Critical Health Assessments To Have Done Before You Have Serious Problems
Skin Cancer Screening
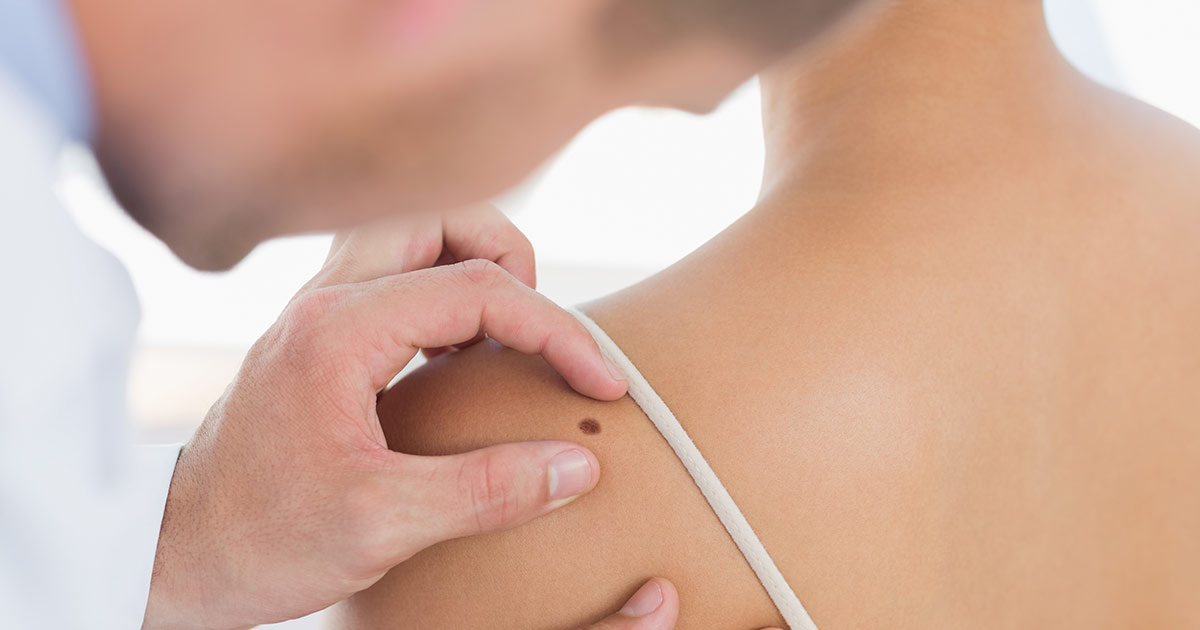
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, and although it is often treatable, malignant melanoma is extremely hard to treat and often results in death. It is important to be screened for skin cancer before any symptoms evolve. When abnormal tissue is discovered early on, it is much easier to treat.
Screening tests are routine, as they are administered when no symptoms are present and should be done on a bi-annual basis. If screening test results are abnormal, then diagnostic tests may be conducted to provide clearer results. Patients should remember if they have an irregular or unusual colored mole, it is critical to have it examined, just to be safe.
Colon Cancer Screening
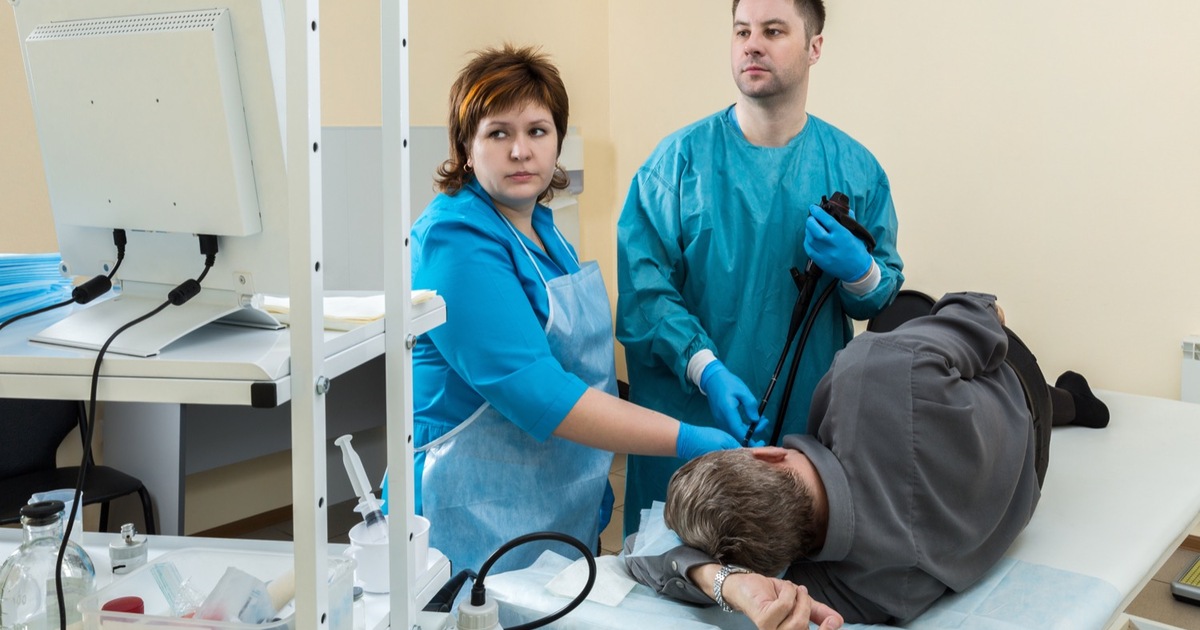
Even without a family history or symptoms, individuals are still at risk of developing colon cancer. The American Cancer Society states colorectal cancer is the third cancer-related cause of death in the United States, which is why early detection is so critical. Cancers caught in early stages allow for more possibilities of treatment. If patients have no history of colorectal cancer or polyps, family history related to colorectal cancer, history of inflammatory bowel diseases, prior cancer treatments that involved abdominal radiation, or an established or possible hereditary colorectal syndrome, they are considered to be at average risk. Thus, it is recommended for them to begin the colon cancer screening tests around forty-five years old, and as long as they are in good health, continue until they are roughly seventy-five years old.
Those who do have some of the listed risk factors are considered high risk and should begin screenings before forty-five years old, have them done more often, and discuss which screening options are most appropriate for them. Screening tests include a colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and a double contrast barium enema. The frequency of these tests vary, but typically the most popular test, the colonoscopy, is done every ten years for those with no risk factors apart from age or every five years for those with a history of polyps.
