13 Telltale Clues Your Body Is Fighting Chronic Inflammation
7. The Influence of Genetics on Inflammation Susceptibility
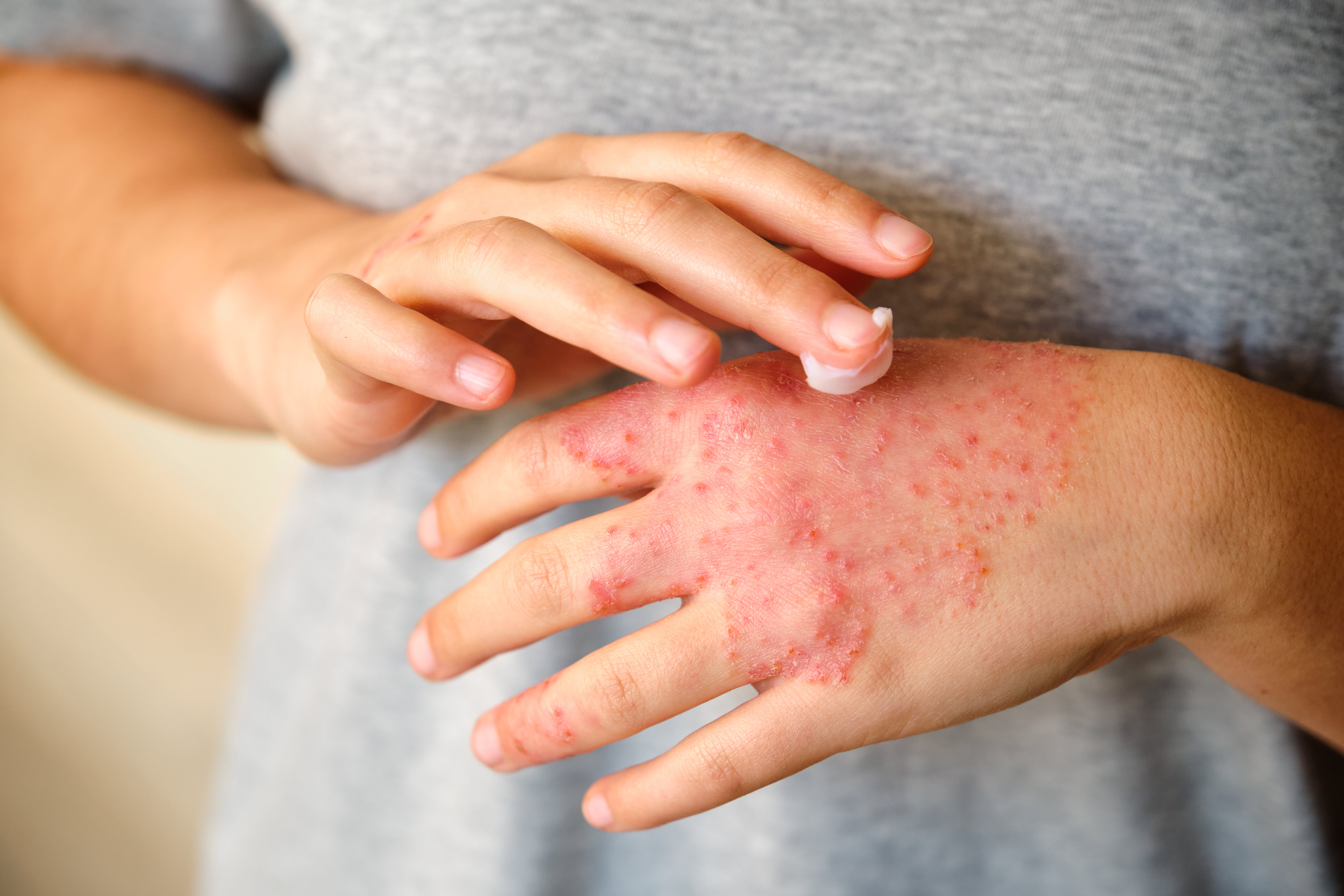
Genetic factors can influence an individual's susceptibility to chronic inflammation. Certain genetic variations can affect immune function, making some people more prone to inflammatory diseases. For example, specific gene mutations have been linked to conditions like Crohn's disease and psoriasis. Understanding one's genetic predisposition can guide personalized approaches to managing inflammation. Genetic testing and family history assessments can provide valuable insights, allowing for tailored interventions that address the unique needs of each individual. This personalized approach to inflammation management represents a significant advancement in preventive healthcare.
8. Environmental Toxins and Their Role in Inflammation
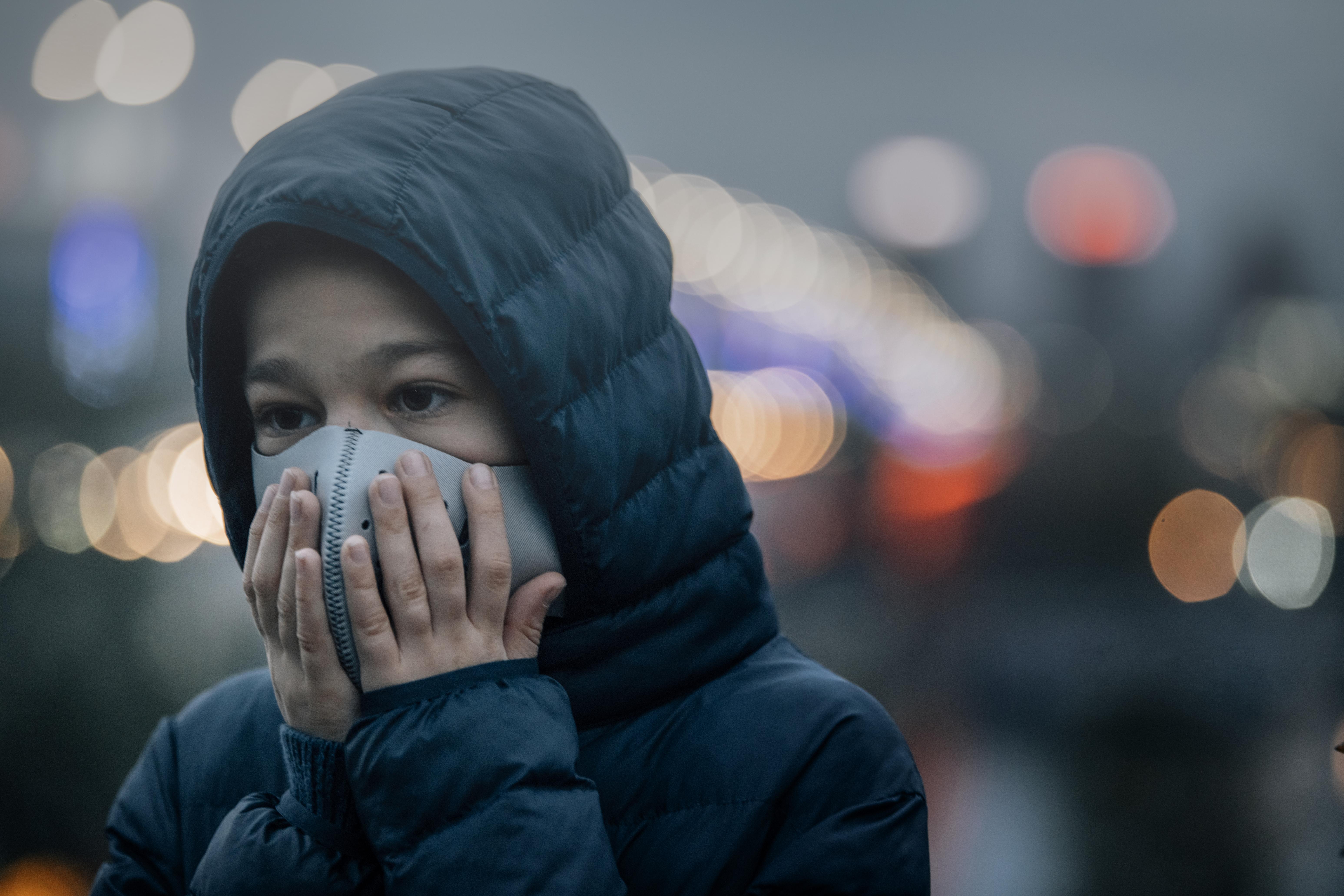

Exposure to environmental toxins is an often-overlooked factor in chronic inflammation. Pollutants, chemicals, and heavy metals can trigger inflammatory responses by disrupting cellular function and immune activity. For instance, air pollution has been linked to increased inflammation and respiratory diseases. Reducing exposure to environmental toxins and adopting detoxification strategies can help mitigate their impact on inflammation. This includes using air purifiers, choosing organic products, and supporting liver function through diet and hydration. Understanding the role of environmental toxins in inflammation highlights the need for public health initiatives and personal measures to reduce exposure and promote health.
