20 Symptoms of Endocarditis to Look Out For
9. Shortness Of Breath Or Coughing
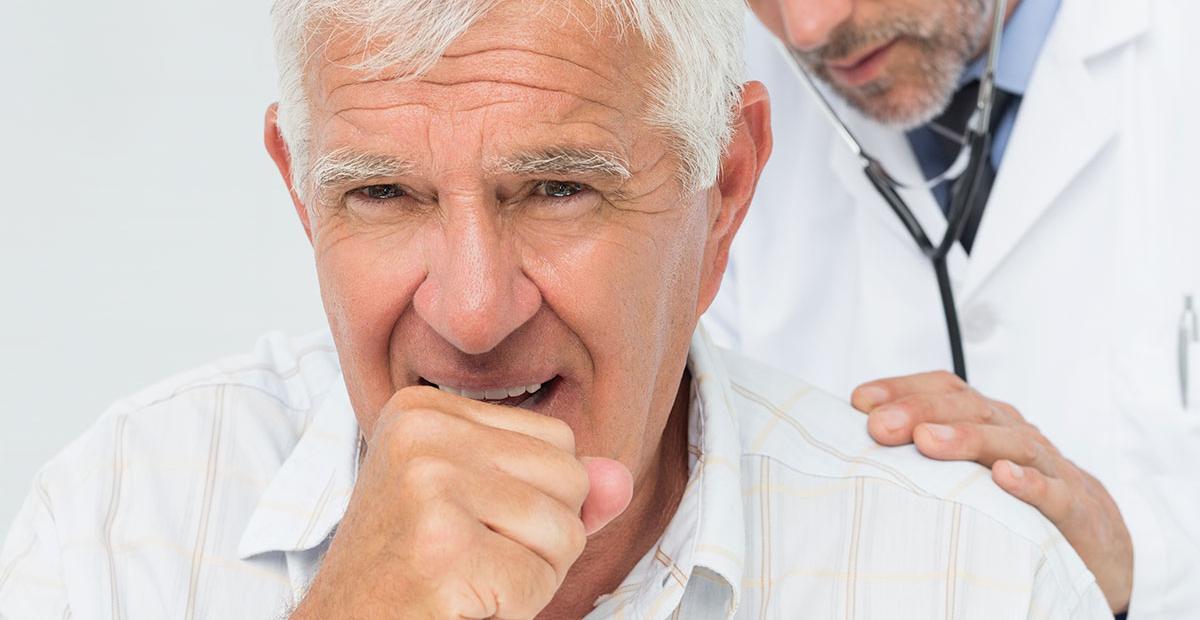

Endocarditis develops when bacteria attach to vulnerable parts of the heart tissue and colonize. The valves of the heart are the most affected structures in the heart by bacterial endocarditis. Subacute endocarditis causes the tissues that make up the leaflets in the heart to become damaged to the point where the body initiates the mechanism used to repair damaged tissues. When this process occurs frequently over time, scar tissue begins to build on the valve leaflets because damaged tissue is replaced with dense and fibrous tissue. The buildup of fibrous scar tissue on the valve leaflets causes them to be unable to open properly. If this scar tissue from endocarditis builds on one of the pulmonary valves, it can cause blood to back up into the lungs. When blood backs up in the lungs it causes pulmonary hypertension, which produces symptoms like coughing and shortness of breath.
10. Blood In The Urine
Most individuals affected by blood in the urine (hematuria) due to endocarditis are affected by subacute endocarditis that has developed over time. The emboli that form in an affected individual's blood due to the infection in their heart become lodged in the kidneys and can cause sections of the kidney tissue to shut down or die. This damage to the kidney tissues is the result of infarcts in the organs due to an obstruction of oxygenated blood. When the infection in an individual's heart moves to their kidneys, it can cause them to develop a condition referred to as interstitial nephritis. Interstitial nephritis causes the tissues of the kidneys to swell and become damaged, which can leak blood into the urine. If an individual's endocarditis is caused by an infection with streptococcus bacteria, they can develop an infection in the kidneys called proliferative glomerulonephritis.
