12 Hidden Tick Bite Signs That Demand Immediate Action
7. Neurological Symptoms

Neurological symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or facial palsy can develop following a tick bite and are particularly associated with Lyme disease. These symptoms occur when the bacteria affect the nervous system, leading to conditions such as Lyme neuroborreliosis. Facial palsy, or Bell's palsy, is characterized by the sudden weakness or paralysis of facial muscles, often affecting one side of the face. Neurological symptoms require immediate medical attention to prevent long-term damage. Diagnostic tests, including blood tests and imaging studies, can help determine the extent of neurological involvement and guide treatment decisions. Timely intervention with antibiotics and supportive therapies can improve outcomes and reduce the risk of persistent neurological issues.
8. Skin Changes Beyond the Bullseye Rash
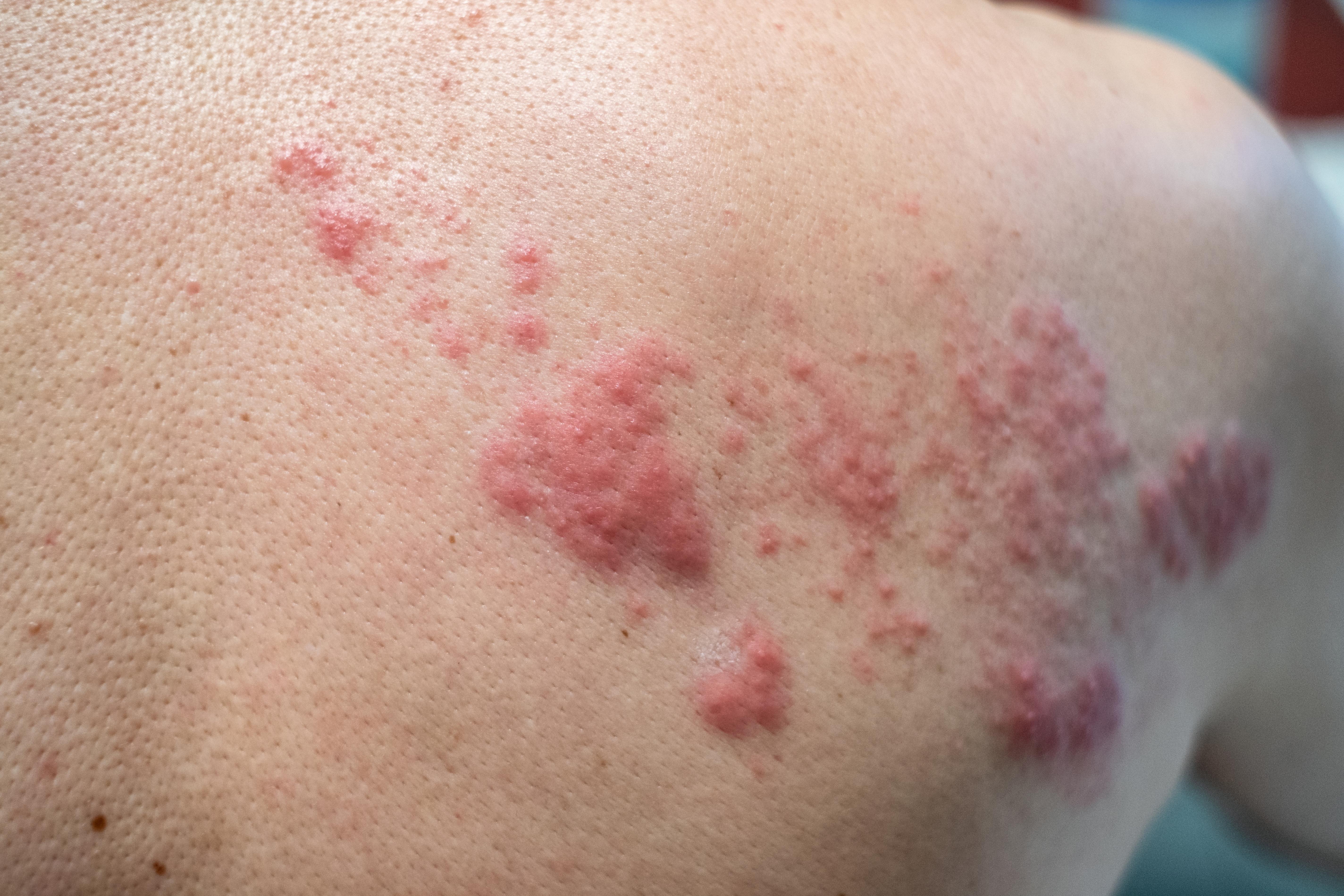
While the bullseye rash is the most recognized skin manifestation of a tick bite, other skin changes can also occur and should not be ignored. These can include multiple rashes, small red or purple spots, or a generalized rash that spreads across the body. Such skin changes can be indicative of conditions like Rocky Mountain spotted fever or Southern tick-associated rash illness (STARI). These skin manifestations can provide important clues to the underlying condition and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional. In some cases, a biopsy of the rash may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Early recognition and treatment of tick-borne illnesses associated with skin changes can prevent serious complications and improve patient outcomes.
