What Causes And Increases The Risk Of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis?
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is actually a grouping of neurological diseases that progressively worsen over time. Unfortunately, ALS currently has no cure, and even the treatment options do not do much to slow or reverse the progression of symptoms. In amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, upper and lower motor neurons in the brain, which are responsible for relaying messages to the spinal cord and muscles, die or degenerate over time. This causes the muscles to not receive messages and stop functioning over time. While there is no cure, scientists have determined several causes of ALS. Get to know these major causes now.
Chemical Imbalance
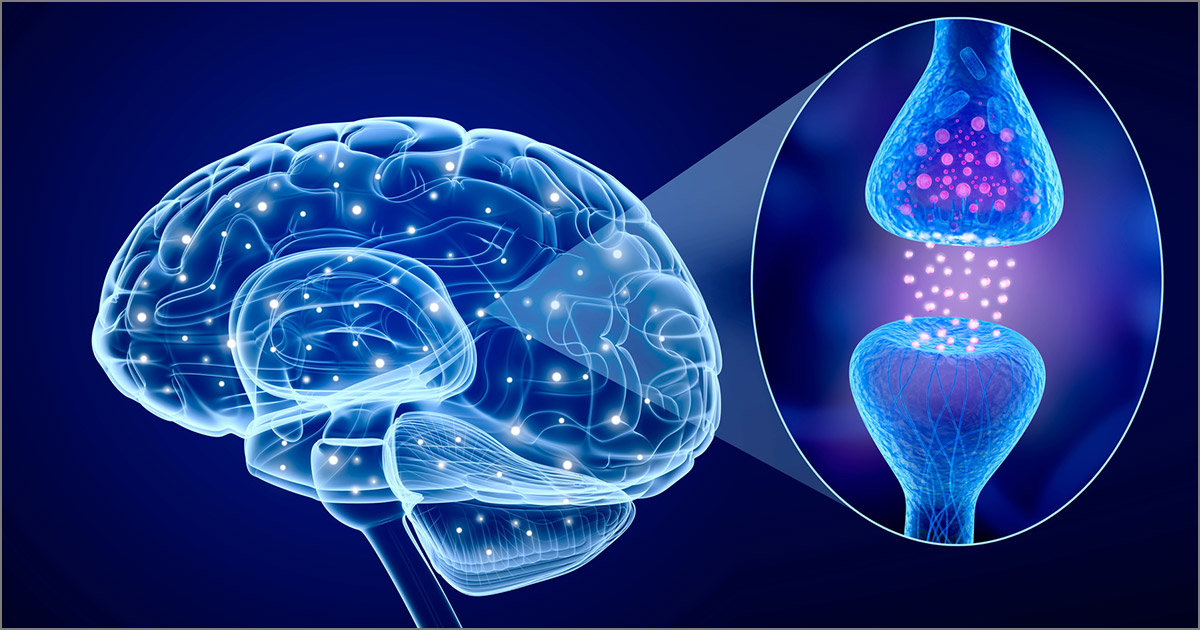
One of the potential causes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is the presence of elevated levels of glutamate in the body. This nonessential amino acid cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, but inside of the brain, it acts as one of that organ's most important chemical messengers. Unfortunately, when a neural injury occurs, it can result in too much extracellular glutamate in the body. Since glutamate becomes deadly to neurons at this elevated level, its overabundance seems able to cause cognitive impairments ranging from Alzheimer's disease and epilepsy to ALS. Anyone with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis will likely be told by their doctor to avoid glutamate supplements because of the chemical imbalance that has already been caused.
Continue reading learn about more causes of ALS now.
Gene Mutation
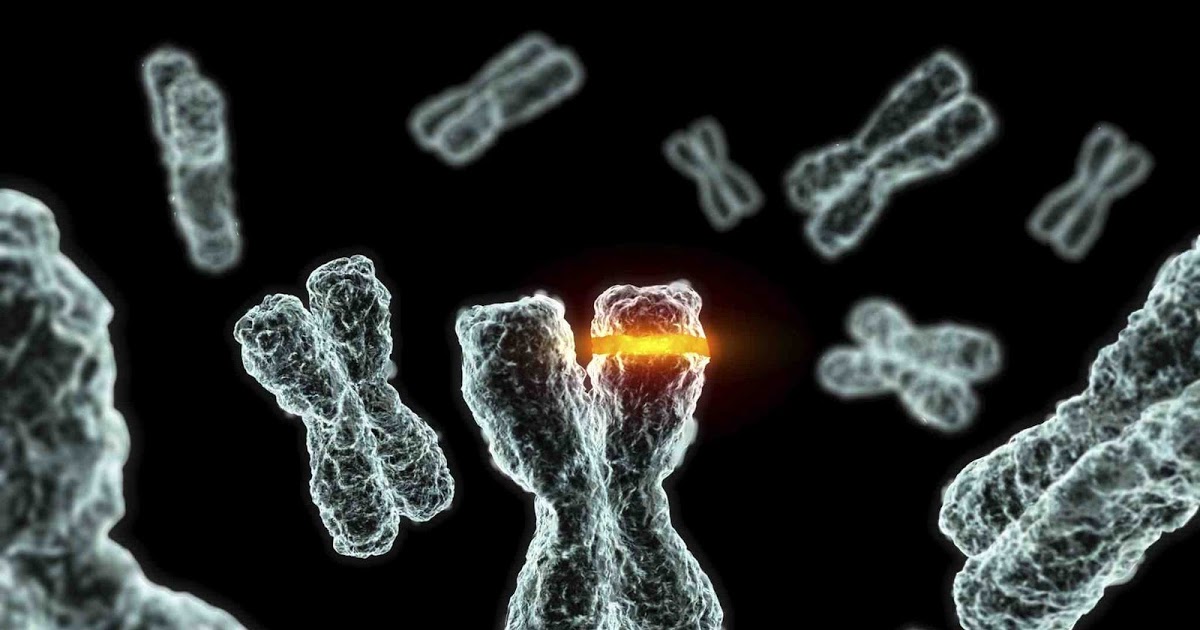
There are two types of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: sporadic and familial. While sporadic ALS occurs at random and accounts for the majority (roughly ninety to ninety-five percent) of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis cases, an estimated five to ten percent is due to genetic mutation. Thus, they are considered familial. Genetic mutations have actually been detected in patients with both types of ALS. One potential genetic mutation linked with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is that of the protein angiogenin. Another highly likely cause is gaining a new and very harmful function of the protein known as superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), which causes the SOD1 gene to mutate. Mutations also impact messenger RNA (mRNA), which acts as a messenger between proteins and their corresponding genes. Errors in the RNA-making process might cause different genetic mutations to occur and result in ALS.
Learn more about the causes of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis now.
