Common Symptoms Of Mastocytosis
Losing Consciousness
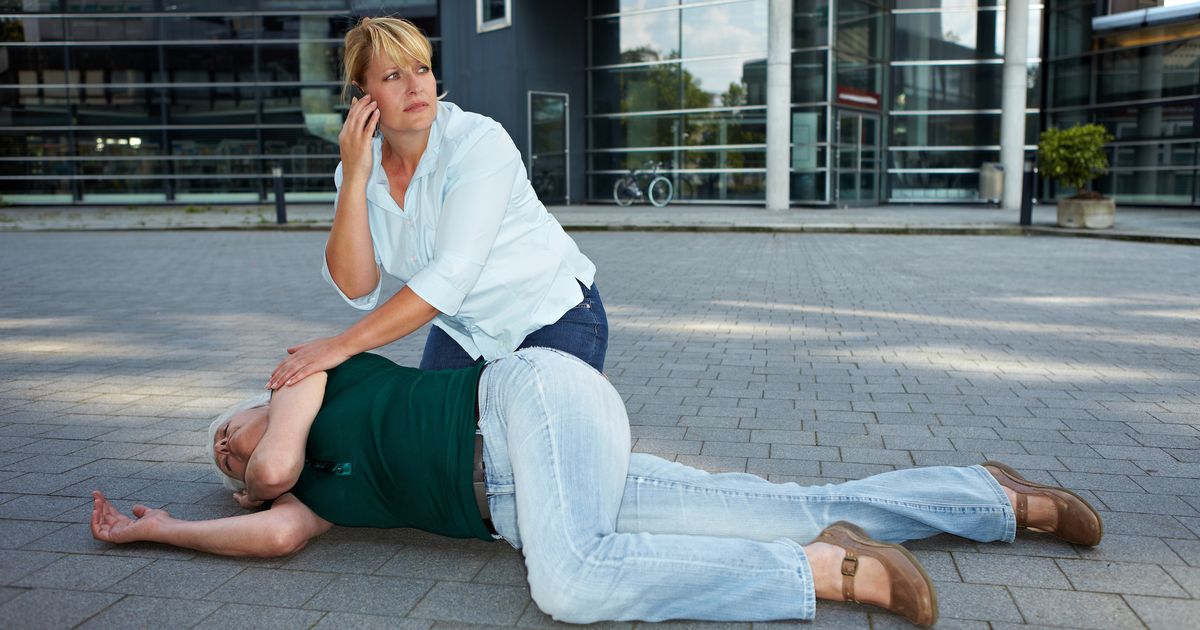

Fainting or loss of consciousness in affected individuals is the result of a sudden, dramatic decrease in their blood pressure. Low blood pressure causes a reduction in the amount of blood that reaches the tissues of the individual's brain. Poor blood flow to the brain causes a decrease in the amount of oxygen delivered to such tissues. Without oxygen, the brain tissues begin to shut down, causing the individual to faint or lose consciousness. The dramatic fall in blood pressure is attributed to the activation and degranulation of mast cells. The accumulated mast cells release histamine and activate other immune system components in the body that cause the blood vessels to become excessively dilated. This reaction occurs when the individual's tissues are triggered by some type of antigen, medication, or other endogenous factors like emotional anxiety, heat, or physical exertion. The reason the immune system induces vasodilation is to allow other immune cells and factors to diffuse through the vessel walls into the affected tissues faster and easier. The idea is for the body's natural pathogen fighting and damage mediating mechanisms to reach the site more efficiently. The most common triggers for fainting in individuals affected by mastocytosis are venom and certain medications.
Reveal more symptoms of mastocytosis now.
Anemia
Over ninety percent of adults affected by systemic mastocytosis develop lesions in their bone marrow. These lesions of mast cells cause the crowding out of other immature cells that are meant to grow into mature and functional red blood cells. Anemia is defined as a condition where an individual does not have enough functional red blood cells to meet the oxygen demands of their body. When some mechanism stops the bone marrow from producing an adequate amount of red blood cells, an individual will become anemic. Symptoms of anemia include pale skin color, loss of energy, pale skin, leg cramps, insomnia, problems with concentrating, breathlessness, headaches, rapid heartbeat, cold extremities, chest pain, and weakness. Other hematological abnormalities that can develop in mastocytosis patients can contribute to the loss of iron and other components in the blood due to excessive destruction and abnormal bleeding, which may also cause anemia to develop.
Continue for more details on the warning signs of mastocytosis now.
