10 Stubbornly Hidden Causes of Persistent Foot Pain
Foot pain is a common ailment that affects millions of individuals across the globe, yet it remains a complex issue often misunderstood or underestimated. Our feet are intricate structures composed of 26 bones, 33 joints, and over a hundred muscles, tendons, and ligaments. They bear the weight of our bodies, absorb shock, and provide balance and mobility. Despite their vital role, we often neglect them until pain disrupts our daily lives. Persistent foot pain can significantly affect one's quality of life, limiting mobility and hindering daily activities. Understanding the root causes of foot pain is crucial for effective treatment and prevention. This article delves into the top 10 culprits behind persistent foot pain, offering insights into each condition's nature, symptoms, and potential remedies. By unraveling these causes, we aim to shed light on a topic that is both medically significant and personally impactful for many.
1. Plantar Fasciitis - The Common Foe
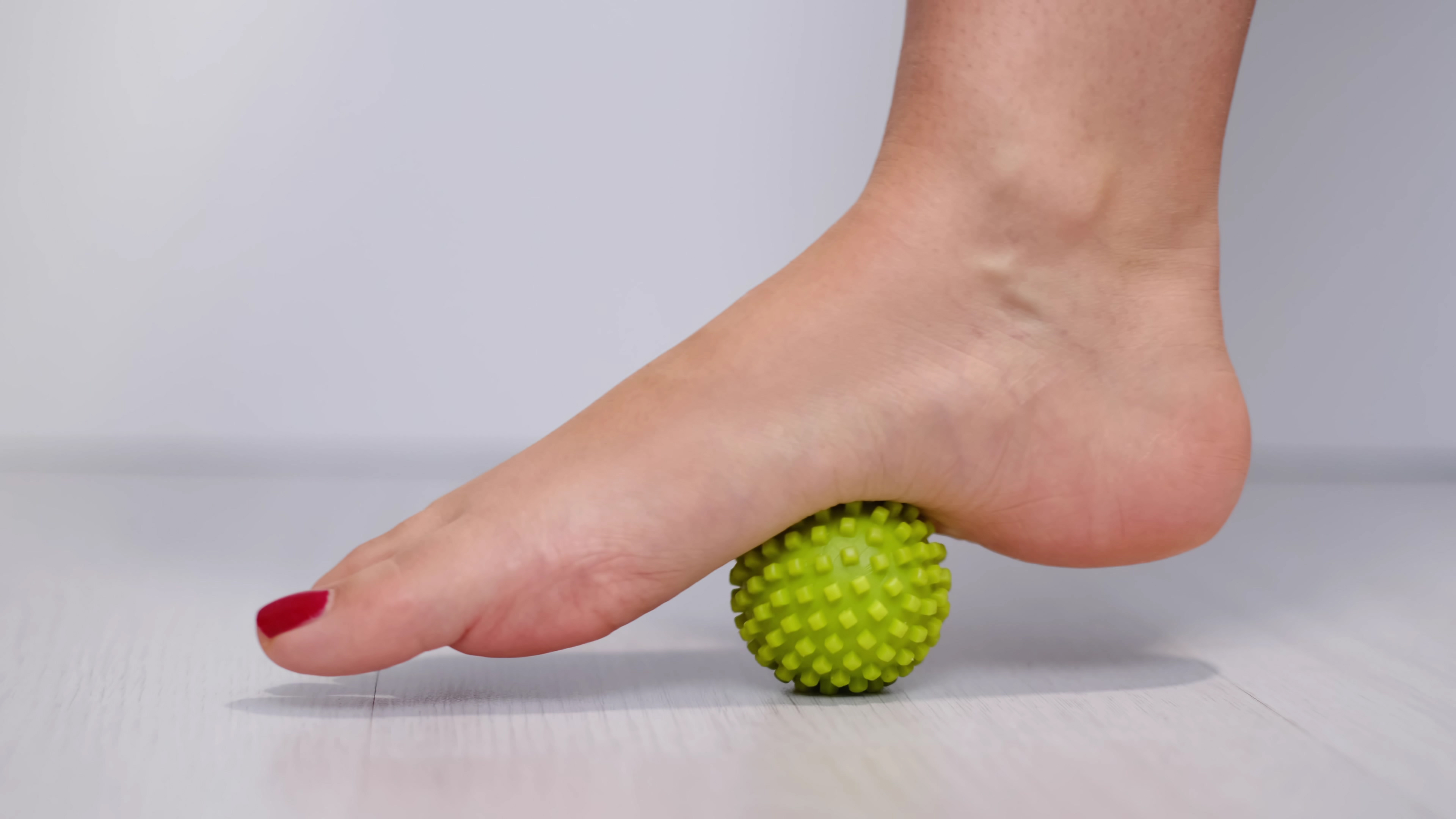

Plantar fasciitis is one of the leading causes of foot pain, affecting millions worldwide. This condition involves inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs across the bottom of the foot, connecting the heel bone to the toes. The pain is often described as a sharp, stabbing sensation in the heel, particularly noticeable during the first steps in the morning or after prolonged periods of rest. Factors contributing to plantar fasciitis include overuse, obesity, and inadequate footwear. Athletes, especially runners, are particularly susceptible due to the repetitive stress placed on their feet. Treatment typically involves rest, stretching exercises, and supportive footwear. In severe cases, physical therapy, orthotics, or even surgical intervention may be necessary. Understanding plantar fasciitis is crucial, as early intervention can prevent chronic discomfort and further complications.
2. Bunions - The Misaligned Menace

Bunions are bony bumps that form on the joint at the base of the big toe, leading to significant discomfort and pain. This deformity occurs when the big toe pushes against the next toe, causing the joint to protrude and become swollen. Bunions can be hereditary, but they are often exacerbated by wearing tight, narrow shoes that squeeze the toes together. Women are more frequently affected due to the prevalence of high-heeled, pointed footwear in fashion. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and redness around the affected joint, with the potential for calluses or corns to develop. Treatment focuses on relieving pressure on the bunion through proper footwear, orthotic devices, and anti-inflammatory medications. In severe cases, surgical correction may be considered. Addressing bunions early can prevent progression and alleviate pain, emphasizing the importance of proper foot care and footwear choices.
3. Achilles Tendinitis - The Overuse Injury
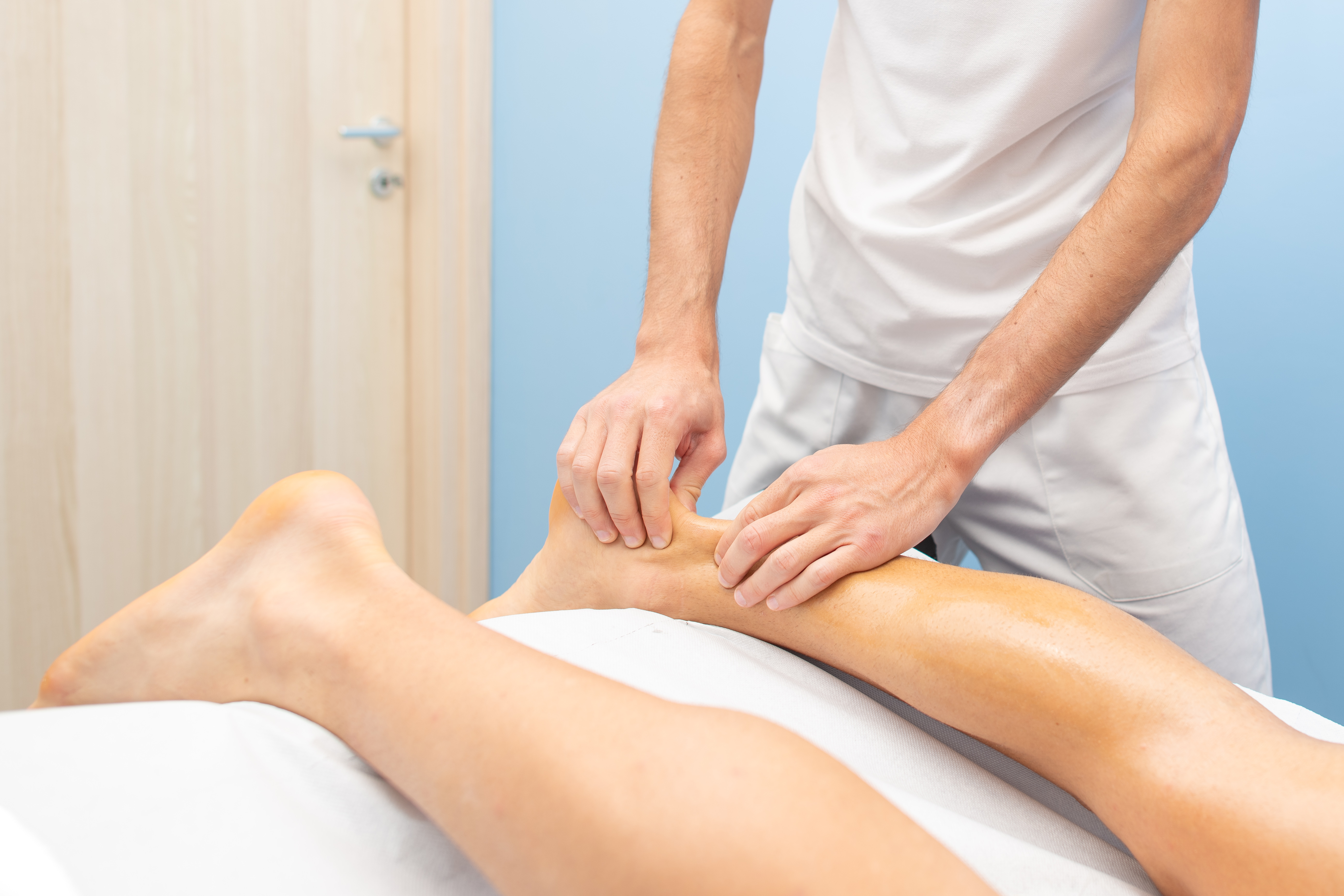
Achilles tendinitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the Achilles tendon, the largest tendon in the body that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. This condition is often the result of repetitive stress and overuse, particularly in athletes who engage in activities that involve running or jumping. Symptoms include pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon, especially in the morning or after exercise. Risk factors include sudden increases in physical activity, tight calf muscles, and inappropriate footwear. Treatment involves rest, ice application, stretching exercises, and anti-inflammatory medications. In some cases, physical therapy or orthotics may be recommended to support recovery. Understanding the causes and treatment of Achilles tendinitis is essential for preventing long-term damage and ensuring a swift return to physical activity.
4. Flat Feet - The Underestimated Agony

Flat feet, or fallen arches, occur when the arches of the feet collapse, causing the entire sole to come into contact with the ground. This condition can be congenital or develop over time due to injury, obesity, or arthritis. While some individuals with flat feet experience no symptoms, others may suffer from foot pain, swelling, and difficulty standing on their toes. The lack of arch support can also lead to problems in the ankles, knees, and lower back. Treatment focuses on providing adequate support through custom orthotics, supportive footwear, and exercises to strengthen the foot and ankle muscles. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary. Recognizing the impact of flat feet and addressing the condition early can prevent further complications and improve overall foot health.
5. Morton's Neuroma - The Nerve Entrapment
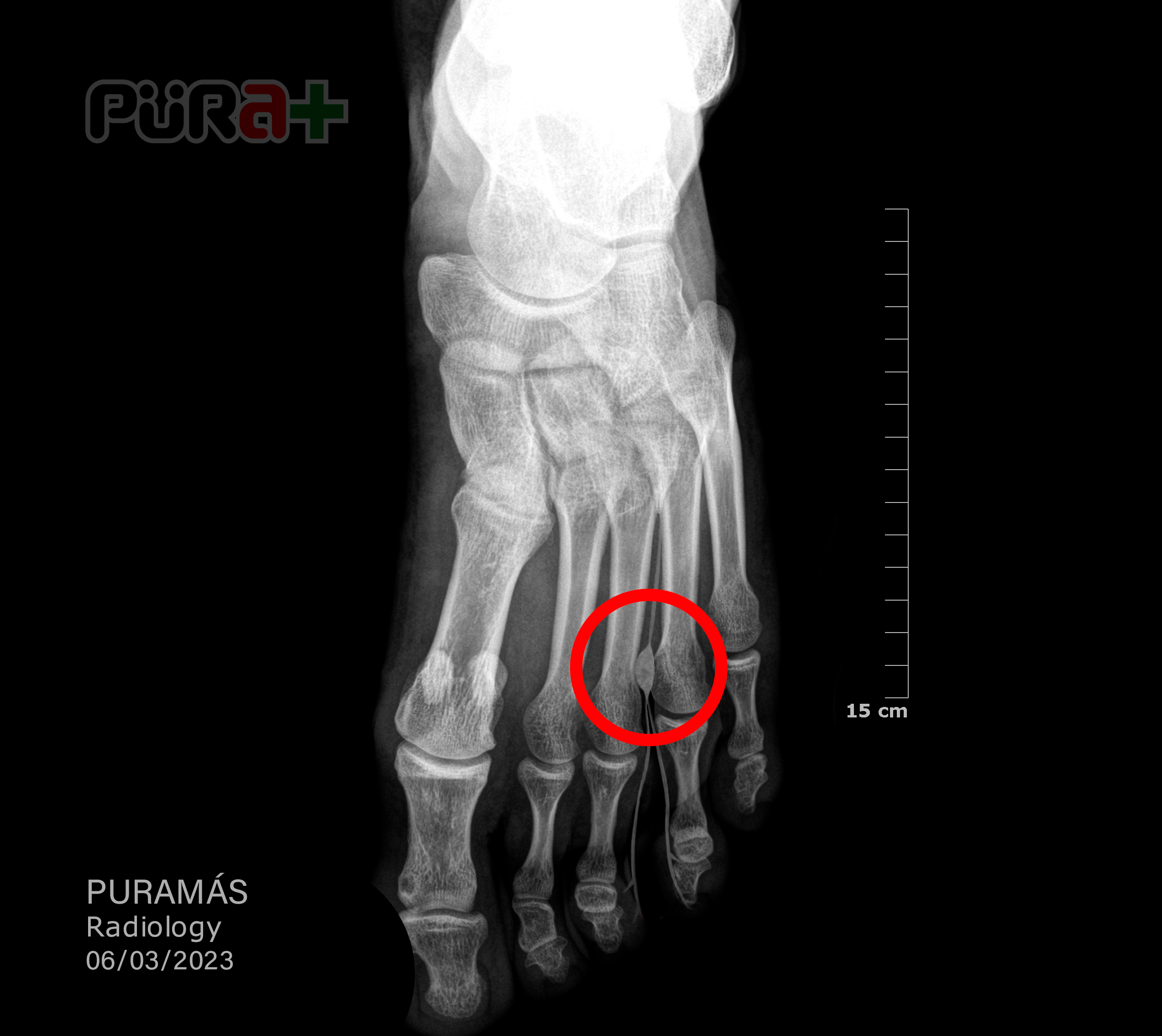
Morton's neuroma is a painful condition affecting the ball of the foot, commonly between the third and fourth toes. It involves thickening of the tissue surrounding one of the nerves leading to the toes, often resulting from irritation, injury, or pressure. Symptoms include sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot, tingling, or numbness in the toes. High-heeled or tight shoes can exacerbate the condition, as they place additional pressure on the forefoot. Treatment aims to relieve pressure on the affected nerve, often through changes in footwear, orthotic devices, and anti-inflammatory medications. In persistent cases, corticosteroid injections or surgical removal of the affected nerve may be considered. Understanding Morton's neuroma is crucial for preventing chronic pain and maintaining foot health, especially for those who frequently wear restrictive footwear.
6. Arthritis - The Degenerative Dilemma
Arthritis is a broad term encompassing over 100 different conditions characterized by inflammation of the joints. In the feet, the most common types are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis results from the wear and tear of joint cartilage, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that attacks the joints. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion, often leading to significant discomfort and mobility issues. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression through medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or replace damaged joints. Understanding arthritis and its impact on foot health is essential for effective management and maintaining quality of life.
7. Gout - The Inflammatory Intruder
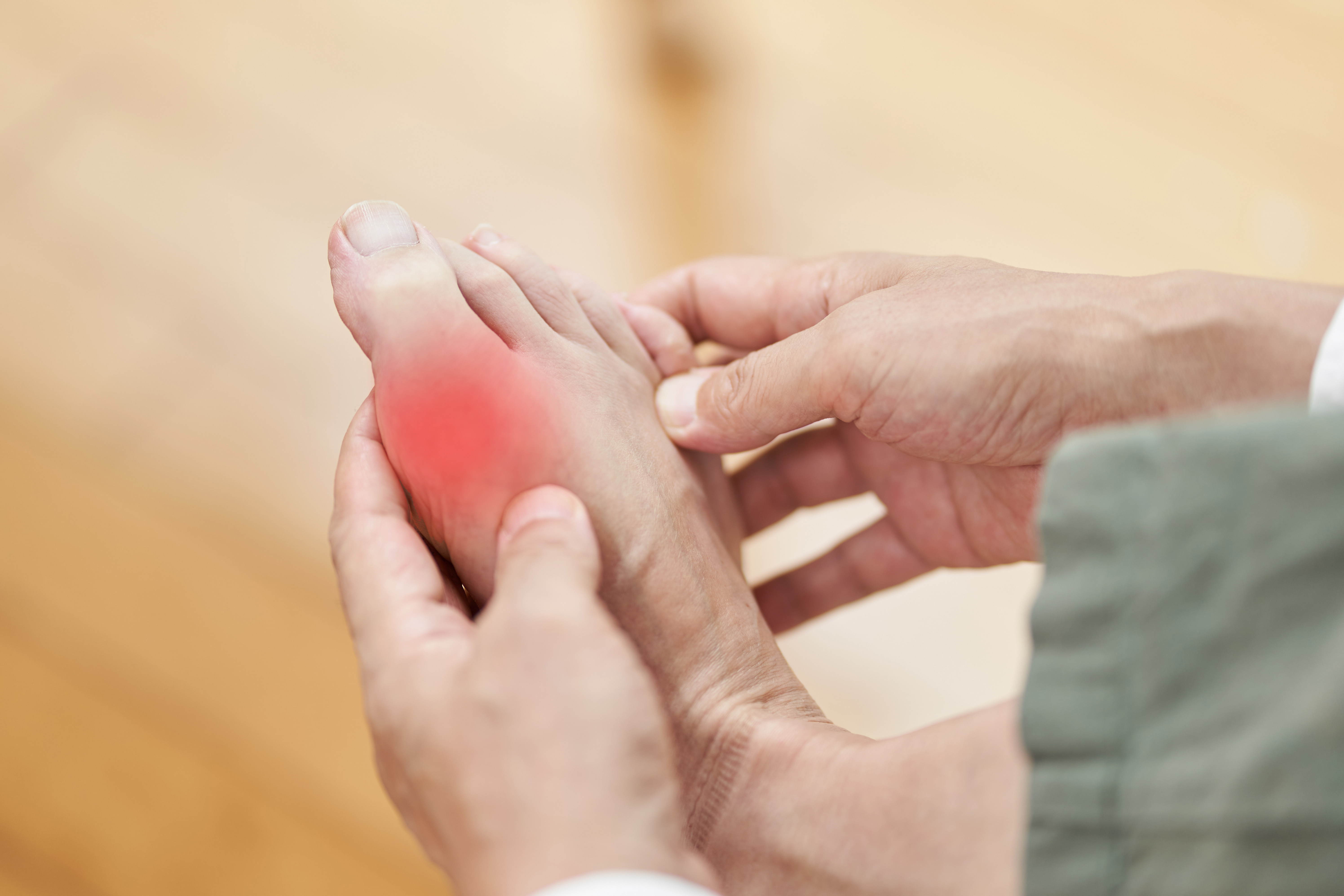
Gout is a form of arthritis characterized by sudden, severe attacks of pain, redness, and swelling in the joints, often affecting the big toe. It results from the accumulation of urate crystals in the joint, caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. Factors contributing to gout include genetics, diet, obesity, and certain medical conditions. Symptoms typically appear suddenly, often at night, and can be excruciating, leading to significant discomfort and immobility. Treatment involves medications to reduce inflammation and lower uric acid levels, as well as lifestyle modifications to prevent future attacks. Understanding gout and its triggers is crucial for effective management and prevention, particularly for those with a family history of the condition.
8. Diabetic Neuropathy - The Silent Threat
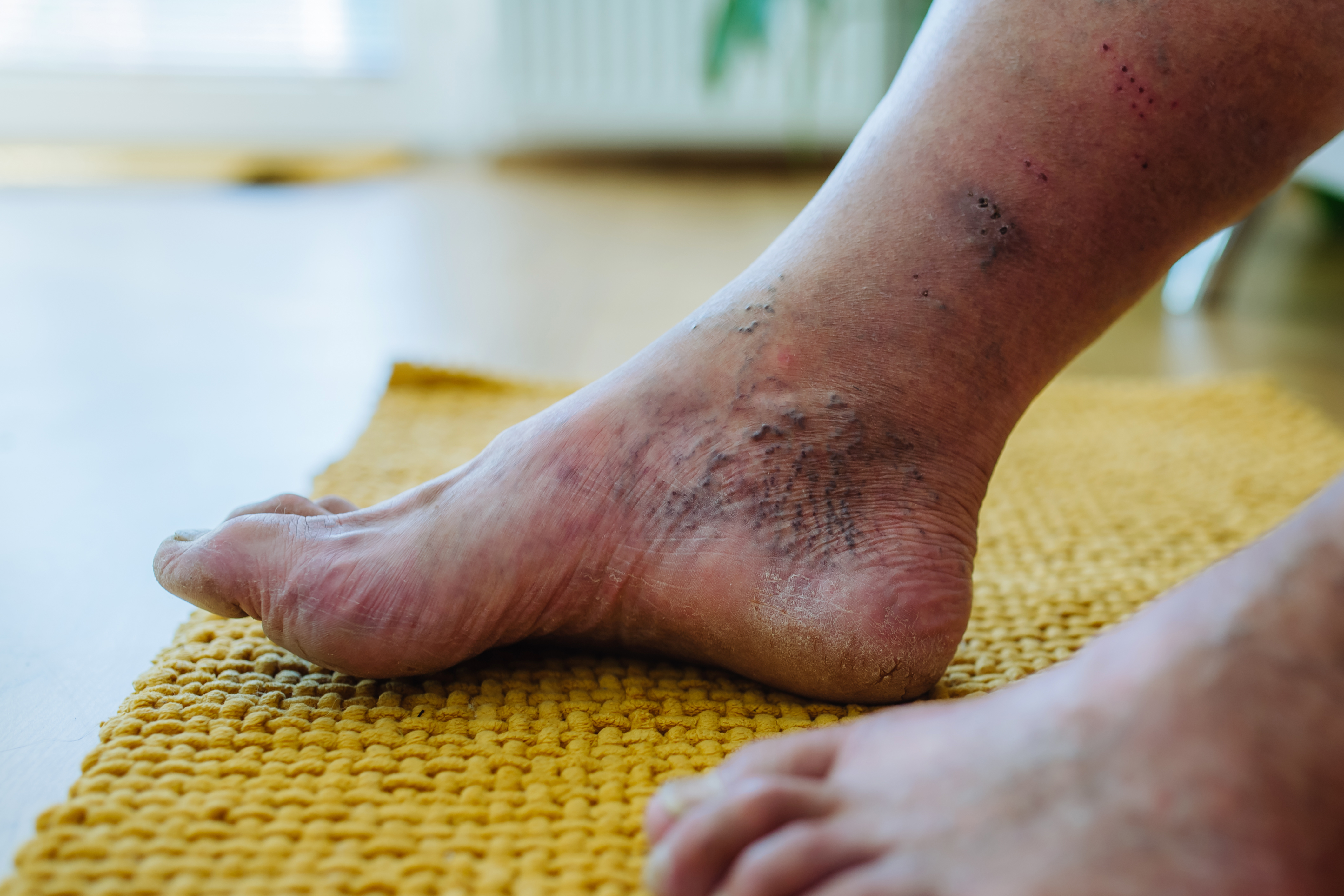
Diabetic neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur in individuals with diabetes, often affecting the feet and legs. High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to symptoms such as pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness. This condition can significantly impact foot health, increasing the risk of ulcers, infections, and even amputations if not managed properly. Treatment focuses on controlling blood sugar levels, managing symptoms, and preventing complications through regular foot care and monitoring. Understanding diabetic neuropathy and its impact on foot health is essential for individuals with diabetes, as early intervention can prevent severe complications and maintain quality of life.
9. Stress Fractures - The Subtle Saboteur

Stress fractures are tiny cracks in a bone caused by repetitive force or overuse, often affecting the weight-bearing bones of the foot. Athletes, particularly runners and dancers, are at higher risk due to the repetitive stress placed on their feet. Symptoms include pain that worsens with activity and subsides with rest, swelling, and tenderness. Risk factors include sudden increases in physical activity, inadequate footwear, and poor bone density. Treatment involves rest, ice application, and supportive footwear to allow the bone to heal. In severe cases, immobilization or surgical intervention may be necessary. Understanding stress fractures and their prevention is crucial for athletes and active individuals to maintain foot health and prevent long-term damage.
10. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) – The Circulatory Concern

Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) is a condition in which narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the extremities, often affecting the feet and legs. This restricted circulation can lead to pain, cramping, numbness, and slow-healing wounds, making even routine activities like walking or standing uncomfortable. PAD is commonly caused by a buildup of fatty deposits (atherosclerosis) in the arteries, which can be exacerbated by risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, high cholesterol, and hypertension. One of the hallmark symptoms of PAD is intermittent claudication—pain that occurs in the legs or feet during activity but subsides with rest. Left untreated, PAD can lead to severe complications, including ulcers, infections, and an increased risk of amputation. Treatment focuses on improving circulation through lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a heart-healthy diet, and smoking cessation. In more advanced cases, medication or surgical interventions like angioplasty may be necessary. Recognizing PAD early is crucial for preventing further vascular damage and maintaining foot health.
A Path to Pain-Free Feet

Persistent foot pain can significantly impact one's quality of life, but understanding its causes is the first step toward effective treatment and prevention. From plantar fasciitis to stress fractures, each condition presents unique challenges and requires targeted interventions. Proper foot care, supportive footwear, and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing and preventing foot pain. For those with underlying health conditions, such as diabetes or arthritis, regular monitoring and early intervention are essential to prevent complications. By unraveling the top ten culprits behind persistent foot pain, we hope to empower individuals with the knowledge needed to take proactive steps toward maintaining foot health and achieving a pain-free life.