Major Ways To Fight Diabetes
Insulin Therapy
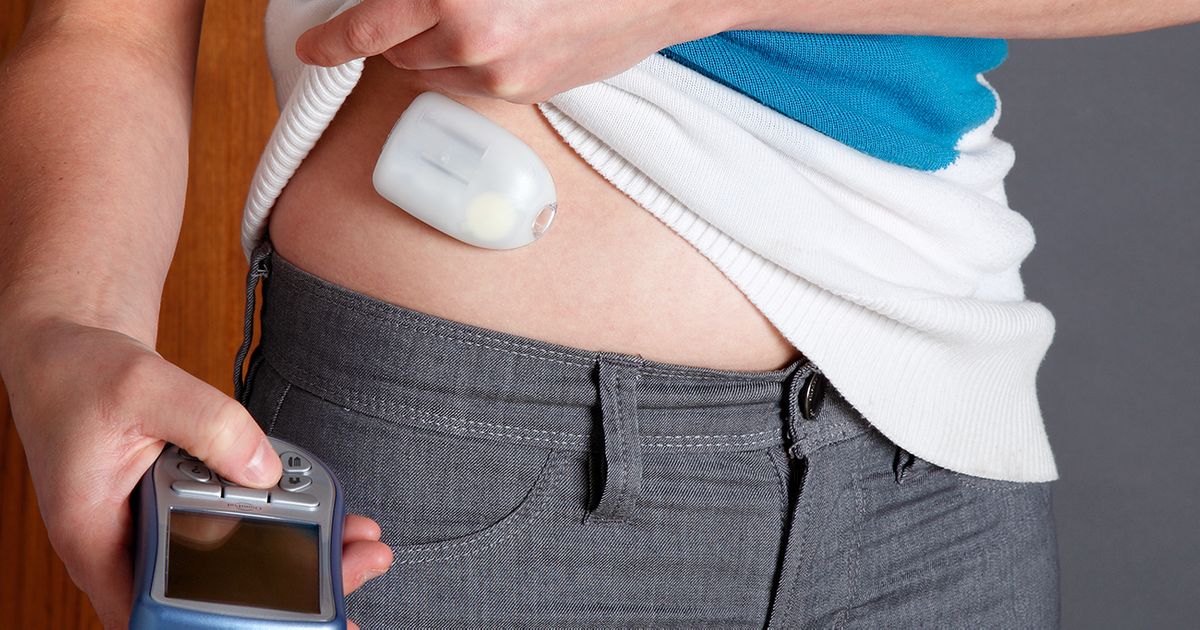
Insulin therapy is a key factor in the treatment of diabetes in the majority of patients. Insulin is the hormone the body secretes to bring high blood sugar levels down when they get too high. The bodies of diabetes patients either do not produce any insulin at all or insulin they are unable to utilize. Insulin therapy refers to the injection of insulin through an insulin pen, subcutaneous shot, or an insulin pump. On average, type 1 diabetes patients will need to have two shots of insulin a day. However, this does vary from case to case and has several influencing factors. Insulin therapy goes hand in hand with regular blood sugar monitoring because it determines when and how much insulin the patient needs at any given time. There are several types of insulin medications that vary in speed and duration of their action mechanism. A physician usually helps the patient create a treatment plan individualized to their diabetes. This treatment plan includes guidelines on how often to monitor blood sugar levels and take insulin medication.
Get to know more about medication and managing diabetes now.
Other Medications
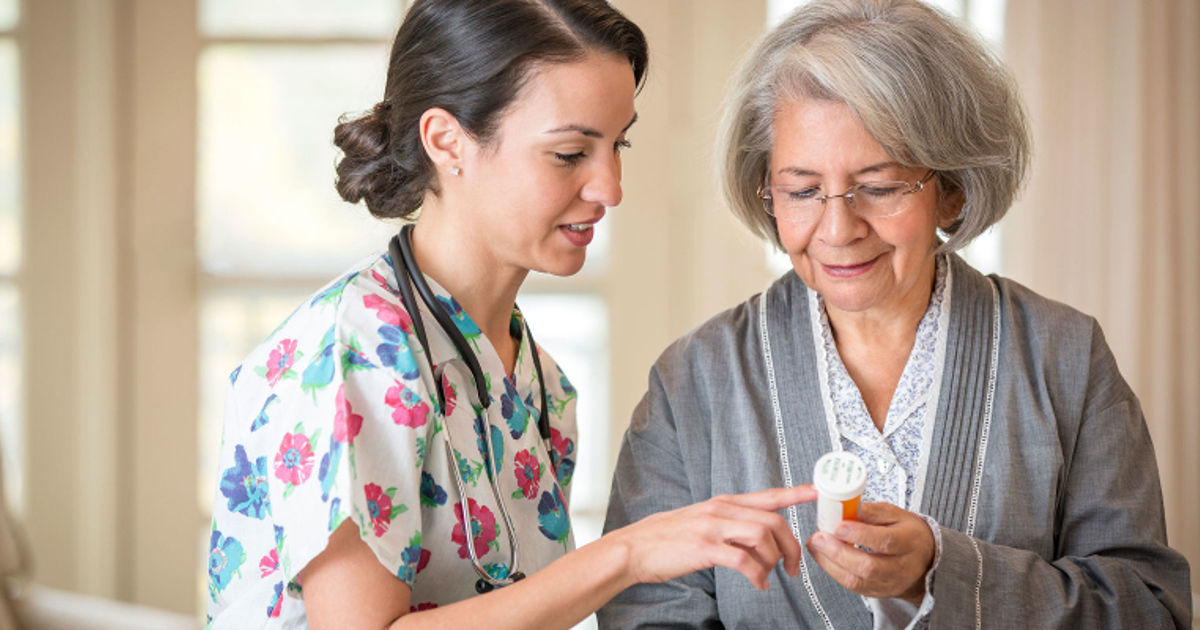

Other medications may be used for a diabetes patient's treatment in addition to insulin, or they may be used alone to manage the disease. Type 1 diabetes patients have to take some form of insulin because they cannot make their own. Individuals with type 2 diabetes, however, have more flexibility with non-insulin options. These individuals may be able to manage their disease with healthy dietary choices, regular exercise, and non-insulin medications. Non-insulin medications commonly used to help treat diabetes work by several different mechanisms. Some medications reduce the amount of glucose the individual's liver produces to help their body utilize insulin more effectively. Another type of medication sometimes used to help type 2 diabetes patients works by stimulating the cells in the pancreas to release insulin. In addition, the kidneys are responsible for the reabsorption of some glucose back into the blood. Some diabetes medications can inhibit this process and allow more glucose to be excreted through the patient's urine. This glucose excretion helps lower blood sugar levels. Medications used in the treatment of diabetes may need to be combined in many cases to manage the disease effectively.
