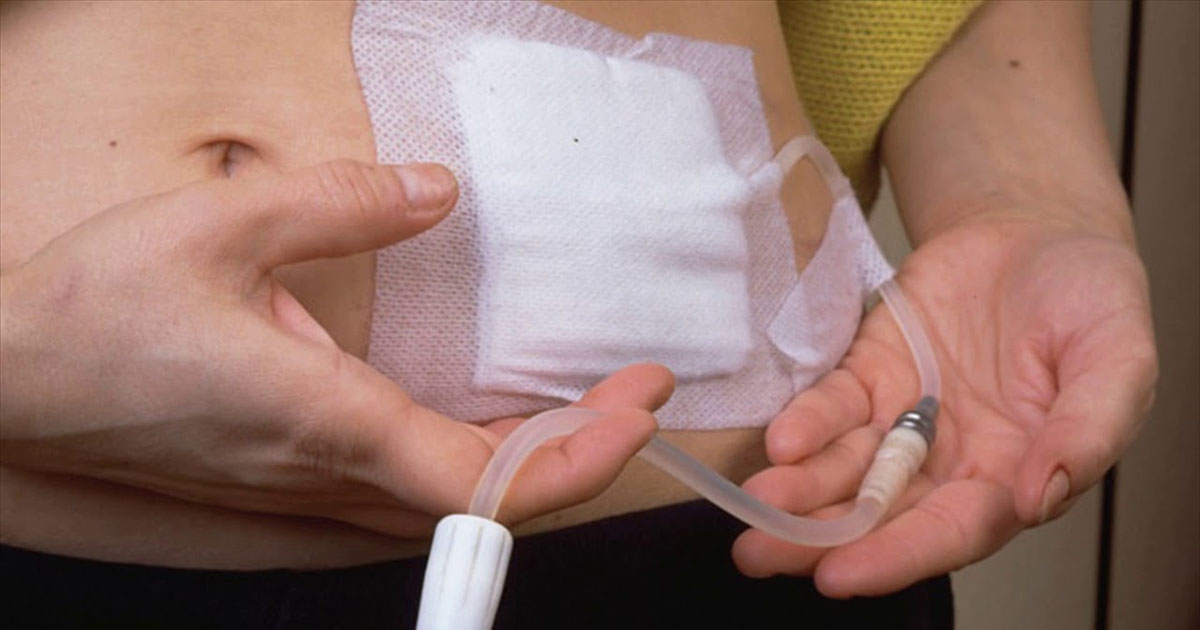
The second type of dialysis, peritoneal dialysis, uses the lining of the abdominal cavity as the dialysis filter to remove excess waste and to balance electrolyte levels within the body. A surgeon will place a catheter in the abdominal cavity through the abdominal wall and is expected to remain there for an extensive period. The dialysis solution is dripped through the catheter and left in the abdominal cavity, where waste products from the blood attach themselves to the dialysis fluid to be drained out hours later. The majority of patients who have to undergo this type of treatment will often instill the dialysate fluid before bedtime, and drain the fluid-filled with waste in the morning. This treatment option is usually decided based on the severity of the patient’s illness and their past medical history, as both forms of dialysis are necessary to save a patient’s life.
