Weird Ways Your Body Might React To Hypoparathyroidism
15. Kidney Stones or Calcifications (Nephrocalcinosis)
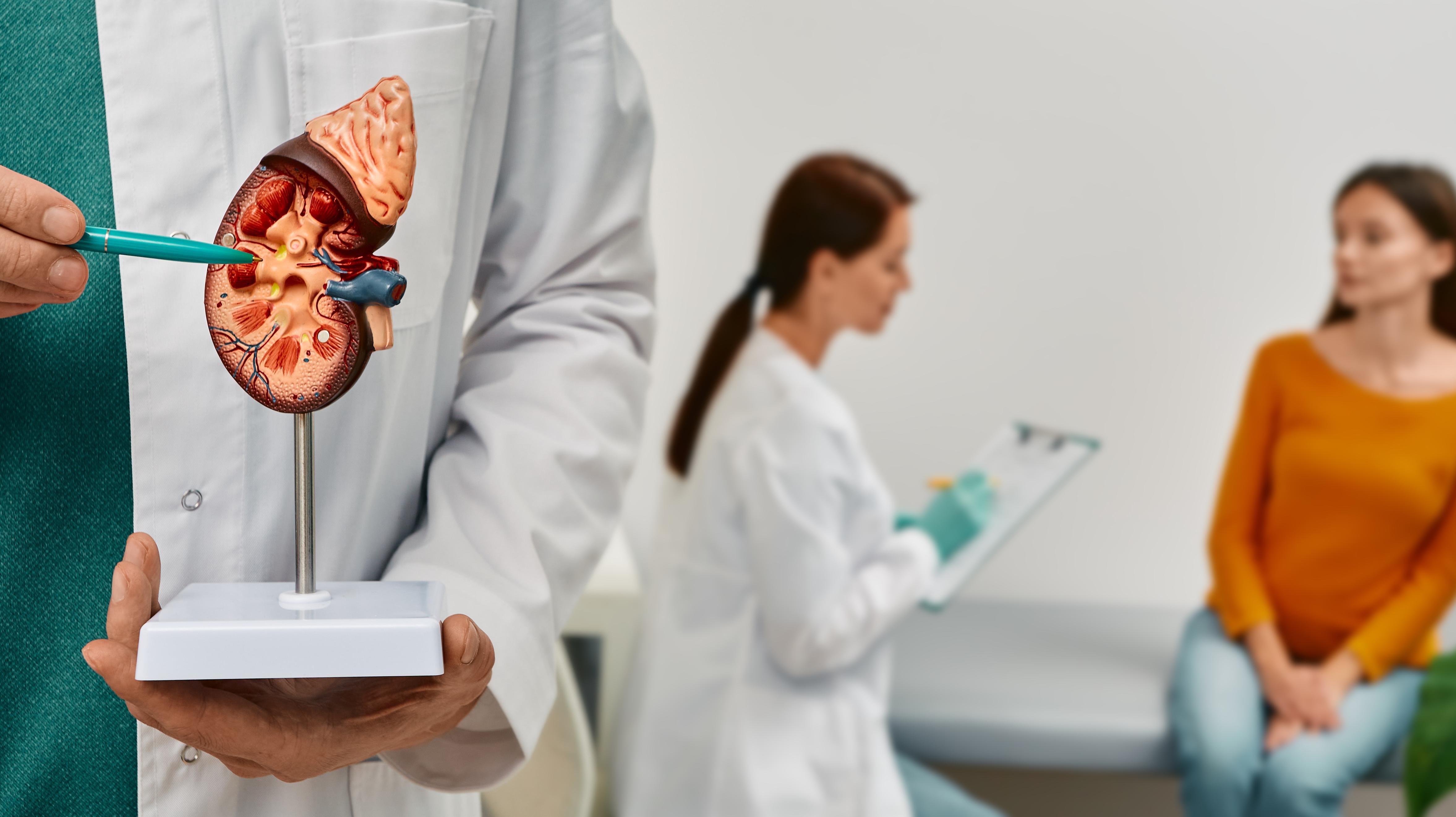
It might seem paradoxical, but while blood calcium is low, managing hypoparathyroidism can sometimes lead to kidney issues. High phosphorus levels can cause calcium-phosphate crystals to form in the kidneys. Additionally, treatment often involves high doses of calcium supplements, which can increase calcium levels in the urine (hypercalciuria), raising the risk of kidney stones. Careful monitoring of urine calcium and phosphorus levels, along with appropriate treatment adjustments, is vital to protect kidney health.
16. Basal Ganglia Calcifications: Brain Changes

Chronic imbalances of low calcium and high phosphorus can lead to calcium deposits forming in specific areas of the brain, most commonly the basal ganglia – structures involved in movement control. While often asymptomatic initially, these calcifications can sometimes contribute to neurological issues over time, including movement problems (see #18) or cognitive difficulties (related to #6). Brain imaging (like CT scans) can detect these changes, highlighting the importance of long-term stable mineral balance.
