Side Effects Of Antidepressants
Antidepressants are used to treat depression, anxiety, other mood disorders, and a variety of physical health conditions. Antidepressants that work correctly can relieve depression symptoms and are an integral part of treatment. The medications alter the chemical balances in the brain so the brain will have the correct number of neurotransmitters. Like any medication, antidepressants have some potential side effects. If the side effects are serious enough to be inhibiting an individual's day-to-day life, they should talk to their doctor about changing their dose or switching medications. If individuals start experiencing unusual mood swings, irrational behaviors, or thoughts of suicide, they should get in contact with their doctor immediately. Many common and non-dangerous side effects can be mitigated through at-home treatment or minor medication adjustments.
Get to know the most common side effects of antidepressants now.
Nausea
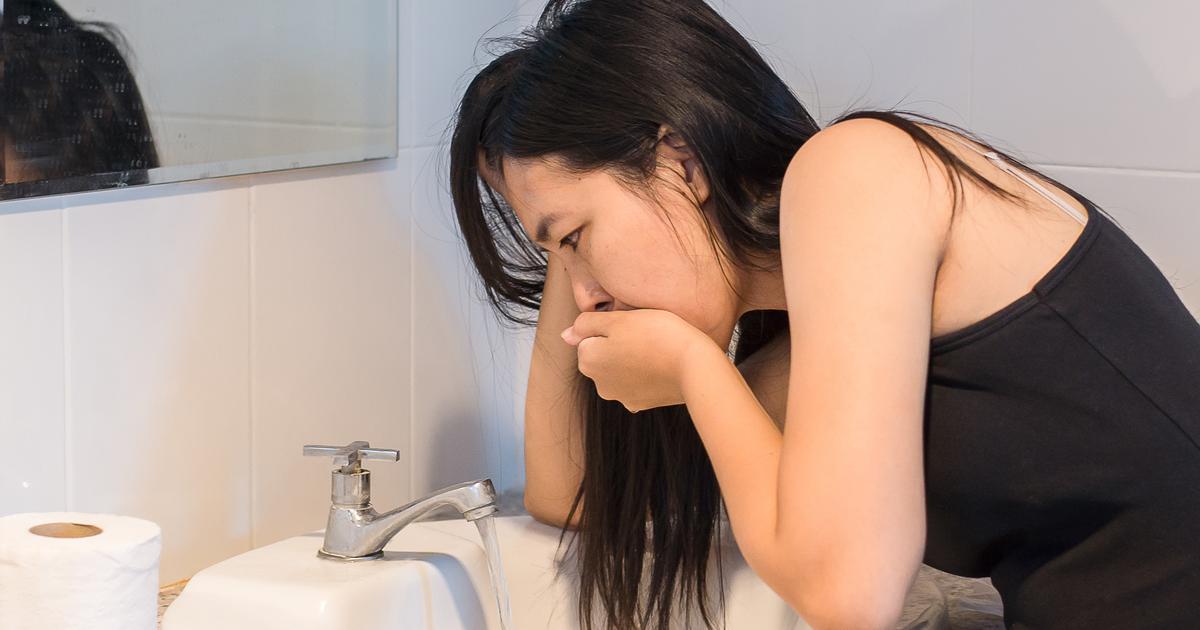

There are multiple different types of antidepressants, and nausea is a potential side effect of nearly all of them. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are the most commonly prescribed type of antidepressant, and they're also the most common type associated with nausea, which may be bad enough to induce vomiting. Most patients find the nausea is worst when they first start a medication, and it may subside after they've taken it for a while. Some patients do find their nausea and vomiting are so persistent and severe that they need to stop taking their antidepressant.
It's rare for antidepressants to cause toxic effects within the digestive tract. Instead, vomiting and nausea are caused by the medication's effect on an individual's central nervous system. With SSRIs, however, the body produces increased serotonin in both the digestive system and brain, which can lead to nausea from both sides. Taking the medication with food can help, as can taking it at bedtime. Antacids can reduce acid reflux symptoms, while ginger ale can soothe the stomach.
Uncover more potential side effects of antidepressants now.
Dry Mouth
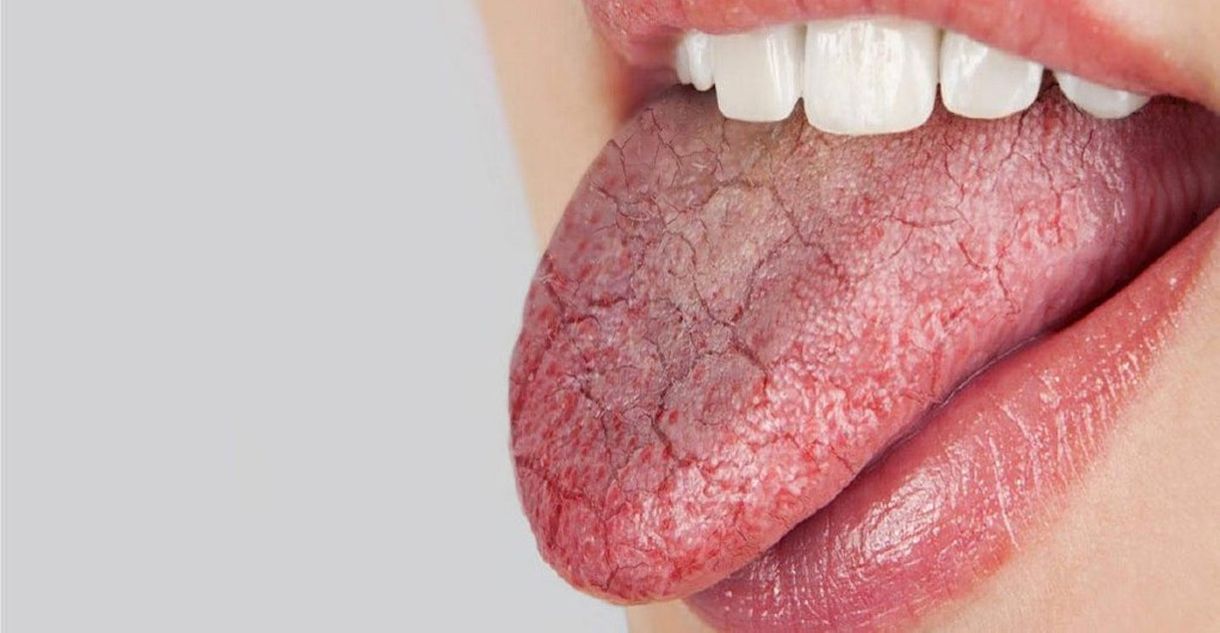
Many medications can cause dry mouth, antidepressants being just one of them. An individual's mouth becomes dry when their salivary glands don't produce enough saliva. Saliva is necessary for breaking down and removing food from the mouth, and a lack of saliva can lead to serious dental problems. If food gets stuck in the teeth without being broken down, it can contribute significantly to tooth decay. Plaque and bacteria also become stronger when there isn't saliva to inhibit their growth. Two factors can cause dry mouth. The first is the salivary gland doesn't produce as much saliva, while the second is an individual's perception of their mouth's dryness becomes more acute. This means it's possible for antidepressants to make a patient's mouth feel drier even if it isn't.
Tricyclic antidepressants have been shown to cause dry mouth more often than SSRIs. Researchers have found age correlates with the prevalence of dry mouth, and older patients have a higher likelihood of impaired salivary function than younger adults.
Read more about the potential side effects of antidepressants now.
