5 Amazing Acupuncture Benefits You Never Knew About
Boosts The Immune System

Several studies have concluded acupuncture boosts the immune system, and the practice is frequently used as an alternative treatment for colds, flu, and autoimmune conditions such as lupus. Research shows an acupuncture session can increase the number of T-cells in the body; these cells can destroy dangerous bacteria and viruses. Scientists believe acupuncture increases T-cells because the body may view the acupuncture needles as a threat, sending white cells and T-cells to fight this off. The boost of T-cells in the body lasts for several days after an acupuncture session. Research also indicates acupuncture increases the body's levels of interferon, one of the messenger hormones of the immune system. To help the immune system, acupuncturists routinely stimulate a point called ST36. Also known as Zusanli, this is located just below the knee, and it is an area that stimulates the production of cytokines and helper T-cells. Stimulation of the Sanyinjiao point, located above the ankle, can also be valuable in the treatment of immune conditions. To maximize the strength of the immune system, most medical acupuncturists recommend monthly acupuncture sessions to their patients. They also suggest patients avoid antibiotics and antihistamines; regular exercise is also helpful.
Treats Repetitive Strain Injuries
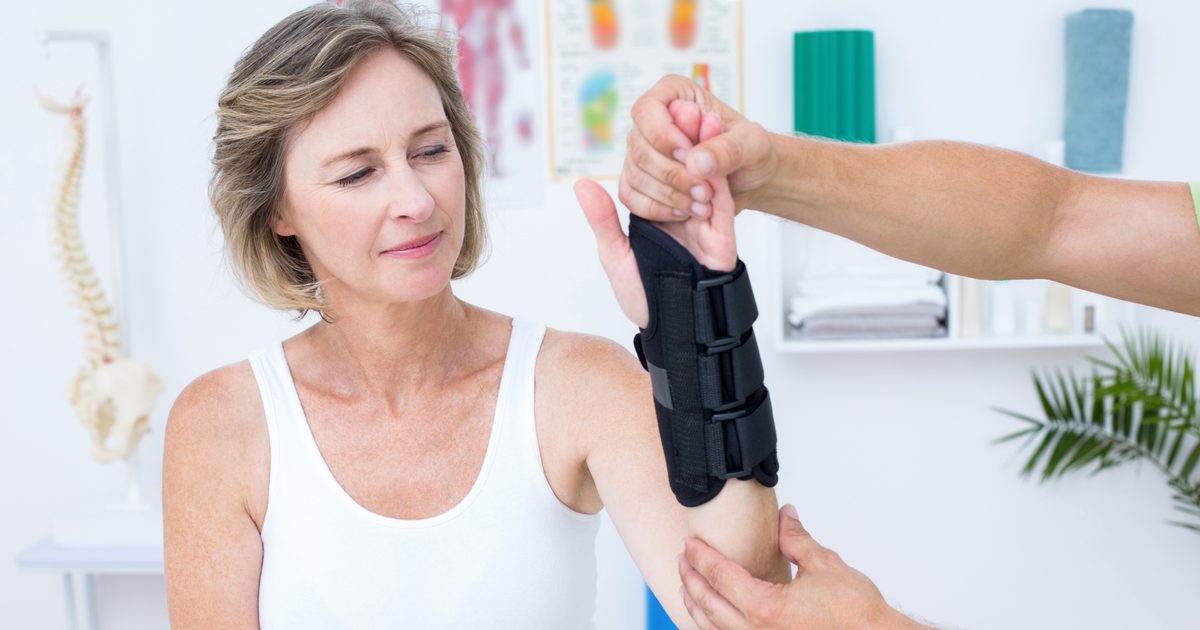
Anecdotal evidence from medical acupuncturists and patients suggests acupuncture treats repetitive strain injuries. These injuries are caused by repetitive motions, normally with the arms, wrists, hands, and fingers. Individuals involved in certain occupations, including musicians, typists, and those who perform manual labor, may be at an increased risk for this condition. In traditional Chinese medicine, this particular injury is triggered by inadequate circulation to the upper limbs. Acupuncture is believed to help alleviate symptoms of repetitive strain injuries by reducing inflammation, relaxing muscles, stimulating circulation, and triggering the release of endorphins (substances made by the body that provide natural pain relief). The practice may also block pain signals from the central nervous system. During an acupuncture session for a repetitive strain injury, the acupuncturist will normally stimulate a point on the wrist known as Lieque, located on the inside of the arm. The Waiguan point, located on the outside of the arm, is another area that may be stimulated.
