How To Diagnose And Treat A Strawberry Hemangioma
A strawberry hemangioma is a type of birthmark that forms from a cluster of extra blood vessels located close to the surface of the skin. This type of birthmark typically develops at some point during the first few weeks after birth, and it may be either flat or elevated from the skin's surface. Strawberry hemangiomas are a dark red, and they can occur anywhere on the body. However, they most often develop on the scalp, face, chest, or back. Hemangiomas are not painful, and they do not normally pose any danger to the patient. Generally, they fade in color by the time children reaches ten years old. Depending on the location of the birthmark, some patients may choose to have it removed for cosmetic reasons.
Tissue Biopsy

Doctors can usually diagnose a strawberry hemangioma with a clinical examination, though occasionally a tissue biopsy may be warranted. This test helps the physician determine what type of hemangioma is present and how deep underneath the skin it may go. A biopsy may be ordered if the doctor believes the location of a strawberry hemangioma could pose a risk to a vital organ, and the procedure may also be performed if it is of a large size. Tissue biopsies for strawberry hemangiomas are usually performed by plastic surgeons or dermatologists. To perform the biopsy, the doctor first gives the patient an injection of a local anesthetic to numb the area around the hemangioma. For pediatric patients and individuals who are afraid of needles, a topical numbing cream can sometimes be applied before the injection to provide additional pain relief. After the area is numb, the doctor removes a small piece of tissue from the hemangioma and closes the wound with stitches. The tissue is then placed underneath a microscope, where it is examined by a pathologist. Depending on the results of the biopsy, doctors may recommend no further treatment is needed, or they may suggest the entire strawberry hemangioma be removed.
MRI Or CT Scan
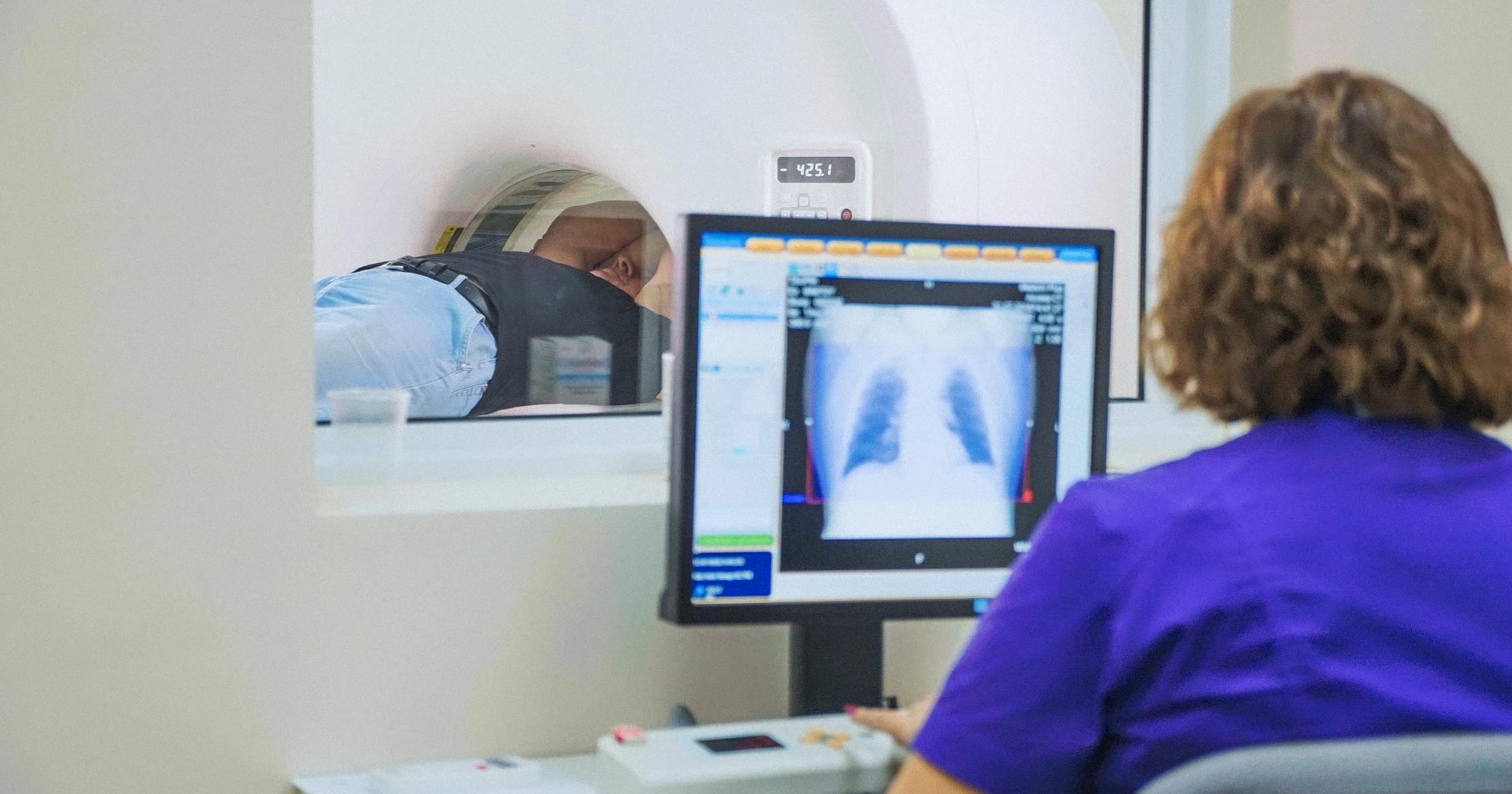
Patients who have large strawberry hemangiomas that may threaten a vital organ typically need to have an MRI or CT scan. These imaging studies are performed by radiologists, and they help doctors get a more detailed view of the depth of the birthmark and find out more information about the blood vessels that may be involved. CT scans use radiation for imaging, and MRI scans use magnetic fields to produce images. Doctors will recommend a particular type of scan after assessing the patient's overall health. Both tests are painless, and the patient simply lies on a table while the imaging device works above them. If a patient is anxious, they may be given a mild sedative in advance of the procedure. Sometimes, the doctor may ask for the scan to be completed with and without contrast. For scans completed with contrast, the patient either drinks a solution or is injected with a substance that enables the area in question to be seen more clearly on the scan. MRI and CT scans can be particularly useful if surgery to remove a hemangioma has been recommended.
