Guide To Cardioversion
Cardioversion is the name for a medical procedure done to restore a normal heartbeat. It usually involves shocking the heart with electricity by placing electrodes on the patient's chest. However, some patients may use medications for this procedure instead. Cardioversion tends to be scheduled and performed in a hospital. It generally does not involve the need for overnight observation. Thus, patients can leave the same day. Most patients find that cardioversion successfully restores their heart to its normal rhythm.
Cardioversion is a common treatment for arrhythmias. Specifically, it is a treatment for fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat. It will also act as a treatment for tachycardia, which comprises a range of abnormally fast heartbeats. Patients may need to take anticoagulants for blood clots before undergoing this procedure. It is also worth noting that patients will receive intravenous medication for cardioversion. Patients need to understand this procedure fully before they undergo one.
Chemical Versus Electrical Cardioversion
Chemical and electrical cardioversion are two different procedures. However, they have the same end goal of restoring the heart's rhythm. Chemical cardioversion refers to the use of medication to control the heart's rhythm. Electrical cardioversion occurs when electric shocks are used to return the heart to its normal rhythm. Chemical cardioversion might treat several different arrhythmias, but the most common one is atrial fibrillation. This occurs when the atria quiver instead of beating fully. The condition increases an individual's risk of a stroke. Doctors may recommend cardioversion for individuals who have only had one episode.
Chemical cardioversion does not require sedation, and it is a less traumatic procedure than the alternative. Many doctors start with chemical cardioversion and move to the electrical form if it does not work. Having chemical cardioversion first increases the likelihood of electric shock working. The risks of chemical cardioversion tend to be lower. However, it also tends to take longer to see results. It also may not be as effective as electrical cardioversion.
Continue reading to reveal the reasons that this procedure is performed now.
Reasons The Procedure Is Performed
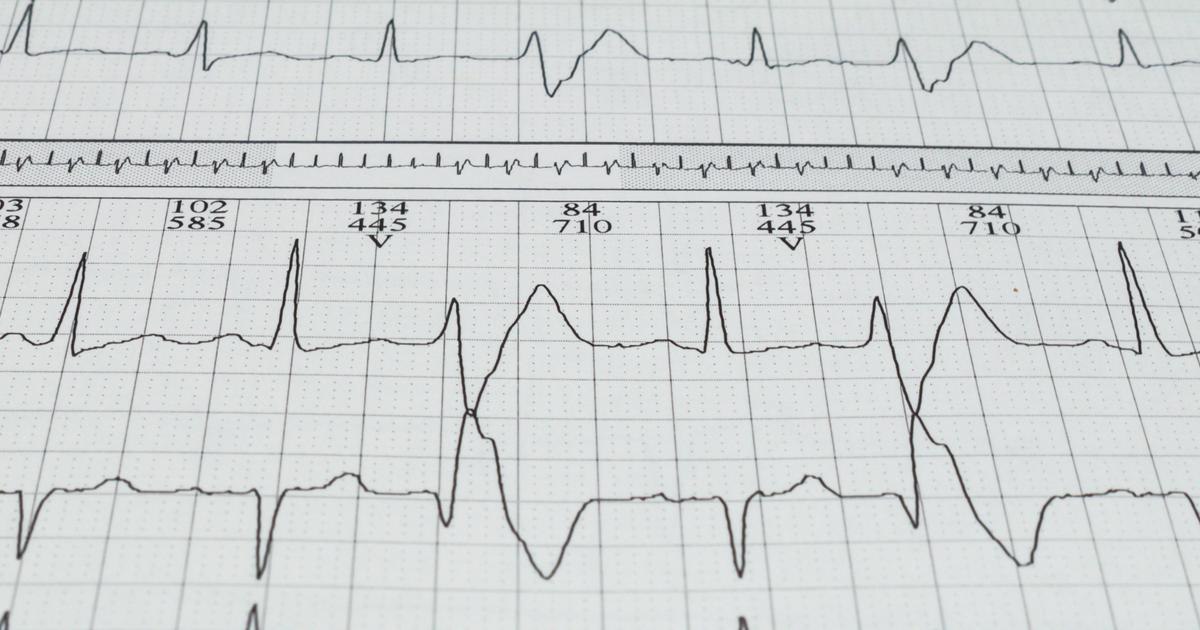
Cardioversion may be recommended if patients have certain heart rhythm problems. This includes an irregular heartbeat or a too-fast heartbeat. It is more likely to be recommended for patients whose heart condition places them at an increased risk of stroke. Suppose an individual's symptoms are only mild and not interfering with their day-to-day life. In that case, their doctor may decide that the risks are not worth the benefits. An irregular heart rhythm occurs when there is an issue with the electrical signals being sent to the heart.
In most cases, the procedure is scheduled well in advance. However, it may be performed on an emergency basis if a patient develops life-threatening symptoms related to their arrhythmia. Electric cardioversion is the most well-known procedure. It is done by sending electric shocks to the heart while a patient is under sedation. It tends to show more immediate results than chemical intervention. This procedure is different from defibrillation, which occurs on an emergency basis when the heart has stopped beating entirely. It involves the use of more powerful electricity to correct the heart rhythm.
Discover how patients can prepare for their procedure next.
