Guide To Understanding Bone Marrow
When Bone Marrow Biopsies Are Recommended
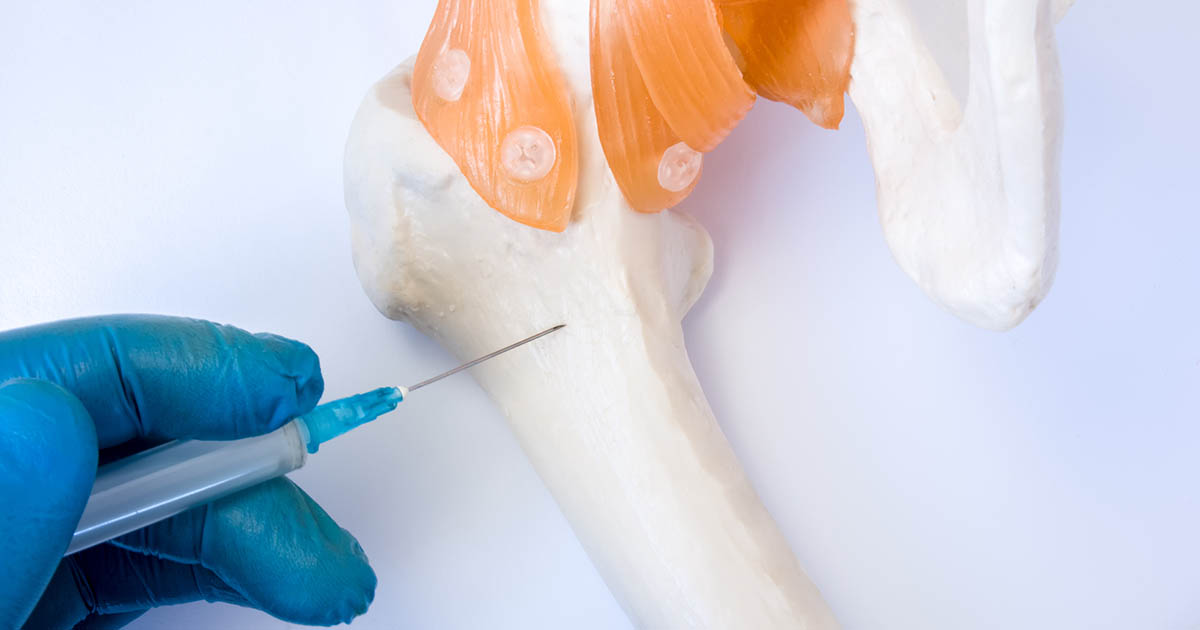
After conducting blood tests, doctors may recommend a bone marrow biopsy if the results show certain abnormalities. A bone marrow biopsy can help doctors find out more about the potential cause of the changes in the patient's blood. For example, the biopsy will help medical staff understand whether the patient's issues could be due to a blood disorder or to certain cancers. A bone marrow biopsy might also be performed for patients with cancer to determine how their treatment is affecting their bone marrow. Biopsies are normally performed at a doctor's office or hospital, and they are usually taken from the pelvic bone. Some patients may be given sedatives to help them relax during the procedure. First, the doctor will numb the skin with a local anesthetic. Next, a needle is inserted into the pelvic bone. The needle is attached to a syringe, and the doctor uses this to withdraw a tiny amount of liquid red bone marrow. The procedure takes around ten minutes, and patients who have not been given sedatives will be able to go home fifteen minutes after the procedure is complete. Patients should keep the biopsy site clean, dry, and bandaged for twenty-four hours after the procedure. Some patients experience minor pain for around one week after the biopsy, though this can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers. The results of a bone marrow biopsy are normally available in one to three weeks.
Read about bone marrow donation next.
Bone Marrow Donation

Bone marrow donation can help save the lives of patients with blood cancers and other conditions that require a bone marrow transplant. Individuals who wish to donate bone marrow can join a national registry by submitting a mouth swab. If an individual on the registry is identified as a potential match for a patient in need, they will have blood tests to determine if their bone marrow would be the most appropriate match for the patient. If selected as a donor, patients will undergo a physical examination before the donation procedure. Bone marrow can be donating using surgical and non-surgical methods, and doctors decide which method is best for the recipient's needs. Most bone marrow donors complete the process using peripheral blood stem cell donation. For five days before their donation, donors receive daily injections of filgrastim to increase the number of blood-producing cells in the bloodstream. On the donation day, the donor will have one needle placed in each arm; each needle is connected to a tube that carries blood into a machine. The donor's blood is removed through the first needle. It travels into the machine that collects the blood-forming cells. The rest of the blood is returned to the donor through the second needle. This donation method may take up to eight hours, and ninety percent of donations performed in this way only require one session. The other method for bone marrow donation is a surgical procedure performed under general anesthesia. During the operation, doctors remove liquid bone marrow from the pelvic bone.
Learn about bone marrow diseases next.
