Common Causes And Complications Of OCD
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a type of anxiety disorder, which is a category of mental illnesses that present with irrational or unusual levels of fear or worry. OCD is a chronic condition that causes uncontrollable and recurring thoughts called obsessions, along with compulsive behaviors the patient feels must be repeated. Each presentation of obsessive-compulsive disorder is different. The precise nature of the compulsions and obsessions is unique. The most well-known manifestation includes cleaning and fear of germs, but OCD often manifests in other ways.
There are several common causes of contributing factors to the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Get familiar with them now.
Certain Brain Abnormalities
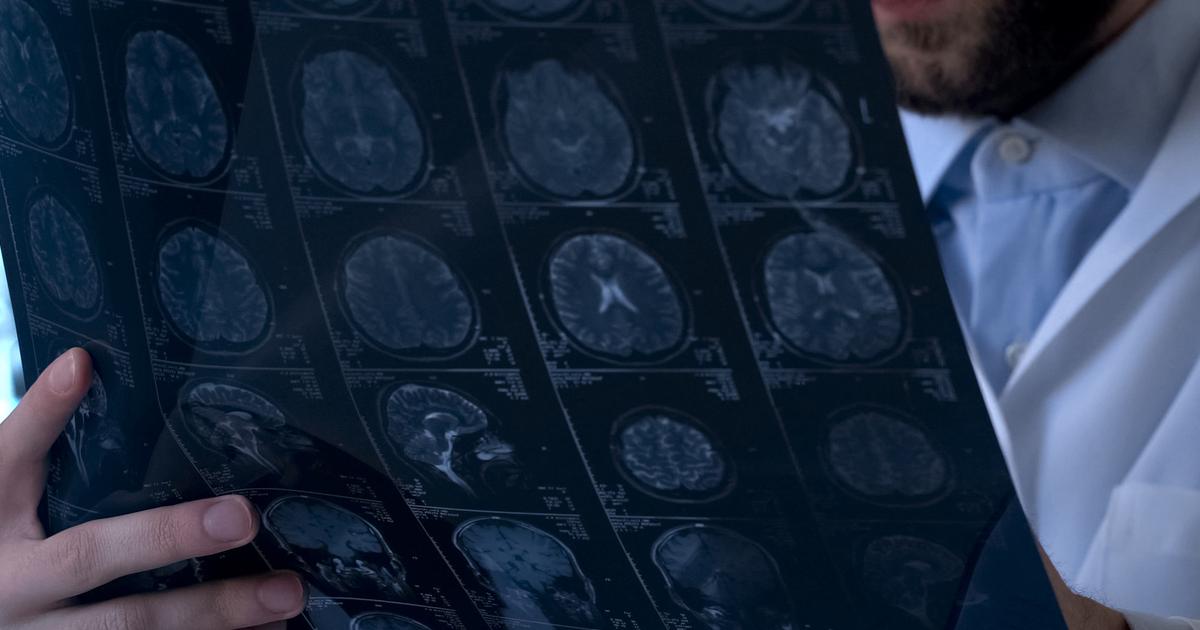
Certain brain abnormalities have been identified in individuals who have obsessive-compulsive disorder. Not everyone with this condition has the abnormalities, and not every person with the abnormalities has OCD. However, there's a marked correlation between them. The research was done by comparing hundreds of different brain scans, and researchers believe the processes and areas of the brain they've identified play a role in the repetitive compulsions that are part of obsessive-compulsive disorder. The study indicates OCD patients can sometimes get stuck in a repetitive cognitive loop that keeps them from stopping the behaviors even when they cause distress. In these patients, the brain has a disproportionately large response to errors, and a disproportionately small response to stop signals. Errors are cognitive processing issues or irrational thoughts. A person without obsessive-compulsive disorder can use 'stop' signals to stop an irrational or intrusive thought from repeating. But someone with this disorder can't stop obsessing over the error, even if they're aware the behavior is irrational and causing distress.
Read more about what can trigger the development of obsessive-compulsive disorder now.
Environmental Factors
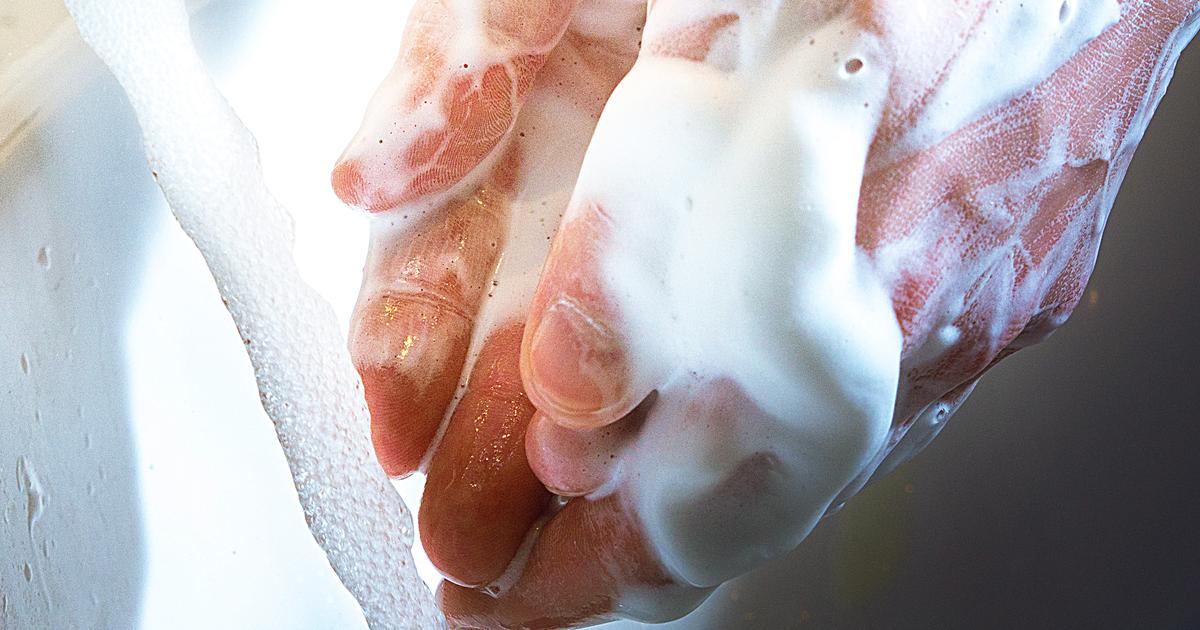

While researchers believe obsessive-compulsive disorder has a basis in neurochemical abnormalities, the way symptoms present is often determined by environmental factors, as is the severity of symptoms. Researchers who study the way the environment shapes brain development believe behavioral conditioning might play a part in an individual's development of compulsions and obsessions. For example, if someone is afraid of germs, they might obsessively wash their hands to relieve the anxiety about germs. Some cognitive behavioral researchers believe the misinterpretation of intrusive thought leads to compulsions and obsessions. Intrusive thoughts happen to everyone. They may involve thoughts about perpetuating harmful behaviors or doing things that frighten the individual. In a neurotypical person, these thoughts can be put aside, but OCD patients become fixated on them. An individual can have dysfunctional beliefs about themselves shaped by their environment. One common belief is an individual can cause or prevent negative outcomes by following their compulsions. Another is the idea having a thought is the same as actually acting upon the thought.
Keep reading to learn more about the causes of obsessive-compulsive disorder now.
