20 Astonishing Varieties of Heart Disease: Your Ultimate Roadmap to Cardiac Chaos
Heart disease isn’t just one condition—it’s a full-blown lineup of cardiac curveballs, each with its own symptoms, risks, and ripple effects. From the silent creep of high blood pressure to the sudden jolt of arrhythmia, the spectrum of heart disorders is broader—and more astonishing—than most people realize. Some types are congenital, present from birth. Others are shaped by genetics, lifestyle choices, or long-term damage to the arteries and heart muscle. The warning signs aren’t always dramatic, which makes early detection crucial. Diagnosis can involve everything from stress tests and echocardiograms to CT scans and cardiac catheterizations. And when it comes to treatment? Options range from medication and lifestyle tweaks to complex surgical interventions. But knowing what you’re up against is half the battle. That’s why we’ve expanded our list to 20 Astonishing Varieties of Heart Disease: Your Ultimate Roadmap to Cardiac Chaos—a no-fluff guide to understanding, spotting, and navigating the many faces of heart trouble.
1. Heart Rhythm Disorders
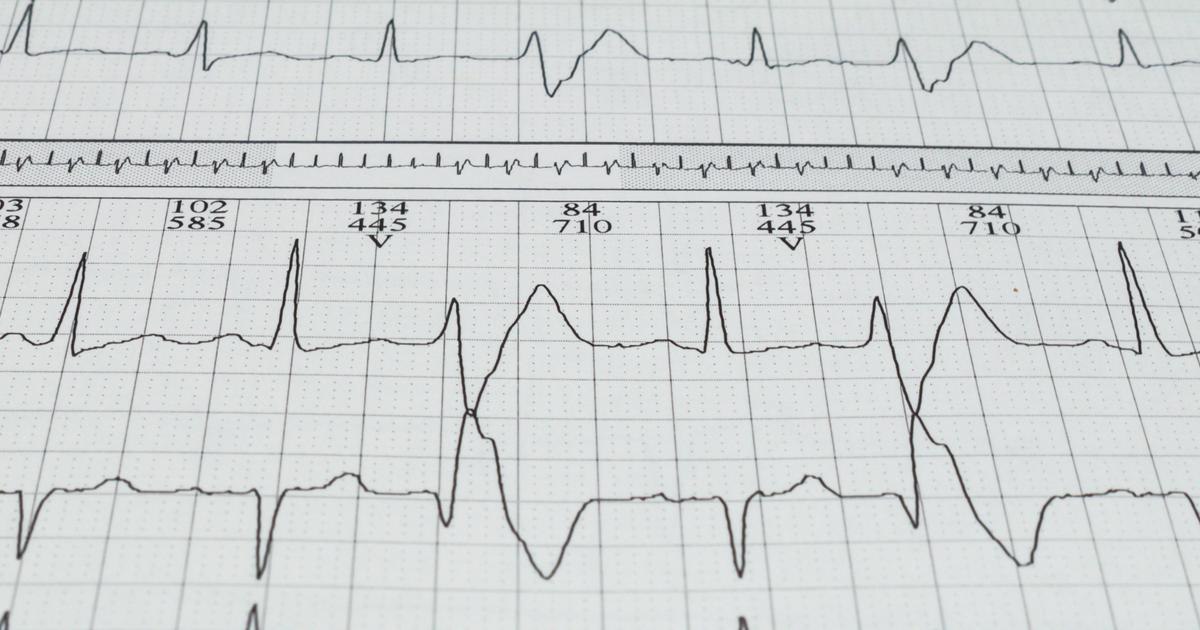
Arrhythmias, also called heart rhythm disorders, are a form of heart disease where an individual's heart cannot maintain a healthy and regular rhythm or beating pattern. Heart rhythm disorders result from a malfunction that occurs with the electrical activity and path in the heart responsible for coordinating the heartbeat. A patient's heart may beat too slow, too fast, or in an abnormal rhythm. The electrical mechanisms in the heart can malfunction from an underlying cause such as scarred heart tissue, coronary artery disease, hyperthyroidism, and hypothyroidism. Other examples of underlying causes include excessive alcohol consumption, stress, certain medications, sleep apnea, heart attack, cardiomyopathy, high blood pressure, smoking, and diabetes. Symptoms of heart rhythm disorders include a racing heartbeat, a slow heartbeat, shortness of breath, sweating, chest pain, dizziness, fainting, and lightheadedness. Common heart rhythm disorders include bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, atrial flutter, supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. Other examples are Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, long QT syndrome, sick sinus syndrome, conduction block, and premature heartbeats.
2. Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is a form of heart disease where an individual's coronary arteries become narrowed or blocked over time. The most common cause of this disease is a condition referred to as atherosclerosis. This condition occurs when the inner walls of an individual's arteries become hard and narrow from the buildup of plaque, a substance made of cholesterol and fatty deposits. When this buildup occurs in one or both of the coronary arteries that supply the muscle tissues of the heart with blood and oxygen, it is referred to as coronary artery disease. This narrowing can cause the tissues in the heart to become damaged when they do not receive enough blood and oxygen. Signs of coronary artery disease can be difficult to distinguish from other heart conditions. Acute issues that tend to occur more often in coronary artery disease patients include stable angina, silent ischemia, development of collateral circulation, and unstable angina. Two other examples are ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. Electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, exercise stress test, chest x-ray, coronary angiogram, and cardiac catheterization are used to diagnose coronary artery disease.
