20 Cause of Petechiae and What You Need to Know About Them
3. Mononucleosis

Mononucleosis is a condition triggered by the Epstein-Barr virus. Also known as glandular fever, patients with this illness might initially be misdiagnosed with strep throat, as both conditions have many of the same symptoms. Some of the most common mononucleosis symptoms include fatigue, fever, swollen lymph nodes, swollen tonsils, a skin rash, and a sore throat. Some patients with mononucleosis may also have a swollen spleen. For many patients, the fatigue caused by this condition is severe enough that it is necessary to take several weeks off of work or school. To diagnose this condition, doctors will check the patient's spleen, lymph nodes, and throat, and they will need to perform blood tests to confirm the diagnosis. Since antibiotics are not effective against viruses, recommended treatments for mononucleosis generally consist of getting sufficient rest, staying hydrated, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers for any fevers or sore throats. Antibiotics will be given to patients with this condition who have a secondary infection such as strep throat, sinus infections, or tonsil infections. Patients may need two or three months to make a complete recovery from mononucleosis. During this time, physicians routinely advise patients to avoid heavy lifting and playing contact sports; these precautions are necessary to prevent a potential rupture of the spleen.
4. Vasculitis
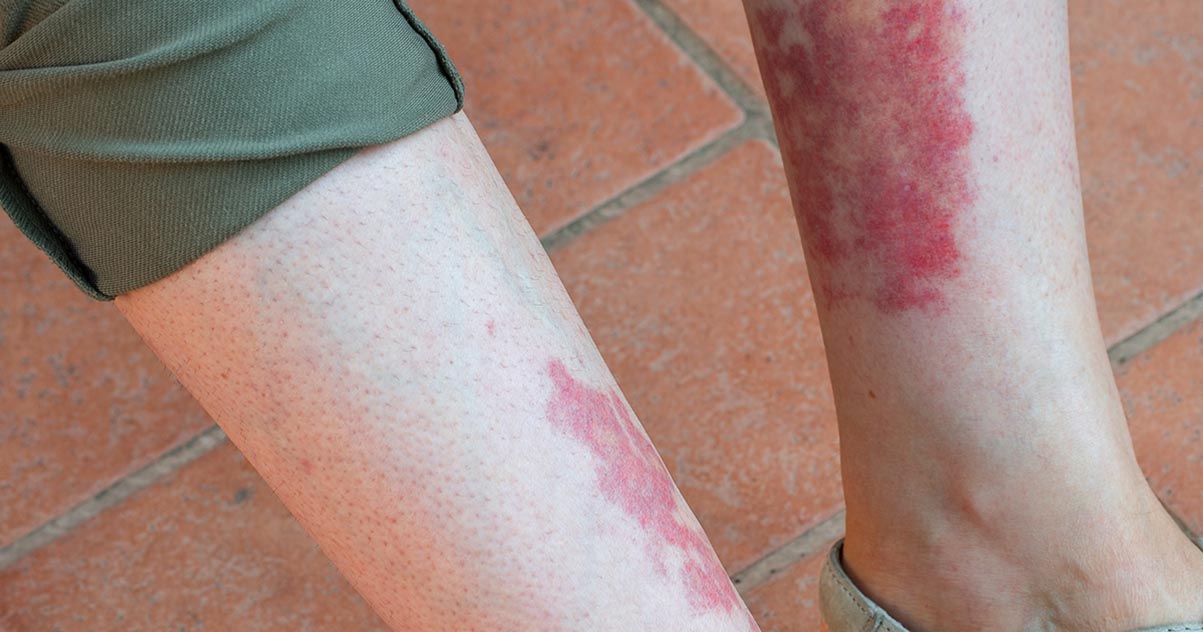
Vasculitis occurs when there is blood vessel inflammation. Blood vessels may become thicker or narrower than they should be, and they might also weaken. There are several forms of this condition, and each patient's symptoms may be different. Symptoms associated with most forms of vasculitis include weight loss, fever, headaches, generalized aches and pains, fatigue, and night sweats. Some patients may experience numbness or other nerve issues. A rash known as Henoch-Schonlein purpura could form over the legs too. To determine the underlying cause for vasculitis, the physician will perform urine and blood tests, and patients might need to have CT scans, angiography, or biopsies. Corticosteroids are often prescribed to reduce inflammation, and some patients might also take methotrexate, mycophenolate, or azathioprine. If vasculitis causes blocked arteries or aneurysms, surgery may be needed.
