Warning Signs of a Staph Infection And What to Do About Them
14. Toxic Shock Syndrome

Toxic Shock Syndrome (TSS) is a rare but life-threatening condition caused by toxins released by certain strains of staph bacteria. TSS is often associated with tampon use, but it can also develop from skin wounds, burns, or surgical incisions. Symptoms of TSS include high fever, a sudden drop in blood pressure, confusion, a sunburn-like rash, muscle aches, and vomiting. If untreated, it can result in organ failure or death. Patients suspected of having TSS require immediate medical care, typically involving intravenous antibiotics, fluids, and supportive therapies to stabilize blood pressure and organ function. Preventing TSS involves practicing good hygiene, using tampons for recommended durations, and ensuring wounds are cleaned and dressed properly. Awareness and prompt treatment are essential in reducing the risk and severity of this potentially fatal condition.
13. Osteomyelitis: Bone Infections
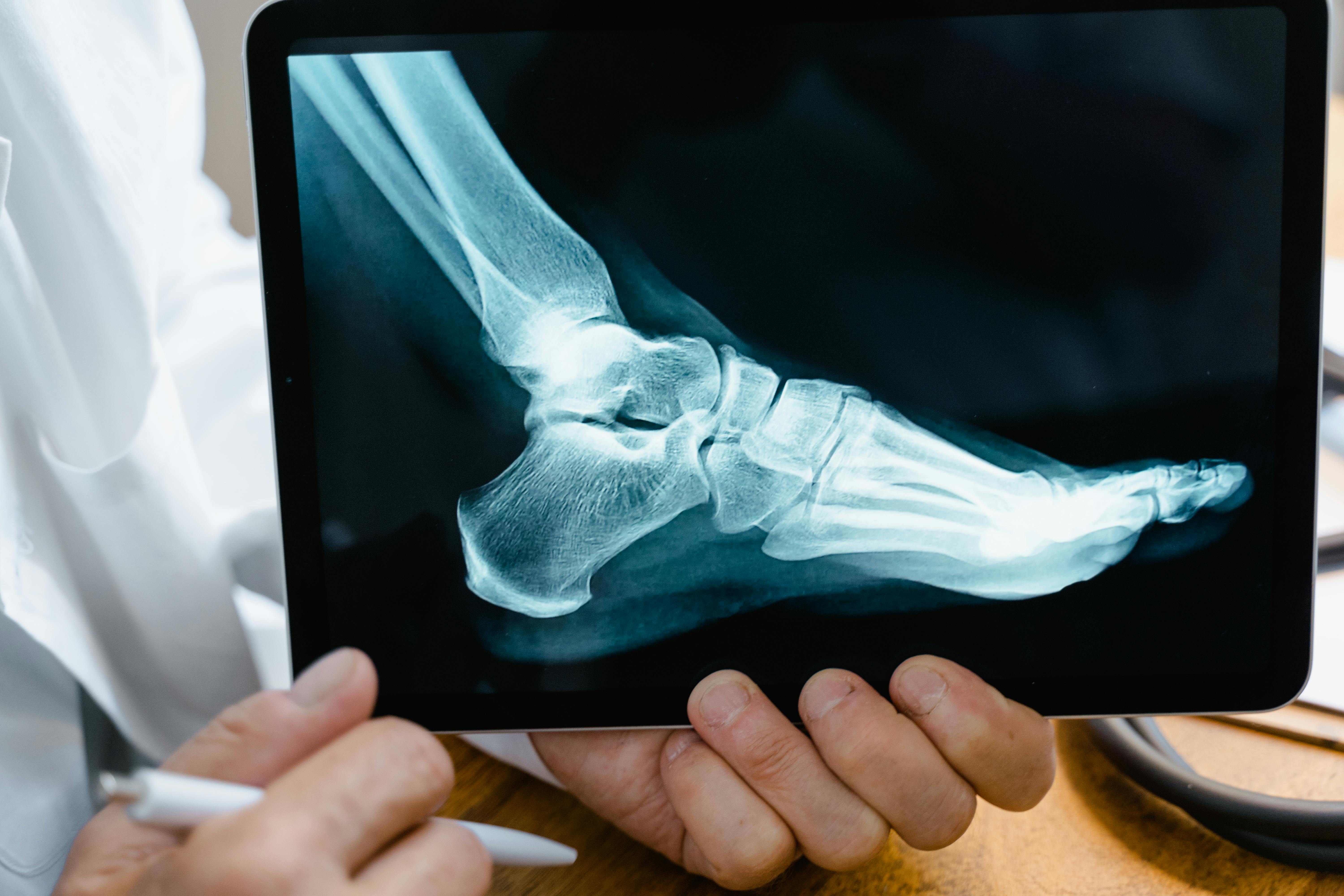
Staph bacteria can cause osteomyelitis, a painful infection of the bone. This occurs when bacteria enter the body through an open wound, surgery, or bloodstream and settle in bone tissue. Symptoms of osteomyelitis include severe bone pain, swelling, redness over the affected area, fever, and fatigue. It can occur in individuals of any age but is more common in those with weakened immune systems or existing bone injuries. If left untreated, osteomyelitis can lead to permanent bone damage or require surgical intervention to remove infected tissue. Treatment involves a combination of antibiotics, often administered intravenously, and in severe cases, surgery to drain abscesses or remove damaged bone. Early intervention is critical to prevent long-term complications. Protecting wounds and maintaining good hygiene can reduce the risk of this rare but serious staph-related condition.
