18 Hidden Causes of High Neutrophil Counts That Doctors Want You to Know
9. Surgery
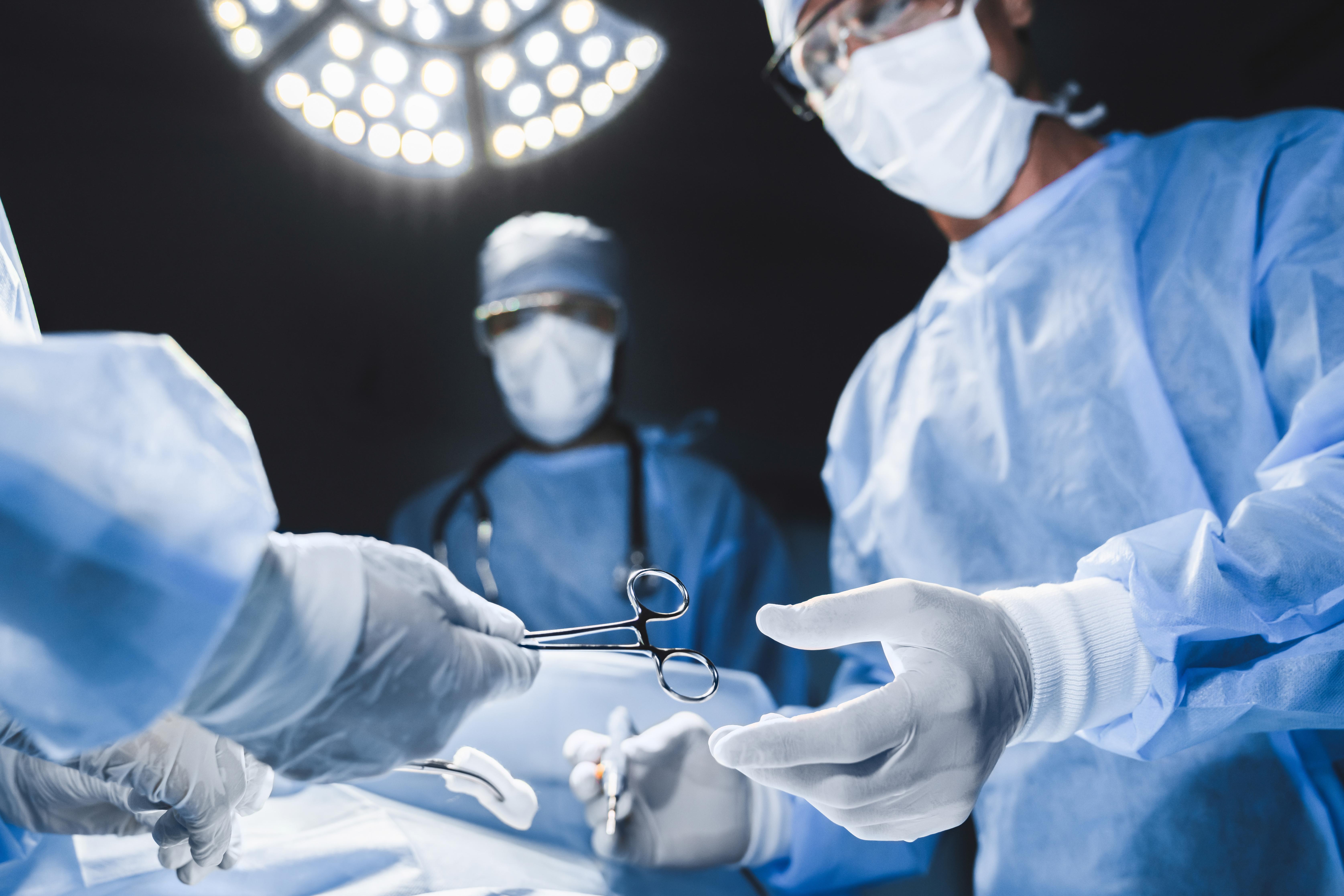
Surgery, even simple and routine surgeries, come with certain risks. One of the most common risks for patients is an infection after surgery, such as around the surgical incision. Unfortunately, this can happen even when the surgeon performs very well in the sterile environment. Infections are also a risk after the patient leaves the hospital and the incision has not completely healed. Infections will trigger an immune response, which can mean that an individual's white blood cell count rises, causing neutrophilia in some instances. In addition, it is also vital to note that a patient's white blood cell count will rise during surgery. This is the body's natural immune response to the abnormal event of surgery. When the surgery is clean and successful, these cells simply clean up dead tissue and things will return to normal after the surgery is over and during recovery. However, this response can sometimes remain, triggering neutrophilia.
10. Injury

Injuries, especially those that cause significant tissue damage and bruising, increase the risk of individuals experiencing neutrophilia. One of the major reasons this happens is that the body will respond to the injury with inflammation. Inflammation signs, of course, include pain, redness, warmth, and swelling. Neutrophils are part of the immune response to an injury. In fact, neutrophils are the first white blood cells to respond to an injury. They are the cells that release chemical signals to attract other immune cells to the injury. The intent is to heal and protect the injury. However, serious injuries can result in extended periods of inflammation, and thus, neutrophilia.
