Guide To Allopurinol
Allopurinol lowers how much uric acid there is in an individual's body. This medication can be taken as an oral tablet or administered as an injection. Tablets are available in doses of one hundred milligrams, as well as three and five hundred milligrams. The starting dose for gout is often one hundred milligrams. Generally, mild cases need a maintenance dose between two to three hundred milligrams daily. Other patients, such as those who are undergoing chemotherapy, may receive this medication intravenously. A standard intravenous dose is between two to four hundred milligrams, up to a maximum of six hundred milligrams daily.
As mentioned, this is a standard gout medicine. Some patients take it as an attempt to achieve immediate gout pain relief. Of course, some individuals will take other gout inflammation medicine as an alternative to allopurinol for gout. This medication also acts as a kidney stone treatment for some patients. Some natural remedies for gout pain and kidney stones may help reduce the patient's reliance on allopurinol. Certain individuals receiving chemotherapy treatment may also require this medication. However, it is vital to understand how it works first.
How It Works

Allopurinol is a xanthine oxidase inhibitor. Medications in this class block the action of an enzyme called xanthine oxidase. This mechanism reduces the uric acid that the body makes. Uric acid is a product of the body's metabolism of purines. Allopurinol is also considered a structural isomer of hypoxanthine, one of the natural purines in the body. It prevents purine synthesis. The medication is metabolized by aldehyde oxidase and xanthine oxidase. It completely metabolizes to oxypurinol in two hours after patients take it orally. The kidneys then excrete oxypurinol for eighteen to thirty hours.
Uses And Benefits
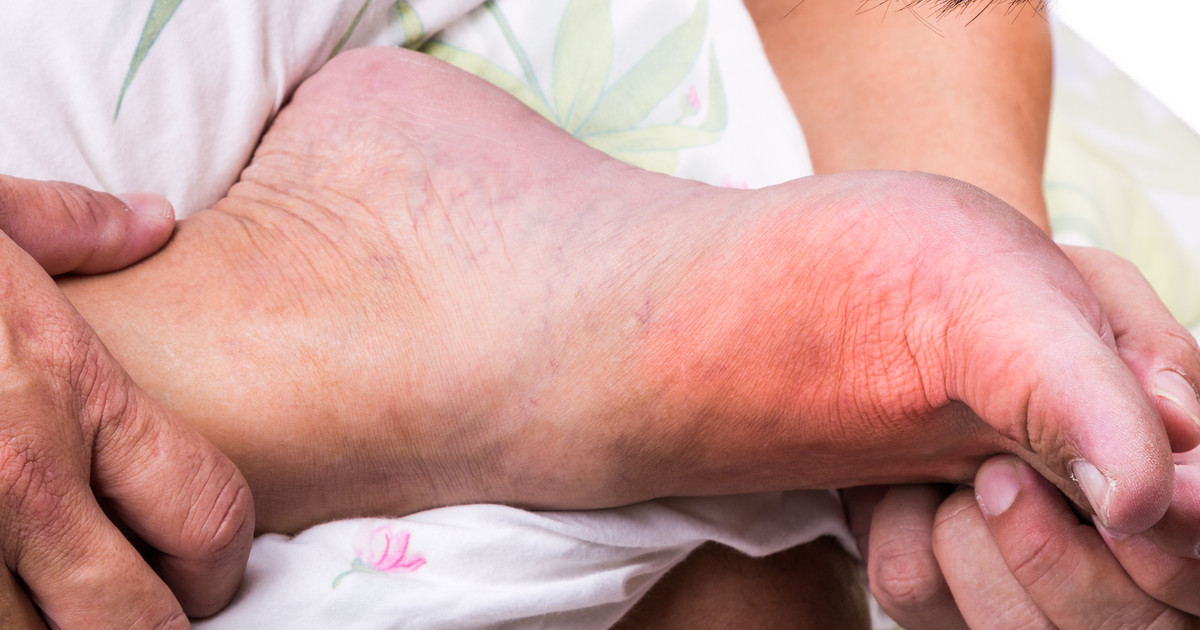
Allopurinol is most commonly used for the treatment of gout and kidney stones. It can help prevent future gout episodes. However, it is not intended to treat symptoms that occur during a gout attack. This medication is also routinely prescribed to reduce uric acid levels in patients undergoing certain types of chemotherapy. Doctors may consider prescribing it for seizures. It may be offered to patients with some types of infections as well.
This medication also relieves pain caused by pancreatic conditions. It can be beneficial in preventing relapses in patients with ulcers. Doctors may also prescribe this medication to kidney transplant patients, as it can help prevent rejection. It may be considered for patients who have had heart bypass operations. This is because this medication may increase survival rates after bypass surgery.
