Botulism 101: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Treatment, And Prevention
Adult Intestinal Colonization Botulism
Adult intestinal colonization botulism is similar to infant botulism; however, the disease targets older children and adults with bowel disorders such as ulcerative colitis and other conditions where there is widespread disruption to gut bacteria, as well as those who have had intestinal bypass surgeries. It occurs when the bacteria is ingested and grows in the digestive tract. According to a study published in Oxford Academic, “patients of adult intestinal colonization botulism have some anatomical or functional bowel abnormality or are using antimicrobials, which may permit protection of normally fastidious Clostridia species.â€
Iatrogenic Botulism
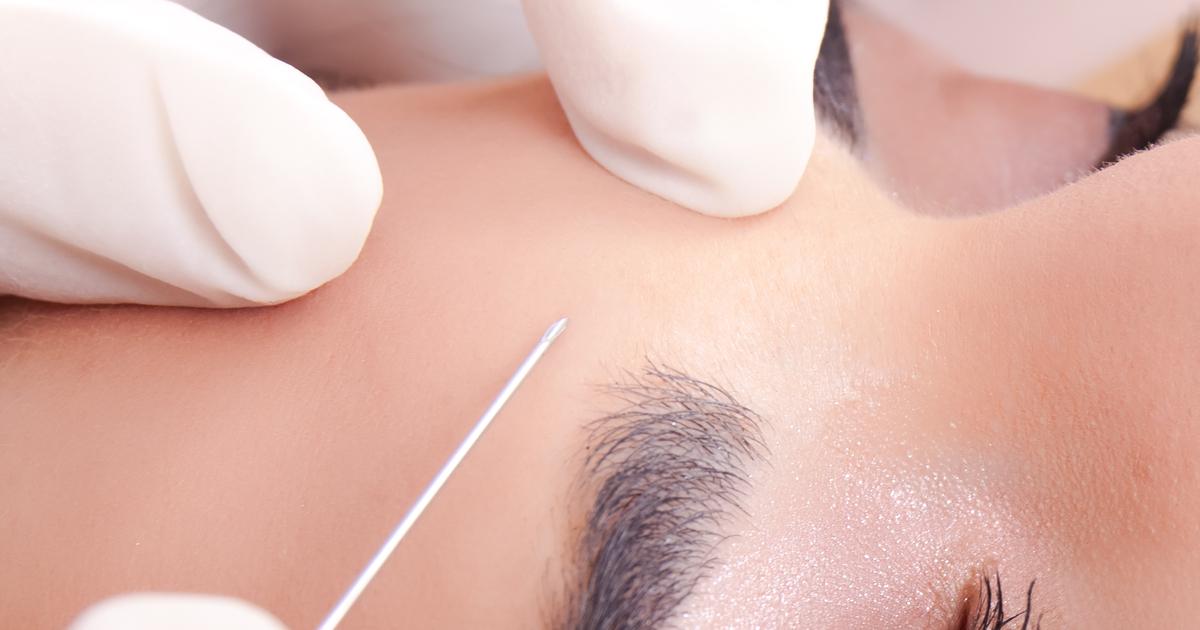
Iatrogenic botulism occurs in those who overdose on the botulism toxin Botox, which develops similarly to the way injectable drug users contract the disease. Botox is used for cosmetic or therapeutic purposes to reduce the appearance of aging. Standard doses of botox injections recommended for cosmetic treatment are too weak to cause botulism to develop; however, higher than normal amounts injected for muscle movement treatment may cause symptoms to appear. One study found four patients who received an injection from an unlicensed, highly concentrated form of botox toxin caused severe botulism.
